Minimum Depth of Binary Tree - Interview Problem
AfterAcademy Tech
•
08 Dec 2019

Difficulty : Easy
Asked in : Facebook, Amazon
Understanding the problem
Problem description: Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
NOTE: The path has to end on a leaf node.
Example:
Input:
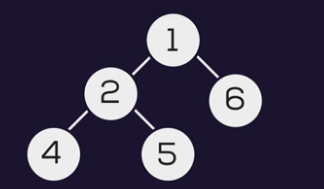
output: 2
Explanation: The minimum depth is 2 through the path from root node 1 to leaf node 6.
The node structure for the BST passed to your function will be
class TreeNode
{
int val
TreeNode left
TreeNode right
}
Solutions
We are discussing two approaches to solve this problem:
- Recursive solution: Solve the problem by calculating the minimum depth of left and right subtree recursively.
- Using Level order traversal: Perform level traversal and return the depth of the first encountered leaf node.
1. Recursive solution
The steps to be followed are:
- Check if the node is a leaf node or not. If it is a leaf node then return 1.
- If the left child is NULL then recur to the right child or if the right child is NULL then recur to the left child.
- If both the children are not NULL then return the minimum of both heights of left and right sub-tree + 1.
This is a Depth First Search(DFS) approach of solving tree problem.
Pseudo code
int findMinDepth(TreeNode root)
{
if(root == NULL)
return 0
if(root.left == NULL and root.right == NULL)
return 1
if(root.left == NULL)
return 1 + findMinDepth(root.right)
if(root.right == NULL)
return 1 + findMinDepth(root.left)
return 1 + min(findMinDepth(root.left), findMinDepth(root.right))
}
Complexity Analysis
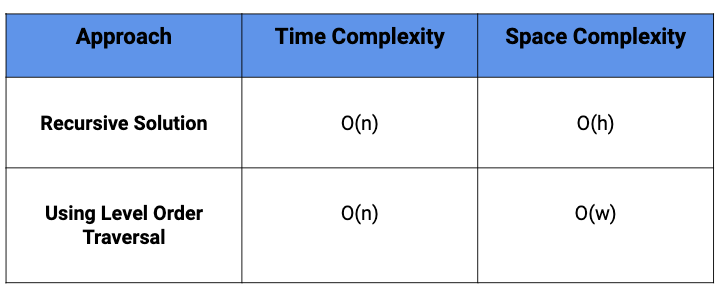
In the above approach, we are traversing each node of the tree only once. Time complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity of recursive algorithm is proportional to the maximum depth of recursion tree generated which is equal to the height of the tree (h). Space complexity: O(h) for recursion call stack.
Critical ideas to think
- What is the space complexity in the worst and best-case scenario?
- Is there some other way to solve this problem recursively?
- Why recursion help us to solve the tree problems easily? Explore the properties of Pre-order, In-Order and Post-Order traversal.
2. Level order Traversal
Level order traversal is the Breadth-First Traversal of the tree where we traverse the tree by accessing the nodes in level by level fashion. For each node, the first node is visited and then it’s child nodes are put in a FIFO queue.
The recursive approach may end up with a complete traversal of Binary Tree even when the topmost leaf is close to root. So we can design a better solution by using the idea of Level Order Traversal. While doing level order traversal, we will return the depth of the first encountered leaf node and return its level.
In the above example:- 1 is the root node is considered at the first level, 2 and 6 at the second level, 4 and 5 at the third level.
Pseudo Code
class TreeNode
{
int data
TreeNode left
TreeNode right
}
class QueueItem
{
TreeNode node
int depth
}
int findMinDepth(TreeNode root)
{
if (root is NULL)
return 0
else
{
// Queue of type QueueItem
Queue Q
QueueItem QI = {root, 1}
Q.enqueue(QI)
while(Q is not empty)
{
QI = Q.dequeue()
TreeNode subroot = QI.node
int depth = QI.depth
//If the first leaf node is seen, then return depth
if (subroot.left == NULL and subroot.right == NULL)
return depth
else
{
if(subroot.left != NULL)
{
QI.node = subroot.left
QI.depth = depth + 1
Q.enqueue(QI)
}
if(subroot.right is != NULL){
QI.node = subroot.right
QI.depth = depth + 1
Q.push(QI)
}
}
}
}
return 0
}
Complexity Analysis
From the FIFO queue, Each item get inserted and deleted only once. Total number of queue operations = 2n.
Time complexity = O(n), where n is the total number of nodes.
Level order traversal require space proportional to the max width of the tree (w) which is equal ot the maximum number of nodes at a given level. Space Complexity = O(w)(Think!)
Critical Ideas to think
- Why we Queue data structure in the level order traversal?
- What is worst and best-case scenario of space complexity?
- Can we write a recursive code for level order traversal? If yes then, compare its performace with Iterative Implementation (level order traversal using queue).
Comparison of different solutions
Suggested problems to solve
- Max depth of the binary tree
- Find diameter of a binary tree
- Count all leaf node in binary tree
- Root to leaf paths with the sum
- Count all node with one child
- Depth of the deepest odd level node
Happy coding!
AfterAcademy Data Structure And Algorithms Online Course — Admissions Open
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Invert a Binary Tree - Interview Problem
Given a binary tree, invert the binary tree and return it. An inverted form of a Binary Tree is another Binary Tree with left and right children of all non-leaf nodes interchanged. You may also call it the mirror of the input tree.

AfterAcademy Tech
Merge two Binary Trees - Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in companies like Amazon, Microsoft. The problem is to merge two binary trees. The overlapping nodes are replaced by the sum of corresponding nodes. We are discussing two ways of solving this.

AfterAcademy Tech
Check if a binary tree is BST or not - Interview Problem
Given the root of a binary tree, check whether it is a binary search tree or not.

AfterAcademy Tech
Recover Binary Search Tree-Interview Problem
Given a Binary Search Tree such that two of the nodes of this tree have been swapped by mistake. You need to write a program that will recover this BST while also maintaining its original structure
