Graph Traversal: Breadth First Search
AfterAcademy Tech
•
10 Feb 2020
In the previous blog i.e. The Introduction to Graph in Programming, we saw what a graph is and we also saw some of the properties and types of graph. We also saw how to represent a graph i.e. using the Adjacency Matrix and Adjacency List. In this blog, we will learn about the Breadth-First Search i.e. BFS that is used to search some node in a graph by traversing it.
Graph traversal is a process of visiting all the nodes from a source node only once in some defined order. The order of traversal of nodes of a graph is very important while solving some graph problems. Also, you must track the nodes that are already visited because, in traversal, you need to traverse a node only once. So, a proper list of the traversed nodes of the graph must be maintained. There are two ways of Graph traversal:
- BFS or Breadth-First Search
- DFS or Depth First Search
In this blog, we will cover the BFS part. So, let's get started.
Breadth-First Search
Breadth-First Search or BFS is a graph traversal algorithm that is used to traverse the graph level wise i.e. it is similar to the level-order traversal of a tree.
Here, you will start traversing the graph from a source node and from that node you will first traverse the nodes that are the neighbours of the source node. After traversing all the neighbour nodes of the source node, you need to traverse the neighbours of the neighbour of the source node and so on.
Based on the source node, the whole graph can be divided into various levels i.e. the nodes that are at distance 1 from the source node are said to be at level 1. Similarly, the nodes that are at distance 2 from the source node are said to be at level 2 and so on. Based on the layers of the graph, the BFS can be performed by the following steps:
- Start with the starting or source node.
- Traverse all the nodes present in level 1 of the graph.
- Move to the next level and traverse all the nodes present in level 2 and so on.
NOTE: There can be more than one path from node i to node j because a graph can contain a cycle. But you should visit a node once. So, you have to keep a record of all the visited nodes so that one node can be visited only once.
The following is an example of Breadth-First Search:
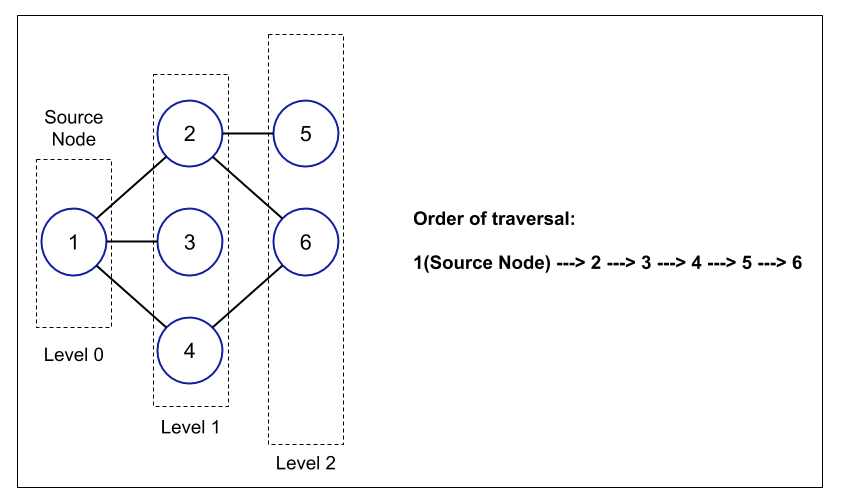
BFS implementation
In order to implement BFS, we need to take care of the following things:
- Traversal should be level wise i.e. first level 1 will be traversed, followed by level 2, level 3, and so on.
- The nodes should be visited once. None of the nodes should be visited twice.
So, to apply the above conditions, we make the use of Queue data structure that follow First In First Out(FIFO) order. We will insert the nodes in the queue and mark it as visited and after that, all the neighbour nodes of that node will also be inserted in the queue. Since it follows FIFO order, the node entered first will be visited first and their neighbours will be added in the queue first. During insertion of nodes in the queue, we will check if the nodes are visited or not. If it is visited then we will not add those nodes in the queue. Otherwise, we will add the node in the queue.
