Merge two Binary Trees - Interview Problem
AfterAcademy Tech
•
06 Jun 2020

Difficulty: Easy
Asked in: Amazon, Microsoft
Understanding the Problem:
You are given two binary trees and you need to merge them into one binary tree.
To solve this problem, you can imagine putting one of the binary tree on top of the other in order to cover the other. Some of the nodes of the two trees will be overlapped while the others are not. Write a program to merge both the trees into a new binary tree.
Possible questions to ask the interviewer:
- Which node to keep in case of overlapping nodes? (Ans: You need to sum both the node’s value and use this value for node in merged tree.)
- What to do in case if one of the tree has NULL node? (Ans: Just keep the value of the second tree in the merged tree.)
For example:
Input 1: Input 2:
Tree 1 Tree 1
1 5
/ \ / \
3 2 2 3
/ \
5 1
Tree 2 Tree 2
2 2
/ \ /
1 3 3
\ \ /
4 7 1
Output:
Merged tree: Merged tree:
3 7
/ \ / \
4 5 5 3
/ \ \ / \
5 4 7 1 1
The solutions are below, why not to try it once before proceeding? Try it out here.
Solutions
We are going to discuss two solution approaches in this article. In the first approach, we will use recursion and the second one will be an iterative solution using stack.
- Recursive Solution
- Iterative Solution
Recursive Solution
Solution idea
We will start from the root node of both the trees and will traverse them in a preorder fashion. At each step of the traversal, we will compare the corresponding nodes of the trees. We will use recursion for proceeding to the next nodes. We will call the same method recursively for both left and right subtrees.
Solution steps
- Traverse both the trees T1 and T2 in preorder fashion.
- If the overlapping nodes in both the trees have not NULL values, we will update the first tree’s node value with the sum of the two values.
- If either of the corresponding nodes has NULL values, update the other node’s value into T1’s node.
- Recur for left and right subtrees
- Return the first tree T1’s root as it has the merged values from both the trees.
Pseudo-code
class treeNode
{
int value
treeNode left
treeNode right
}
treeNode mergedBinaryTree(treeNode root1, treeNode root2)
{
if(root1.value == NULL)
return root2
if(root2.value == NULL)
return root1
root1.value += root2.value
root1.left = mergedBinaryTree(root1.left, root2.left)
root1.right = mergedBinaryTree(root1.right, root1.right)
return root1
}
Complexity Analysis
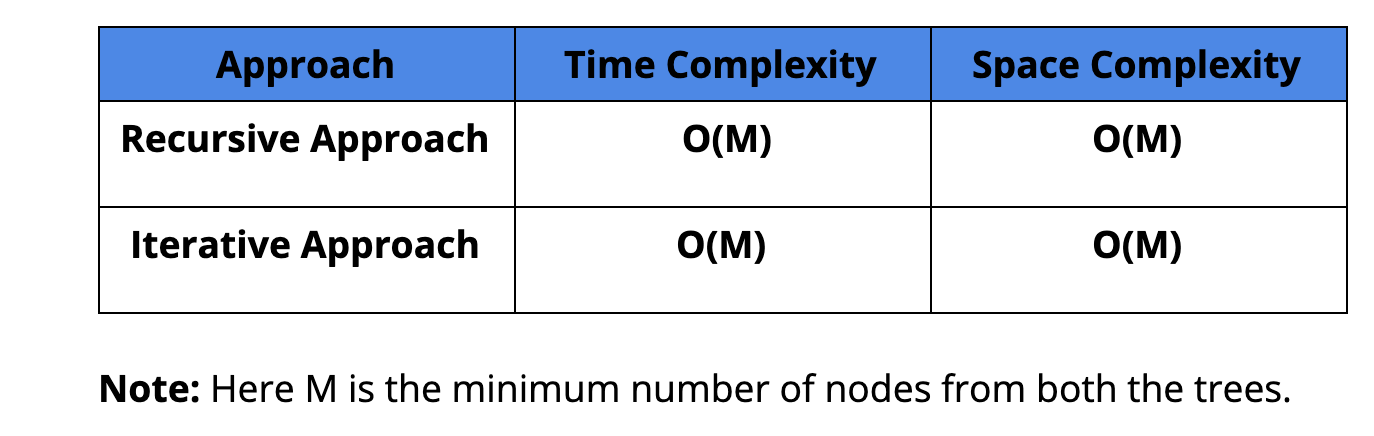
Time Complexity: O(M), here M represents the minimum of nodes(overlapping or non-overlapping) from both the tree.
Space Complexity: O(M) (The average case will be logM)
Critical ideas to think!
- What will be the condition for the worst-case space complexity of O(M)? (Hint: The space complexity is related to the depth of the tree.)
Iterative Solution
Solution idea
We need to compare the nodes of both the trees T1 and T2. For this we need to traverse all the nodes(minimum of the two). Here also we will traverse the trees but instead of using recursion, we will use stack to solve this problem iteratively.
Solution steps
