Invert a Binary Tree - Interview Problem
AfterAcademy Tech
•
10 Dec 2019

Asked in: Google, Amazon
Difficulty: Medium
Understanding the problem
Problem description: Invert a binary tree.
An inverted form of a Binary Tree is another Binary Tree with left and right children of all non-leaf nodes interchanged. You may also call it the mirror of the input tree.
NOTE: The tree is binary so there could be a maximum of two child nodes. This problem was originally inspired by this tweet by Max Howell .
Now, figure out that what does the interviewer mean when he says invert a binary tree, it would be helpful when you start looking at an example.
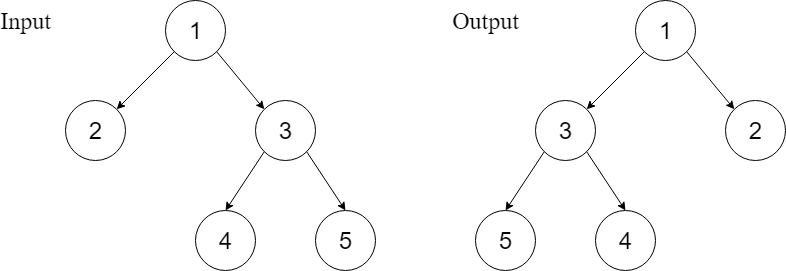
Example 1
Example 2
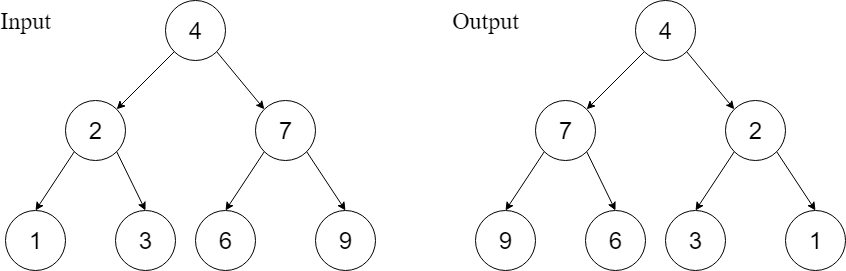
Explanation : You can observe that the root’s left pointer started pointing towards the right child and the right pointer towards the left child and a similar condition is noticed for all the sub root nodes.
The node structure for the BST passed to your function will be
class TreeNode
{
int val
TreeNode left
TreeNode right
}
Recursive and iterative solutions
We will be discussing three approaches to solve this problem
- Recursive solution (similar to pre-order traversal) : Solve the problem by swapping the left and right child for the root of each subtree recursively.
- Using Iterative Preorder Traversal : We can convert the above recursive solution to iterative using stack.
- Using Level order traversal : iterative approach using queue
1. Recursive Solution
The key insight here is to realize that in order to invert a binary tree we only need to swap the children and recursively solve the two smaller sub-problems (same problem but for smaller input size) of left and right sub-tree. This looks similar to the idea of pre-order traversal.
The steps to be followed are :
- When the tree is empty return NULL. This is also our base case to stop recursive calls.
- For every node encountered we swap its left and right child before recursively inverting its left and right subtree.
Pseudo Code
// Function to invert given binary Tree using preorder traversal
void invertBinaryTree(TreeNode root)
{
// base case: if tree is empty
if (root == Null)
return
// swap left subtree with right subtree
swap(root.left, root.right)
// invert left subtree
invertBinaryTree(root.left)
// invert right subtree
invertBinaryTree(root.right)
}
Complexity Analysis
In the above approach, we are traversing each node of the tree only once. Time complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity of this algorithm is proportional to the maximum depth of recursion tree generated which is equal to the height of the tree (h).
Space complexity: O(h) for recursion call stack, where h is the height of the tree.
Critical ideas to think
- Can we use idea similar to post-order traversal for solving this problem? or, can we use some other recursive idea for solution?
- Why recursion help us to solve the tree problems easily? Explore the properties of Pre-order, In-Order and Post-Order traversal.
- What is the space complexity in the worst and best-case scenario?
2. Using Iterative Preorder Traversal
Here, a Iterative Preorder Traversal is used to traverse the tree using a LIFO stack. To convert recursive procedures to iterative, we need an explicit stack during the implementation.
Solution Steps
- When the tree is empty return NULL.
- Create an empty stack S and push root node to stack.
- Do following while S is not empty :
- Pop an item from stack S and swap the left child with right child
- Push right child of popped item to the stack S.
- Push left child of popped item to the stack S
Right child is pushed before left child to make sure that left subtree is processed first.
Pseudo Code
// Iterative Function to invert given binary Tree using stack
void invertBinaryTree(TreeNode root)
{
// base case: if tree is empty
if (root is null)
return
// create an empty stack and push root node
stack S
S.push(root)