The following is the pseudocode of Breadth-First Search:
BFS (G, s): //here, G is the graph and s is the source or initial node
Q.enqueue( s ) //here, Q is queue for storing nodes. So, we are inserting node "s" in the queue Q
also mark "s" as visited node
while ( Q is not empty)
//removing that vertex from queue whose neighbour will be visited now
v = Q.dequeue( ) //this will return the node inserted first in the queue
//processing all the neighbours of v
//if the node "w" is already visited, then ignore it
//if the node "w" is not visited, then insert it into the queue
for all neighbours w of v in Graph G
if w is not visited
Q.enqueue( w ) //Stores w in Q to further visit its neighbour
mark w as visited.
Let's understand the above pseudocode with the help of one example.
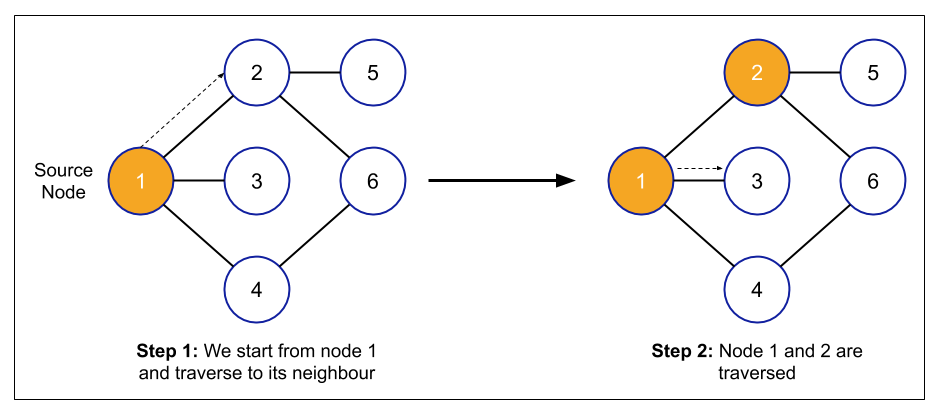
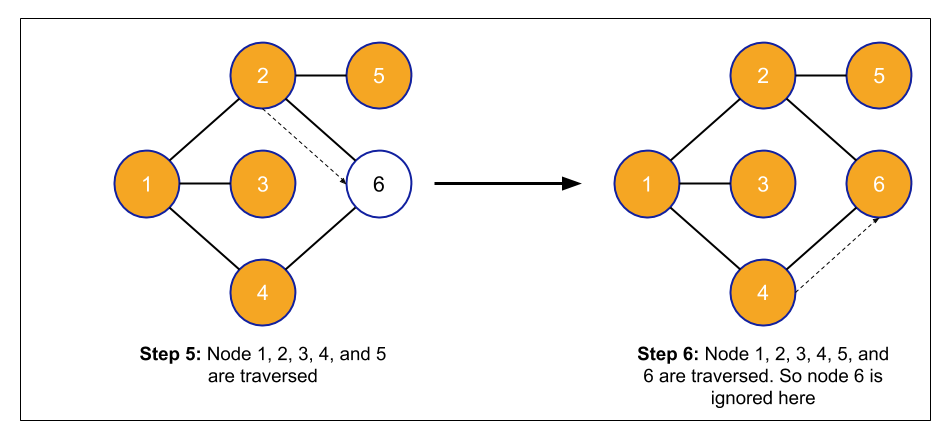
The following process will be followed in different iteration:
First Iteration
- The sources node "1" will be deleted from the queue.
- The neighbours of node 1 will be traversed(if any).
- If the neighbours are already visited, then ignore it. Otherwise, add it to the queue and mark it as visited. So, node 2, node3, and node 4 will be added in the queue.
