Find The Height Of a Binary Tree
AfterAcademy Tech
•
03 Nov 2020
Difficulty: Easy
Asked in: Amazon, Goldman Sachs
Understanding The Problem
Problem Description
Given a binary tree, write a program to find the maximum depth of the binary tree.
Problem Note
- The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node to the leaf node.
- A leaf is a node with no child nodes.
Example
Input: Given binary tree,
[5, 3, 6, 2, 4, -1, -1, 1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1]
5
/ \
3 6
/ \
2 4
/
1
Output: return its depth = 4
Solutions
The height of a binary tree is the maximum distance from the root node to the leaf node. We can find the height of the binary tree in two ways.
- Recursive Solution: In a recursive function, for each child of the root node, we can increment height by one and recursively find the height of the child tree.
- Iterative Solution: We can do a level order traversal and for each new level, we can increment the height by one.
The node structure passed to the function is:
struct TreeNode{
int val
TreeNode left
TreeNode right
}
You can try practising this problem here.
1. Recursive Solution
To solve a tree's problems, recursive solutions are very intuitive. Like in this case, a very intuitive approach is to find the maximum of height from the left subtree and the right subtree of the root node and return the maximum height + 1.
In other words, We can define a subproblem as, If the root node has left child or right child then find the maximum height of the trees whose root is the left child and the right child. Add 1 to the maximum height of the children tree(Why?).
Solution Steps
- Check if the root is NULL then return 0
- Return the maximum(left subtree of root, right subtree of root) + 1
Pseudo Code
int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root){
height = max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right))
return height + 1
}
return 0
}
Complexity Analysis
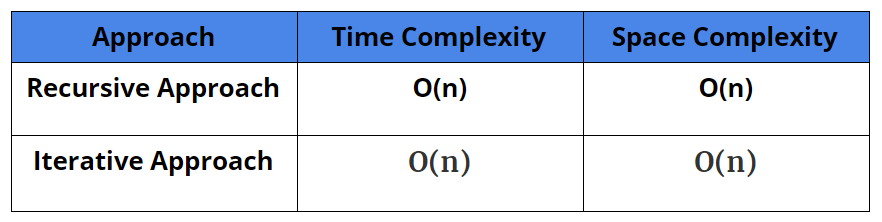
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
Critical Ideas To Think
- Why did we add 1 with the height in pseudocode? Answer: The root node itself contributes to the path of maximum height from root to leaf node.
- Why space complexity is O(n)? Answer: The tree can be skew, in such cases the recursion stack uses the space.
- What is the base case for the recursion? Answer: If the root is NULL then we return 0. (Why?)
2. Iterative Solution
One can think of an iterative solution if you consider solving this problem using BFS traversal or Level Order Traversal. For each new level encountered while traversing from the root node, we can increment the height of the tree by one.
How can we implement level order traversal to find height?
We will take a Queue and add root to it. And we can initialize a variable height to maintain the maximum height of the tree.
Now, we will dequeue all the nodes of the Queue from the front and will enqueue the left and right child of the dequeued nodes in the rear which represent the next level of the tree. For each such cycle, we can increment the height by one. We will continue doing this until no nodes left in the Queue.
Solutions Steps
- Create a Queue and push the root node in it
- Dequeue all the nodes of Queue and enqueue all the children of the dequeued nodes —
- For each such step, increment the height by 1
3. Repeat step 2 until the Queue becomes empty.
Pseudo Code
int maxDepth(TreeNode *root) {
// Base Case
if (root is NULL)
return 0
// Create an empty queue for level order tarversal
Queue q
q.push(root)
int height = 0
while (true) {
int currLevelNodes = q.size()
if (currLevelNodes == 0)
return height
height = height + 1
while (currLevelNodes > 0)
{
TreeNode node = q.front()
q.pop()
if (node.left is not NULL)
q.push(node.left)
if (node.right is not NULL)
q.push(node.right)
currLevelNodes = currLevelNodes - 1
}
}
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
Critical Ideas To Think
- Why did we return the
heightonly whencurrLevelNodeis 0? - Why did we pop all the nodes inside the Queue? How did that help us to filter the nodes of the current level and the next level of the tree?
Comparison of Different Solutions
Suggested Problems To Solve
- Find the average of levels of binary tree
- Postorder traversal of binary tree
- Level order traversal of Binary tree
- Iterative preorder traversal of Binary tree
- Find the nth node in the inorder traversal of binary tree
Please comment down below if you have a better insight in the above approach.
Happy Coding, Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Find Diameter of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, you need to compute the length of the diameter of the tree. The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two nodes in a tree. This path may or may not pass through the root.

AfterAcademy Tech
Invert a Binary Tree - Interview Problem
Given a binary tree, invert the binary tree and return it. An inverted form of a Binary Tree is another Binary Tree with left and right children of all non-leaf nodes interchanged. You may also call it the mirror of the input tree.

AfterAcademy Tech
Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, write a program to find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree. The question is asked previously in Amazon, Facebook, Adobe and requires an understanding of tree data structure.

AfterAcademy Tech
Path Sum In Binary Tree
Given a binary tree and a sum, write a program to determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals the given sum.Its an easy problem based on Binary tree traversal and a famous interview question
