Check if a binary tree is BST or not - Interview Problem
AfterAcademy Tech
•
12 Nov 2019

Level: Easy
Asked in: Microsoft, Google, Amazon, Ebay
Understanding the Problem
Problem Description: Given the root of a binary tree, check whether it is a binary search tree or not.
Binary Search Trees follow the following properties:-
- All nodes in the left subtree of a node have values less than the node’s value
- All nodes in the right subtree of a node have values greater than the node’s value
- Both left and right subtrees are also binary search trees
Problem Note: The inorder traversal of a binary search tree explores tree nodes in sorted order. (Getting an approach yet?)
For example :
Input: Root 10 is given for this tree
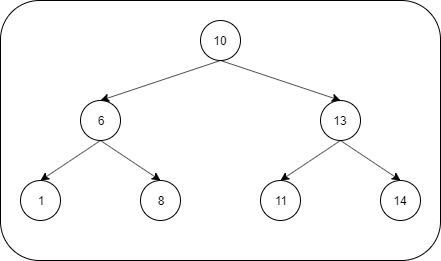
Output: True
Input: Root 10 is given for this tree
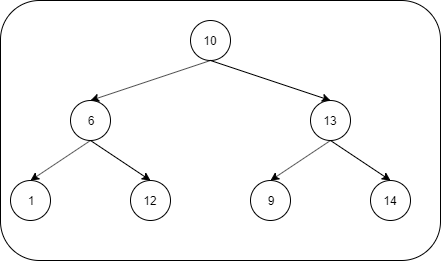
Output: False, the right child of the left child of root is greater than the root
The node structure for the BST passed to your function will be
class BSTNode{
int val
BSTNode *left
BSTNode *right
}
Common Mistake
A quite common naive solution for this problem involves just recursively checking if the left child’s value is less than the current node’s value and the right child’s value is greater than the current node’s value.
boolean isBST(BSTNode root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return True
if (root.left and root.left.val > root.val)
return False
if (root.right and root.right.val < root.val)
return False
if (isBST(root.left) and isBST(root.right))
return True
return False
}
What’s wrong with this particular implementation?
- This does not check if there is an element in the entire left subtree which is greater than the current node’s value.
- Or if there is an element in the right subtree which is smaller than the current node’s value.
- This implementation returns True for the second example above, which is obviously wrong.
Brute force and Efficient solutions
We will be discussing three possible solutions for this problem:-
- Brute Force Approach: Get maximum value from left subtree and minimum value from the right subtree and check if root’s value falls within that range
- Optimized Brute Force: Pass the allowed range for left and right subtrees as function arguments
- Using Inorder Traversal: Store the inorder traversal of the tree and check if it's in sorted order
1. Brute Force Approach
We need to check is the left subtree of a node contains any element greater than the node’s value and whether the right subtree of a node contains any element smaller than the node’s value.
We shall design two helper functions getMin(root) and getMax(root) which will get the minimum and maximum values of the tree with a given root. Then we will check :
- If the node’s value is greater than the maximum value in the left subtree or not
- The node’s value is lesser than the minimum value in the right subtree or not. Basically, we will check if this expression holds true or not: getMax(root.left) < root.val < getMin(root.right)
Pseudo-Code
int getMin(root)
{
BSTNode temp = root
while(temp.left != NULL)
temp = temp.left
return temp.val
}
int getMax(root)
{
BSTNode temp = root
while(temp.right != NULL)
temp = temp.right
return temp.val
}
boolean isBST(BSTNode root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return True
int max_left = getMax(root.left)
int min_right = getMin(root.right)
if (max_left > root.val || min_right < root.val)
return False
if (isBST(root.left) && isBST(root.right))
return True
return False
}
Complexity Analysis
We are traversing and calling getMax(root.left) and getMin(root.right) for each node.
Time complexity: n * (Time complexity of finding max in left subtree + Time complexity of finding min in right subtree) = n * O(n) (Think!)= O(n²)
Space Complexity: O(height), stack space for recursion in worst case = O(n) (Why?)
Critical Ideas to think
- Think about recursive implement of getMin(root) and getMax(root). Also, compare the time and space complexity of both the implementation.
- Try to explore the best and worst-case scenario of time and space complexity.
- Can we design a better solution which checks each node only once?
2. Optimized Brute Force
In the previous approach, we are traversing some parts of the tree many times. Instead of calling getMin(root) and getMax(root) for each node, we traverse down the tree keeping track of min and max allowed value for each node.
