Kth Largest Element in a BST-Interview Problem
AfterAcademy Tech
•
11 Dec 2019

Difficulty: Medium
Asked in: Amazon
Understanding the Problem
Problem Description: Given a Binary Search Tree, find the Kth Largest element in the given tree.
For example, suppose we are given the following binary search tree
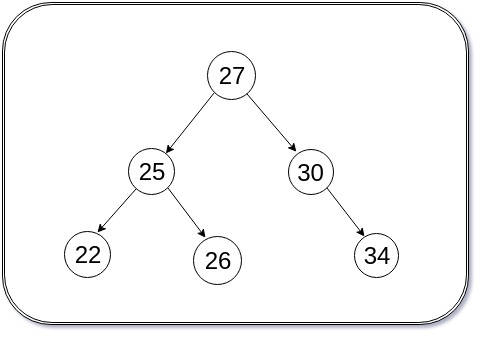
Input: We are given 27 as root of this binary search tree and 2 as a value of K.
Output and Explanation: In this case, the output should be 30 as it is the second largest element in the given BST. Similarly, if the value of K is 3, the output should be 27 because it is the third largest element in the given BST.
The node structure passed to your function will be →
class BSTNode
{
int data
BSTNode left
BSTNode right
}
Possible follow up questions to ask the interviewer
- Can I use extra space? (Ans: You can but try to optimize if possible.)
- What to return if we are given an empty tree? (Ans: Just return -1 in this case.)
- What to return if there are repeated elements?(Ans: Return any of them)
Hint: →Can you think of any binary search tree property which can help?
Solutions
We are going to see three different approaches to solve this problem:→
- Brute Force Approach → Performing inorder traversal and storing the elements in an array.
- By using reverse inorder traversal → Reverse inorder will help to get the elements sorted in descending order.
- By using reverse morris traversal → Morris traversal is used to traverse BST without using recursion.
- By using augmented BST--> We can augment our BST in order to keep count of the right elements.
1. Brute Force Approach
A very simple solution is to perform inorder traversal and store the elements of BST in an array which will give us all elements in sorted order. By traversing the array in reverse order and maintaining a count, we can return the Kth largest element.
Pseudo-Code:
void getInorder(BSTNode root, int A[])
{
if(root==NULL)
return
getInorder(root.left, A)
A.append(root.data)
getInorder(root.right, A)
}
int KthLargestBST(BSTNode root, int K)
{
if(root == NULL)
return -1
int A[]
getInorder(root, A)
int count = 1
int index = A.length - 1
while(count < K)
{
index = index - 1
count = count + 1
}
return A[index]
}
Complexity Analysis :
Time Complexity: Traversing the tree for storing elements in an array + Traversing the array in reverse order = O(n) + O(n) = O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n) (We are using an extra array of n size, where n is the number of nodes.)
Critical ideas to think!
- Can we solve this problem without using extra space?
- Explore the recursive and iterative implementation of In-order traversal? Why in-order traversal is important in the case of BST?
- Inorder Traversal gives us elements in ascending order, what if we can get elements in descending order?
2. Using Reverse Inorder Traversal
The idea is to do reverse inorder traversal of BST which helps to explore all the nodes in decreasing order. While doing the traversal, we keep track of count of nodes visited so far. When the count becomes equal to K, we stop the traversal and return the value stored in the node.
Pseudo-Code:
int KthLargestBST (BSTNode root, int K, int &count )
{
if(root == NULL || count >= K)
return -1
KthLargestBST (root.right, K, count)
count = count + 1
if(count == K)
return root.data
KthLargestBST (root.left, K, count)
}
Complexity Analysis
Time complexity: Traversing tree in reverse in-order = O(n)
Space complexity: O(h) for recursion call stack, where h is the height of the tree.
Critical ideas to think!
- What is the worst and best-case scenario of space complexity?
- Explore and prepare list of problem which can be solved using reverse in-order traversal.
- Can we do the inorder traversal of a BST without recursion?
3. Using Reverse Morris Traversal
Morris Traversal is just traversing the tree in inorder fashion without using recursion and stack. Since it does not use recursion or stack, it saves us a lot of space.We will here use reverse morris traversal to get elements in descending order and then use a count variable to get the Kth element.