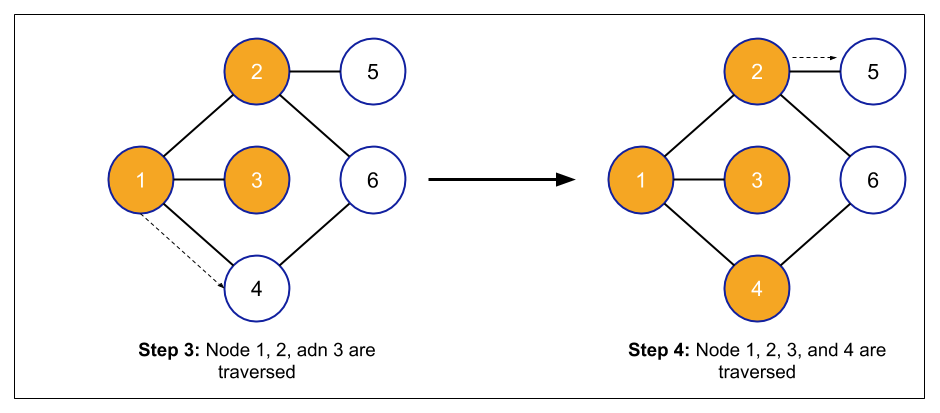
Second Iteration
- Node 2 will be deleted from the queue.
- The neighbours of node 2 will be traversed(if any).
- If the neighbours are already visited, then ignore it. Otherwise, add it to the queue and mark it as visited. So, node 5 and node 6 will be added in the queue.
Third Iteration
- Node 3 will be deleted from the queue.
- The neighbours of node 3 will be traversed(if any).
- If the neighbours are already visited, then ignore it. Otherwise, add it to the queue and mark it as visited.
Fourth Iteration
- Node 4 will be deleted from the queue.
- The neighbours of node 4 will be traversed(if any).
- If the neighbours are already visited, then ignore it. Otherwise, add it to the queue and mark it as visited.
Fifth Iteration
- Node 5 will be deleted from the queue.
- The neighbours of node 5 will be traversed(if any).
- If the neighbours are already visited, then ignore it. Otherwise, add it to the queue and mark it as visited.
Sixth Iteration
- Node 6 will be deleted from the queue.
- The neighbours of node 6 will be traversed(if any).
- If the neighbours are already visited, then ignore it. Otherwise, add it to the queue and mark it as visited.
Application of BFS
- Shortest Path: When you are dealing with the unweighted graph i.e. there is no weight on the edges of the graph, then the shortest path from one node to other can be found by using BFS.
- Neighbour places: While finding some nearest hotel or something else, the GPS of your phone can use BFS for finding the neighbouring nodes.
- Cycle detection: BFS can be used to detect cycles in a graph. This is possible because in BFS we are maintaining a list of visited nodes.
- Crawlers: The crawlers in search engine use BFS for directing one page to another. For example, if you are at some page p1 and the page p1 is having the link of page p2 and page p3, then page p2 and p3 are the neighbours of page p1. So, here BFS can be used to crawl the neighbouring pages.
- Finding nodes connected to a particular node: You can find all the nodes connected to a particular node by using the Breadth-First Search.
- Route finding: BFS can be used to find if there is a route between two cities or not. Here, the cities are the nodes of the graph and the path between these cities are the edges of the graph.
These are some of the applications of Breadth-First Search.
Graph questions
- Is Graph Bipartite?
- Number of Islands
- Word Ladder Problem
- Smallest Multiple with 0 and 1
- Course Schedule
- Knight on Chessboard
Happy Learning, Enjoy Algorithms!
Team AfterAcademy!
AfterAcademy Data Structure And Algorithms Online Course - Admissions Open
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Graph Traversal: Depth First Search
In this blog, we will learn Depth First Search that is used for Graph Traversal i.e. the Depth First Search is used to traverse each and every node of a graph. So, let's learn together.
AfterAcademy Tech
Binary Search
Given a sorted integer array arr[] of n elements and a target value k, write a program to search k in arr[]. The famous binary search algorithm is easy to implement and the best optimization technique for performing searching operations

AfterAcademy Tech
Search in a 2-D Matrix
You are given a matrix arr of m x n size. Write a program to searches for a value k in arr. This arr has the following properties: - Integers in each row are sorted from left to right. - The first value of each row is greater than the last value of previous row. This is a basic optimization problem that will clear the concept of searching.

AfterAcademy Tech
How to traverse in a tree?
It is important to know traversal techniques in a tree before solving tree problems. We have discussed the 3 primary traversals in a tree at length in this blog with both recursive and iterative implementations.