To achieve this we pass the allowed range as a function argument while recursing for left and right subtree. Here we are looking at each node only once and initial values for min and max should be INT_MIN and INT_MAX.
For example, The allowed ranges are denoted in square brackets near the node
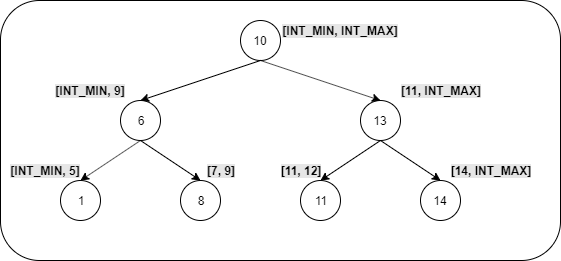
Pseudo-Code
boolean helper(BSTNode root, int range_min, int range_max)
{
if(root == NULL)
return True
if (root.val < range_min || root.val > range_max)
return False
if (helper(root.left, range_min, root.val-1))
if (helper(root.right, root.val+1, range_max))
return True
return False
}
boolean isBST(BSTNode root)
{
if (helper(root, INT_MIN, INT_MAX))
return True
return False
}
Complexity Analysis
Here each node is visited only once.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(height), recursion stack space in worst case = O(n)
Critical Ideas to think
- How tracking the min and max node range help us to solve the problem? Try to explore the code via an example
- Why are we passing parameter range_max = root.value-1 for the left subtree and range_min = root.value + 1 for the right subtree?
3. Using Inorder Traversal
We know that the inorder traversal of a binary search tree gives a sorted order of its elements. We shall use this to our advantage and traverse the tree in inorder fashion and store the elements in an array. We shall then traverse the array in a linear manner and check if its in sorted order or not.
Pseudo-code
void storeInorder(BSTNode root, int arr[])
{
if (root == NULL)
return
storeInorder(root.left, arr)
arr.append(root.val)
storeInorder(root.right, arr)
}
boolean isBST(BSTNode root)
{
int arr[] // Auxiliary array to store inorder
storeInorder(root, arr) // Traverses the array in inorder fashion and stores the result in arr
// Lets check if arr is in sorted order or not
for(i = 1 to arr.length - 1)
if (arr[i] < arr[i-1])
return False
return True
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: Inorder traversal of BST for storing elements in arr[] + Single loop to check arr[] is sorted or not = O(n) + O(n) = O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n) for storing elements in an array + O(height), for recursion stack space in worst case = O(n)
Critical Ideas to think
- Can we solve this problem without using Auxiliary Array?
- Explore problems in the BST which can be solved using the in-order traversal.
Comparison of different solutions
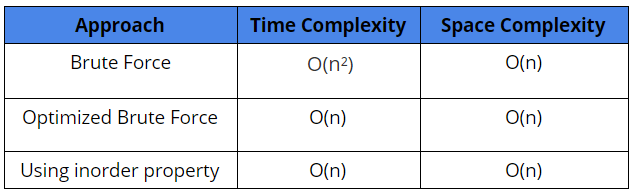
Suggested problems to solve
- Check if the given binary tree is a full binary tree or not
- Check whether the given binary is perfect or not
- Check if a binary tree is a subtree of another binary subtree
- Check if a binary tree is a complete tree or not
- Check if given binary tree is Heap or not
- Check if given binary tree is SumTree or not
Please comment down below if you have alternative approaches or find an error/bug in the above approaches.
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
AfterAcademy Data Structure And Algorithms Online Course - Admissions Open
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Invert a Binary Tree - Interview Problem
Given a binary tree, invert the binary tree and return it. An inverted form of a Binary Tree is another Binary Tree with left and right children of all non-leaf nodes interchanged. You may also call it the mirror of the input tree.

AfterAcademy Tech
Merge two Binary Trees - Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in companies like Amazon, Microsoft. The problem is to merge two binary trees. The overlapping nodes are replaced by the sum of corresponding nodes. We are discussing two ways of solving this.

AfterAcademy Tech
Recover Binary Search Tree-Interview Problem
Given a Binary Search Tree such that two of the nodes of this tree have been swapped by mistake. You need to write a program that will recover this BST while also maintaining its original structure

AfterAcademy Tech
Minimum Absolute Difference in a BST-Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in Google technical interview. Given a BST(Binary Search Tree) with non-negative values, write a program to find the minimum absolute difference between values of any two nodes.
