Path Sum In Binary Tree
AfterAcademy Tech
•
01 May 2020

Difficulty: Easy
Asked in: Amazon, Microsoft, Yahoo
Understanding the problem
Given a binary tree and a sum, write a program to determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals the given sum.
Problem Note
- A leaf is a node with no children.
Example 1
Input: Given the below binary tree and sum = 22
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ \
7 2 1
Output: true
Explanation: There exist a root-to-leaf path 5->4->11->2 which sum is 22.
The node structure passed to your function will be
class TreeNode
{
int val
TreeNode left
TreeNode right
}
Solutions
- Recursive DFS solution: Make a DFS traversal while passing the sum through “call by value” and reduce the sum by the node value. Return true if sum becomes zero at any leaf node.
- Iterative Approach using Queue: Add all nodes to a queue and store the sum value of each node to another queue. When it is a leaf node, check the stored sum value.
You may try to solve the problem here: Path sum in a binary tree
Learning via problem-solving is the best way to crack any interview!
1. Recursive DFS Solution
This problem could be solved by making a simple DFS or preorder traversal through the tree. If you will think that, all we have to do is to check if any path from the root to any leaf will sum up to the given sum.
Example →
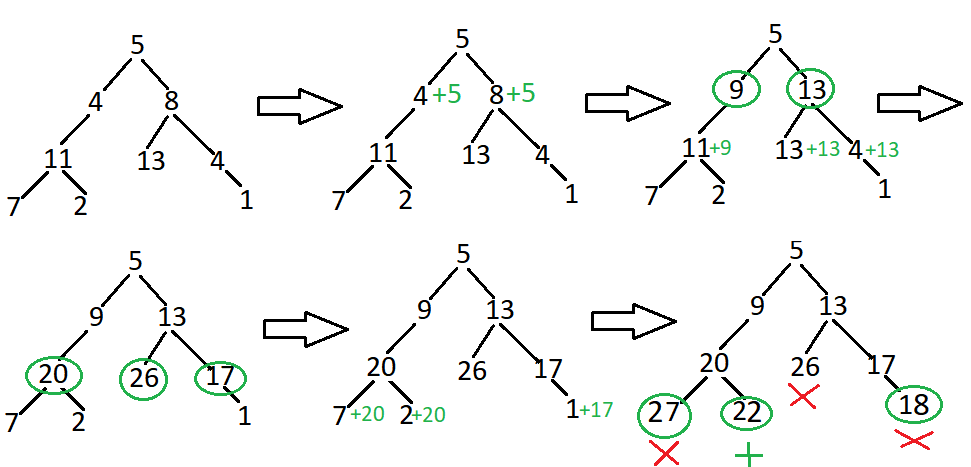
Let's consider the above example, there are many paths like 5->4->11->7 or 5->4->11->2 and so on. This seems like a simple preorder traversal in which we will perform some check on the root node, then recursively go to the left subtree and after checking all the left subtree, we go to the right subtree.
In this case, If we will try to think of a similar way of traversal with passing another argument, i.e. sum with every level of traversal, its value decreases by the root value of that subtree, then all we have to check if the leaf node is equal to the sum at that state, If that is so, then return True otherwise return False.
Solution Steps
- If
rootis null return false - Subtract
rootnode.valfrom the given sum to get new sum
- now make two recursive calls for both left and right for the root node
3. if the root node visited is a leaf node and its value is equal to the new sum then return true
Pseudo Code
int pathSumExists(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if(root is NULL)
{
return false
}
if(root.val == sum and root.left is NULL and root.right is NULL)
{
return true
}
return pathSumExists(root.left, sum - root.val) or pathSumExists(root.right, sum - root.val)
}
Complexity Analysis
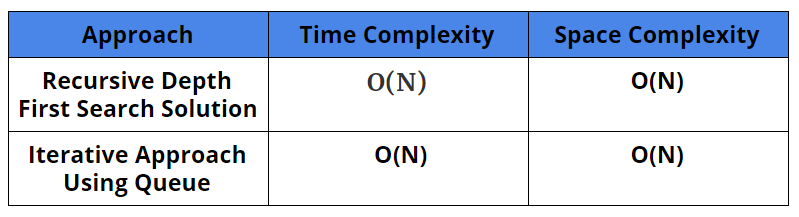
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n) (How?)
