Maximum path sum in a binary tree
AfterAcademy Tech
•
19 Dec 2019

Asked in: Directi, Amazon
Difficulty: Medium
Understanding the Problem
Problem description: Given a non-empty binary tree, find maximum path sum. For this problem, a path is defined as any sequence of nodes from some starting node to any node in the tree along with the parent-child connections.
Note: The path may start and end at any node of the tree.
Example 1:
Input: 1
/ \
2 3
Output: 1+2+3 = 6
Example 2:
Input: 5
/ \
-1 8
/ / \
11 13 7
/ \ \
-7 2 -1
Output: 13+8+7 = 28
The node structure for the BST passed to your function will be
class TreeNode{
int val
BSTNode left
BSTNode right
}
Possible questions to ask the interviewer:
- Could the node value be negative? (Ans: Yes)
Brute force and Efficient solutions
We will be discussing two possible solutions for this problem:
- Brute force approach: Traverse left and right subtree of each node and calculate maximum possible sum path.
- Recursive approach: We calculate the maximum path sum rooted at each node and update the max sum during the traversal.
1. Brute Force
We can update the max path sum passing through each node T in the tree by traversing the T's left subtree and right subtree.
Solution steps
- Assume we have nodes numbered 1 to N
- sum(i) = Maximum sum of a path containing node(i). Clearly the solution of the problem is max(sum(1), sum(2), ...., sum(N))
- Now, what is the maximum sum of a path containing a particular node(i)?
- left_result: maximum path sum starting at node(i).left
- right_result: maximum path sum starting at node(i).right
- sum(i) = max(left_result, 0) + max(right_result, 0) + node(i).val
Pseudo Code
//driver functionint maxPathSum(TreeNode root){
int answer = INT_MIN
answer = max_path_sum_helper(root, answer)
return answer
}
void helper(TreeNode root, int sum_so_far, int &result){
if(root == NULL)
return
result = max(result, sum_so_far + root.val)
helper(root.left , sum_so_far + root.val, result)
helper(root.right, sum_so_far + root.val, result)
}
void max_path_sum_helper(TreeNode root, int &answer){
if(root is NULL)
return
left_result = INT_MIN
right_result = INT_MAX
// Find maximum path sum starting from root.left
helper(root.left , 0, left_result )
// Find maximum path sum starting from root.right
helper(root.right, 0, right_result)
left_result = max(left_result , 0)
right_result = max(right_result, 0)
answer = max(left_result + right_result + root.val, answer)
max_path_sum_helper(root.left, answer)
max_path_sum_helper(root.right, answer)
}
Complexity Analysis
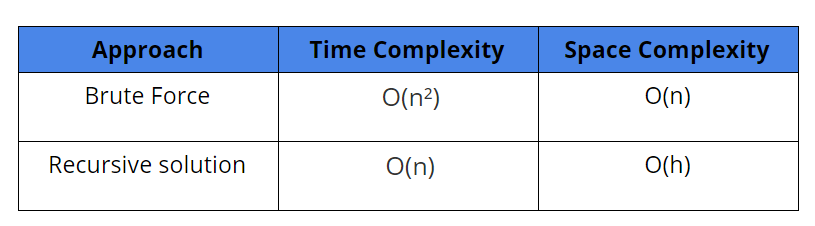
Time Complexity: Time complexity for sum(i) is O(N). The total time complexity is O(N²). (Think!)
Space Complexity: Space complexity is O(N).
Critical ideas to think!
- How can you try to compute the max sum for any node if you have the max sum for their left and right sub-tree?
- Why did we take max(left_result, 0) in the function max_path_sum_helper()?
2. Recursive Approach
Each node can be the root of the final maximum path sum. The root here means the topmost node in a path. We calculate the maximum Path Sum rooted at each node and update the max sum during the traversal.
There can only be four different cases when a particular node is involved in the max path.
- Its the only Node
- Max path through Left Child + Node
- Max path through Right Child + Node
- Max path through Left Child + Node + Right Child
In this algorithm, we can use post-order traversal and return the maximum sum in the subtree starting from the root. We call it left_result and right_result for left and right subtree
Pseudo Code
// driver functionint maxPathSum(TreeNode root){
max_so_far = INT_MIN
max_so_far = helper(root, max_so_far)
return max_so_far
}
int helper(TreeNode root, int max_so_far){
if(root is NULL){
return 0
}
int left_result = max(0, helper(root.left, max_so_far))
int right_result = max(0, helper(root.right, max_so_far))
max_so_far = max(left_result + right_result + root.val, max_so_far)
// return maximum sum starting from root
return max(left_result, right_result, 0) + root.val
}
Complexity Analysis
We are traversing each node only once.Time Complexity = O(N), where N is the total number of nodes. (Think!)
Space Complexity: O(h), where h is the maximum height of the tree.
Critical Idea to think
- How we are computing the answer for any vertex if we have an answer for their left and right child?
- The root of every subtree needs to return maximum path sum such that at most one child of root is involved. (Why?)
- Are we able to keep track of all the four possibilities discussed above?
Comparison of the two solutions
Suggested problems to solve
- Convert binary tree to mirror tree
- Maximum sum path between two leaves in a binary tree
- Find the diameter of a binary tree
Please comment down below if you have alternative approaches or find an error/bug in the above approaches.
Happy coding!
AfterAcademy Data Structure And Algorithms Online Course - Admissions Open
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Path Sum In Binary Tree
Given a binary tree and a sum, write a program to determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals the given sum.Its an easy problem based on Binary tree traversal and a famous interview question

AfterAcademy Tech
Find The Height Of a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, write a program to find the maximum depth of the binary tree. The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node to the leaf node. A leaf is a node with no child nodes.
AfterAcademy Tech
Find Diameter of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, you need to compute the length of the diameter of the tree. The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two nodes in a tree. This path may or may not pass through the root.

AfterAcademy Tech
Invert a Binary Tree - Interview Problem
Given a binary tree, invert the binary tree and return it. An inverted form of a Binary Tree is another Binary Tree with left and right children of all non-leaf nodes interchanged. You may also call it the mirror of the input tree.
