Find the next greater element for every element in an array - Interview Problem
AfterAcademy Tech
•
05 Nov 2019

Level: Medium
Asked in: Amazon, Microsoft
Understanding the Problem
Problem Description: Given an array A[] of size n, you need to find the next greater element for each element in the array. Return an array that consists of the next greater element of A[i] at index i.
The next greater element is the first greater element on an element’s right side in the array. e.g., an element A[j] would be the next greater element of A[i] such that A[j] > A[i] , i < j and j - i is minimum.
For example :
Input: A[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Output = {2, 3, 4, 5, -1}
Input: A[] = {12, 1, 0, 17, 10}
Output: {17, 17, 17, -1, -1}
Possible questions to ask the interviewer:-
- What is the range of elements in the array? (Ans: The array consists of positive integers less than 10⁵)
- What should we do in the case when no greater element exists on the right side of the element in the array? (Ans: The next greater element for such element would be -1)
- Can the array contain duplicates? (Ans: Sure, that's a possibility)
Solutions
We would be discussing two possible solutions for this problem
- Brute Force: Linearly traverse till you find a next greater element
- Using Stack Data Structure: Store elements in a stack and pop them as soon as you encounter a next greater element
1. Brute Force approach
The naive approach to this problem would be to linearly traverse the right side from the element until you find the next element greater of the current element.
Pseudo-Code
int[] findNextGreaterElement(int A[], int n)
{
int ans[]
for( i = 0 to n-1 )
{
bool found = False
for ( j = i+1 to n-1 )
{
if ( A[j] > A[i] )
{
found = True
ans.append(A[j])
break
}
}
if ( found == False )
ans.append(-1)
}
return ans
}
Complexity Analysis
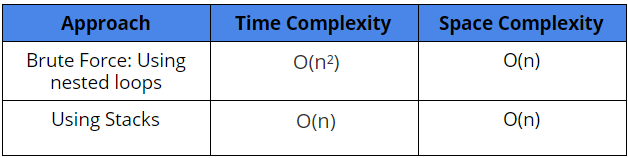
There are two nested loops where worst-case occurs when elements are sorted in decreasing order. Time Complexity = O(n²)
Space Complexity: O(n), for storing ans[] array
Critical ideas to think!
- What is the best-case scenario? Count the total number of comparisons in the worst and the best case.
- Can we improve the time complexity further?
2. Using Stack Data Structure
Stack is an ideal data structure for such problems. It stores the elements or its index for whom the next greater element is not yet found and pops them as soon as it meets the next greater element.
Solution Steps
Stack can be used to store either element values or their indices. Since we need to return an array with the next greater element at corresponding indices, the order is important for us and hence we shall store indices.
- Declare an array ans[] with size n and initialize it with a default value of -1.
- Declare a stack S and push value ‘0’ in it representing the index of the first element.
- Start traversing the array from the second element and at each iteration
- Initiate a while loop that keeps on popping elements as long as the top of the stack is smaller than the current element. The Next Greater Element for all these popped elements will be the current element (Think!).
- At the end of while loop, push the index of the current element in the stack
4. All elements that remain in the stack, in the end, have the next greater element as -1. Since the default value in ans[] was -1, the corresponding indices of these elements are already filled with -1. Return ans[] array
Pseudo-Code
int[] findNextGreaterElement(int A[], int n)
{
int ans[n]
for( i = 0 to n-1 )
ans[i] = -1
Create an integer stack S
S.push(0)
for ( i = 1 to n-1 )
{
while (S.empty()== False && A[S.top()] < A[i])
{
ans[S.top()] = A[i]
S.pop()
}
S.push(i)
}
return ans
}
Complexity Analysis
Note that each element is visited at most twice, first while pushing them onto the stack and second while popping them from the stack. (Think!)
Time Complexity: Initializing ans[] array with -1 + Traversal of the array and Stack Manipulation = O(n) + O(2*n) (Why?) = O(n)
Space Complexity: Stack of size n + ans[] array of size n = O(n) + O(n) = O(n)
Critical ideas to think!
- How the above code works when input is sorted and reverse sorted? Try to visualize the order of push and pop operation for both the scenario.
- Modify the above code when we want to store elements (not the index of the elements) in the stack.
- Can we think of some other data structure for an efficient solution?
- Does this algorithm work fine if the input array contains duplicates?
Comparison of solutions
Suggested Problems to solve
- Given an array, print the next smaller element for every element.
- Find the next greater element for all elements in a circular list
- The Stock Span Problem: Given a list of prices of a single stock for N number of days, find the stock span for each day.
- Find the largest rectangular area possible in a given histogram where the largest rectangle can be made of several contiguous bars.
- Given an array of distinct elements, print the closest greater element for every element.
- Given an array of distinct elements, find the previous greater element for every element.
- Check for balanced parentheses in an expression
- Given a collection of intervals, merge all overlapping intervals.
If you have any more approaches or you find an error/bug in the above solutions, please comment down below.
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Find the most frequent element in an array - Interview Problem
Given an array A[] of size n, find the most frequent element in the array, i.e. the element which occurs the most number of times.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find the majority element in an array - Interview Problem
You are given an array A[] consisting of n elements. You need to find and return the number which appears more than n/2 times.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find whether an array is a subset of another array - Interview Problem
Given two integer array A[] and B[] of size m and n(n <= m) respectively. We have to check whether B[] is a subset of A[] or not. An array B is a subset of another array A if each element of B is present in A. (There are no repeated elements in both the arrays)

AfterAcademy Tech
Find minimum and maximum value in an array - Interview Problem
Given an array A[] of size n, you need to find the maximum and minimum element present in the array.Your algorithm should make minimum number of comparisons.