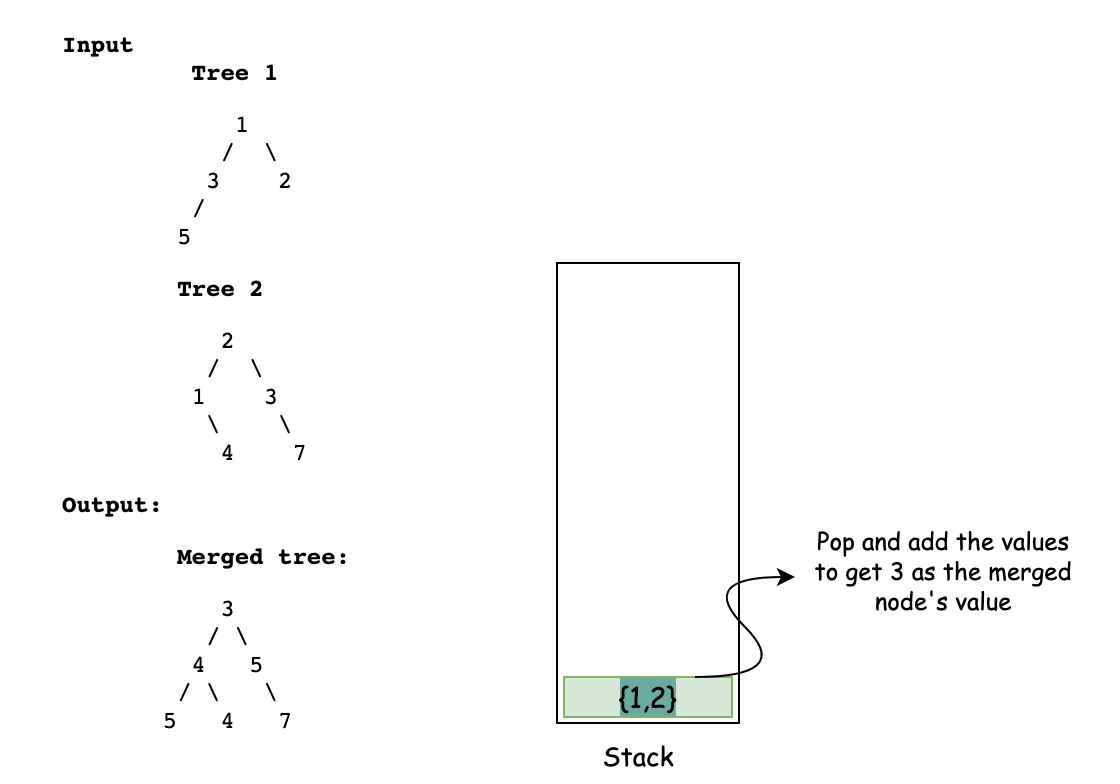
- Create a stack S of type pair that will contain pair of both the trees.
- Push the root of both trees T1 and T2 into stack.
- While the stack is not empty keep popping out the elements.
- If the value of both the elements are present, sum them and update the value of T1’s node with the sum.
- If left or right child of both the trees are available, we will push them to stack.
- In case left or right child of T1 is missing, we will simply update it with T2’s corresponding node.
- If both left and right child are not available, we will continue popping the stack until it is empty.
Solution visualization
Pseudo-code
class treeNode
{
int value
treeNode left
treeNode right
}
class treePair
{
treeNode first
treeNode second
}
treeNode mergedBinaryTree(treeNode root1, treeNode root2)
{
if(root1 == NULL)
return root2
if(root2 == NULL)
return root1
stack <treePair> S //stack S of type treePair
treePair tree_pair
tree_pair.first = root1
tree_pair.second = root2
S.push(tree_pair)
while(not S.isEmpty())
{
treePair t = s.pop()
if(t.first == NULL or t.second == NULL)
continue
t.first.value += t.second.value
if(t.first.left == NULL)
{
t.first.left = t.second.left
}
else
{
tree_pair.first = t.first.left
tree_pair.second = t.second.left
S.push(tree_pair)
}
if(t.first.right == NULL)
{
t.first.right = t.second.right
}
else
{
tree_pair.first = t.first.right
tree_pair.second = t.second.right
S.push(tree_pair)
}
}
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(M), here M represents the minimum of nodes(overlapping or non-overlapping) from both the tree.
Space Complexity: O(M) (The average case will be logM)
Critical ideas to think!
- Can you think of other tree problems that can be solved iteratively using stack?
Comparison of Different Solutions
Suggested Problems to Solve
- Merge two binary search trees.
- Check if two binary trees are mirrors of each other or not.
- Iterative search for a key ‘x’ in a binary tree.
- Check if two binary trees are identical or not? (Try doing it iteratively for sure)
- Count the number of binary search trees present in a binary tree.
Happy Coding!
Team AfterAcademy!!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Invert a Binary Tree - Interview Problem
Given a binary tree, invert the binary tree and return it. An inverted form of a Binary Tree is another Binary Tree with left and right children of all non-leaf nodes interchanged. You may also call it the mirror of the input tree.

AfterAcademy Tech
Recover Binary Search Tree-Interview Problem
Given a Binary Search Tree such that two of the nodes of this tree have been swapped by mistake. You need to write a program that will recover this BST while also maintaining its original structure

AfterAcademy Tech
Check if a binary tree is BST or not - Interview Problem
Given the root of a binary tree, check whether it is a binary search tree or not.

AfterAcademy Tech
Merge Two Sorted Lists - Interview Problem
Merge two sorted linked lists and return it as a new sorted list. The new list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