Pseudo-Code
int KthLargestBST(BSTNode root, int K)
{
BSTNode current=root
BSTNode KthLargest = NULL
int count = 0
while(current != NULL)
{
if(current.right == NULL)
{
count=count+1
if(count == K)
KthLargest = current
current = current.left
}
else
{
BSTNode successor = current.right
while (successor.left != NULL && successor.left != current)
successor = successor.left
if (successor.left == NULL)
{
successor.left = current
current = current.right
}
else
{
successor.left = NULL
count=count+1
if(count == K)
KthLargest = current
current = current.left
}
}
}
return KthLargest.data
}
Complexity
Time Complexity: O(n) (Every edge is traversed 3 times and there are n-1 edges)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical ideas to think!
- Can you find any similarity of this problem with finding Kth largest in an array?
4. Augmented BST Approach
The problem can be solved if we maintain the rank of each node. We can keep track of how many elements are in the right and left subtree during the insertion of elements in a tree. Since we need the Kth maximum, we can keep the track of elements in the right subtree.
Suppose, there are N nodes in the right subtree of the given tree, if the value of K is (N+1) then the root element is the required Kth maximum element. If K<N, we wil keep searching in the right subtree itself using recursion. And if K>(N+1), then in this case we will search for the element in the left subtree.
Note: Here the Node structure is like
class BSTNode
{
int data
BSTNode right
BSTNode left
int rightCount
}
Pseudo-Code:
int KthLargestBST(BSTNode root, int K)
{
if(root==NULL)
return -1
if(root)
{
BSTNode tempTraverse=root
while(tempTraverse)
{
if(tempTraverse.rightCount+1==K)
return tempTraverse.data
else if(K>tempTraverse.rightCount+1)
{
K=K-(tempTraverse.rightCount+1)
tempTraverse=tempTraverse.left
}
else
tempTraverse=tempTraverse.right
}
return -1
}
Critical ideas to think!
- Can you think of the rank which you need to maintain when finding Kth smallest in a BST?
- Can you think about other applications of augmented trees?
- Can you augment a graph node? If so, what are the applications of doing so?
- Can you write the recursive solution of this problem?
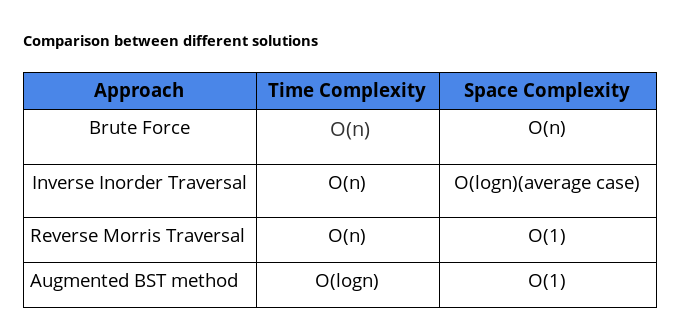
Comparison of different approaches
Suggested Problems to Solve
- Kth smallest element in a BST
- Morris Traversal of a tree
- Kth smallest/largest in an unsorted array
- Merge two BSTs with constant extra space
Happy Coding!! Enjoy Algorithms.
AfterAcademy Data Structure And Algorithms Online Course — Admissions Open
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Minimum Absolute Difference in a BST-Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in Google technical interview. Given a BST(Binary Search Tree) with non-negative values, write a program to find the minimum absolute difference between values of any two nodes.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find the next greater element for every element in an array - Interview Problem
Given an array A[] of size n, you need to find the next greater element for each element in the array. Return an array that consists of the next greater element of A[i] at index i.

AfterAcademy Tech
Largest Rectangle in a Histogram-Interview Problem
You are given an array of integers arr where each element represents the height of a bar in a histogram. Histogram is a graphical display of data using bars of different heights. The bars are placed in the exact same sequence as given in the array. You need to find the area of the largest rectangle found in the given histogram.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find the most frequent element in an array - Interview Problem
Given an array A[] of size n, find the most frequent element in the array, i.e. the element which occurs the most number of times.