Critical Ideas to Think
- How did we check a leaf node?
- How does the leaf node become equal to the sum, if the path traversed is a valid path?
2. Iterative Approach Using Queue
If you understood how the recursive approach is working behind the hood, then you can clone the similar procedure into the iteration.
There are two ways in which you can do that
- Either by modifying the value of the nodes in the tree iteratively using Queue. Each node will store the sum from the root node of the tree up to that node. All we have to check if any leaf node is equal to the given sum.
- Creating two queues, First will be used to make the traversals iteratively through the tree and the second will store the sum up to that node from the root corresponding to the changes in the first queue.
Solution Step
- Make an iterative traversal through the tree using a Queue of tree nodes. (refer here)
- Maintain another Queue of integers that perform the same operations as the first queue of tree nodes.
- The integer queue will store the value from the root node to the current node corresponding to the tree node queue.
- At any point, the current node becomes the leaf node and the corresponding Integer queue’s popped value is equal to the
sum, then return True.
Pseudo Code
Using Two Queues
bool pathSumExists(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if(root is null)
return false
// Queue of tree node
Queue nodes
// Queue of Integers
Queue values
nodes.add(root)
values.add(root.val)
while(nodes is not empty) {
TreeNode curr = nodes.front()
nodes.pop()
sumValue = values.front()
values.pop()
if(curr.left is null and curr.right is null and sumValue==sum){
return true
}
if(curr.left is not null){
nodes.add(curr.left)
values.add(sumValue + curr.left.val)
}
if(curr.right is not null){
nodes.add(curr.right)
values.add(sumValue+curr.right.val)
}
}
return false
}
By modifying the tree nodes.
bool pathSumExists(TreeNode root, int sum){
if(root is NULL)
return false
// Queue of treenode
queue nodes
nodes.add(root)
while(nodes is not empty){
TreeNode curr = nodes.front()
nodes.pop()
if(curr.left is NULL and curr.right is NULL){
if(curr.val == sum)
return true
}
if(curr.left){
curr.left.val = curr.left.val + curr.val
nodes.push(curr.left)
}
if(curr.right){
curr.right.val = curr.right.val + curr.val
nodes.push(curr.right)
}
}
return false
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(N)
Space Complexity: O(N)
Critical Ideas to Think
- What is the difference between the two iterative approaches discussed above?
- How we are traversing through the tree iteratively?
- Is it important to use two queues if we are not liable to change the values of the tree nodes? If yes, Why?
Comparison of Solutions
Suggested Problems to Solve
- Print all-k paths in Binary Tree.
- Sum of nodes from root to leaf in the longest path of a binary tree.
- Root to leaf path product equal to the given number
If you have any more approaches or you find an error/bug in the above solutions, please comment down below.
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Maximum path sum in a binary tree
Given a non-empty binary tree, find maximum path sum. For this problem, a path is defined as any sequence of nodes from some starting node to any node in the tree along with the parent-child connections.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find Diameter of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, you need to compute the length of the diameter of the tree. The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two nodes in a tree. This path may or may not pass through the root.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find The Height Of a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, write a program to find the maximum depth of the binary tree. The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node to the leaf node. A leaf is a node with no child nodes.
AfterAcademy Tech
Invert a Binary Tree - Interview Problem
Given a binary tree, invert the binary tree and return it. An inverted form of a Binary Tree is another Binary Tree with left and right children of all non-leaf nodes interchanged. You may also call it the mirror of the input tree.