// iterate until the stack is not empty
while (S is not empty)
{
// pop top node from stack
TreeNode curr = S.top()
S.pop()
// swap left child with right child
swap(curr.left, curr.right)
// push right child of popped node to the stack
if (curr.right)
S.push(curr.right)
// push left child of popped node to the stack
if (curr.left)
S.push(curr.left)
}
}
Complexity Analysis
For each node in the tree, we are performing push() and pop() operation only once. Total no of stack operations = 2n (Think!)
Time complexity: O(n), where n is the total number of nodes.
Space Complexity: O(n)(Think!)
Critical Ideas to think
- Visualize the stack operations via simple examples.
- Explore the best and worst case scenario of space complexity.
- Design iterative algorithms for in-order and post-order traversal (using stack).
- Can we solve this problem using level-order traversal?
3. Using Level order traversal
We can solve this problem using Level Order Traversal. Here we the traverse the tree using a FIFO Queue.
In each iteration :
- We are deleting one node from the queue : TreeNode curr = Q.dequeue()
- Swapping the left and right child : swap(curr.left, curr.right)
- Inserting left and right child to the queue
if (curr.left)
Q.enqueue(curr.left)
if (curr.right)
Q.enqueue(curr.right)
Pseudo Code
// Iterative Function to invert given binary Tree using queue
void invertBinaryTree(TreeNode root)
{
// base case: if tree is empty
if (root is NULL)
return
// maintain a queue and push push root node
queue Q
Q.enqueue(root)
// iterate untill queue is not empty
while (Q is not empty)
{
// pop top node from queue
TreeNode curr = Q.dequeue()
// swap left child with right child
swap(curr.left, curr.right)
// push left child of popped node to the queue
if (curr.left)
Q.enqueue(curr.left)
// push right child of popped node to the queue
if (curr.right)
Q.enqueue(curr.right)
}
}
Complexity Analysis
For each node in the tree, we are performing enqueue() and dequeue() operation only once. Total no of queue operations = 2n (Think!)
Time complexity: O(n), where n is the total number of nodes.
Space Complexity: O(n) (Think!)
Critical Ideas to think
- Can you use a similar approach if the tree is generic?
- Explore the best and worst case scenario of space complexity.
- Can we write a recursive code for level order traversal? If yes then, compare its performance with Iterative Implementation (level order traversal using queue).
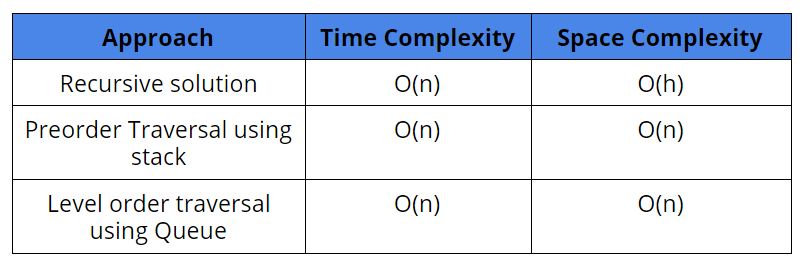
Comparison of different solutions
Suggested Problem to solve
- Convert a given Binary tree to a tree that holds Logical AND property
- Create a mirror tree from the given binary tree
- Find mirror of a given node in a binary tree
- Convert binary tree to threaded binary tree
- Check if two binary trees are equal or not
- Convert a given tree to its Sum Tree
If you have any more approaches or you find an error/bug in the above solutions, please comment down below.
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
AfterAcademy Data Structure And Algorithms Online Course — Admissions Open
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Merge two Binary Trees - Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in companies like Amazon, Microsoft. The problem is to merge two binary trees. The overlapping nodes are replaced by the sum of corresponding nodes. We are discussing two ways of solving this.

AfterAcademy Tech
Check if a binary tree is BST or not - Interview Problem
Given the root of a binary tree, check whether it is a binary search tree or not.

AfterAcademy Tech
Recover Binary Search Tree-Interview Problem
Given a Binary Search Tree such that two of the nodes of this tree have been swapped by mistake. You need to write a program that will recover this BST while also maintaining its original structure

AfterAcademy Tech
Minimum Depth of Binary Tree - Interview Problem
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth. The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
