Binary Search
AfterAcademy Tech
•
18 Jul 2020

Difficulty: Easy
Understanding The Problem
Problem Description
Given a sorted integer array arr[] of n elements and a target value k, write a program to search k in arr[].
Problem Note
- If
kexists, then return its index, otherwise, return -1. - You may assume that all elements in
arr[]are unique.
Example 1
Input: arr[] = [1, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 50], k= 9
Output: 4
Explanation: 9 exists in arr[] and its index is 4.
Example 2
Input: arr[] = [1, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 50], target = 20
Output: -1
Explanation: 20 does not exist in arr[] so return -1.
You may try to solve the problem here.
Solution
We need to return the position of an element that needs to be searched in a sorted array.
The question clearly needs us to perform Binary Search. This searching technique works on the sorted arrays.
The binary search begins by comparing an element in the middle of the array with the target value. If the target value matches the element, its position in the array is returned. If the target value is less than the element, the search continues in the lower half of the array. If the target value is greater than the element, the search continues in the upper half of the array.
By doing this, the algorithm eliminates the half in which the target value cannot lie in each iteration.
This searching technique is far more efficient than the linear search. Look at the example below.
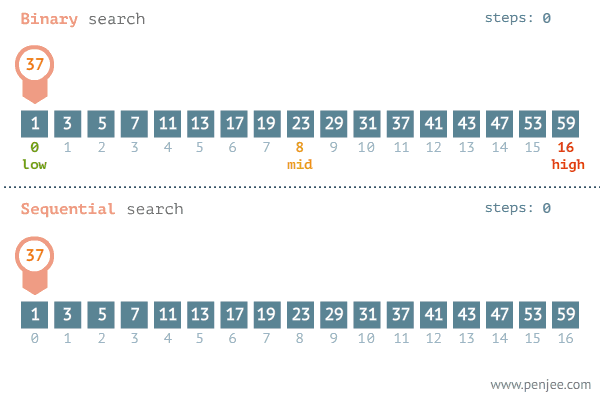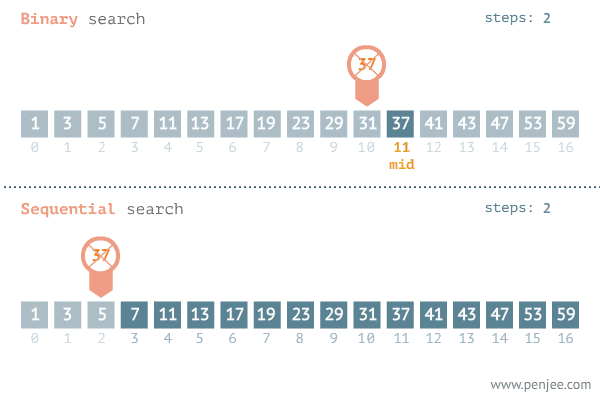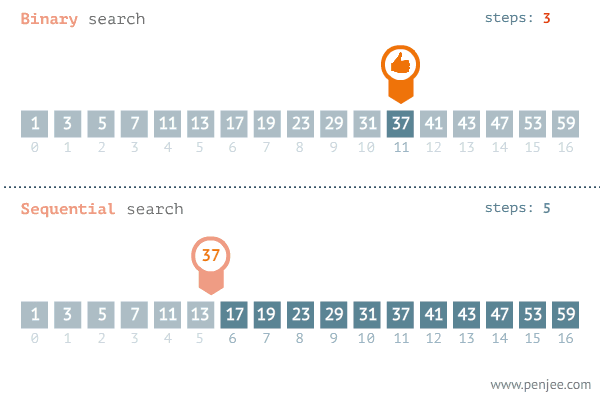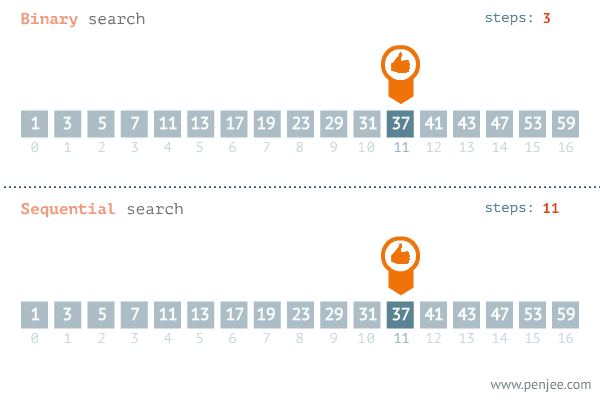
Solution Steps
- Set L to 0 and R to n-1.
- If L > R, the search terminates as unsuccessful.
- Set m (the position of the middle element) to the floor of (l + r) / 2
- If A[m] < T, set L to m+1 and go to step 2.
- If A[m] > T, set R to m-1 and go to step 2.
- If A[m]=T, the search is done and return m.
Pseudo Code
Recursive Binary Search
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int T) {
if (l <= r) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2
if (arr[mid] == T)
return mid
if (arr[mid] > T)
return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, T)
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, T)
}
return -1
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(log n)
Space Complexity: O(log n), considering recursion stack space
Iterative Binary Search
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int T)
{
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2
if (arr[m] == T)
return m
if (arr[m] < T)
l = m + 1
else
r = m - 1
}
return -1
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(log n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
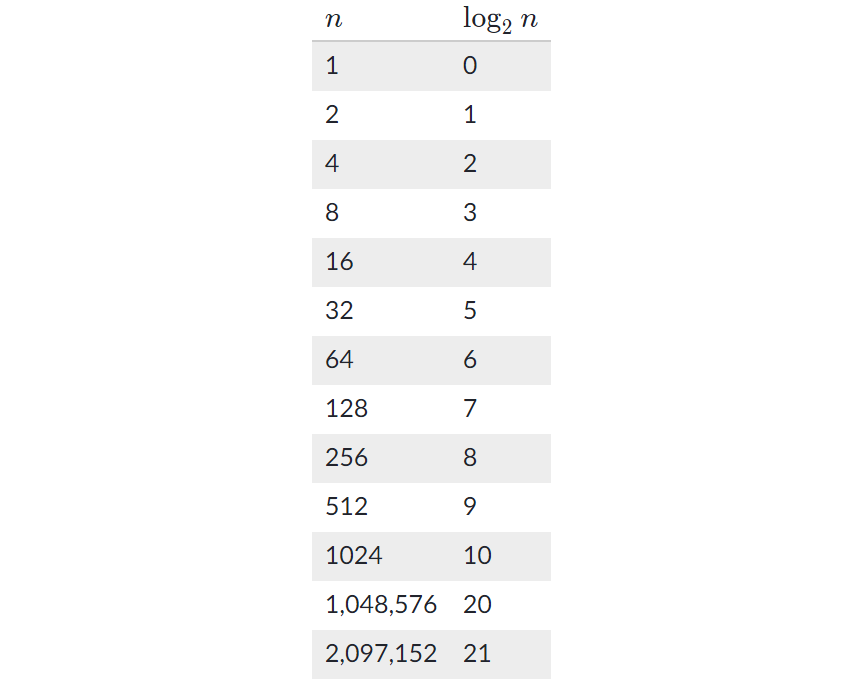
Here’s a table showing the base-2 logarithms of various values of n:
Critical Ideas To Think
- Can we replace
while(l≤r)withwhile(l<r)? If not, then why? - How did we make sure than if the
target < arr[m], then the target will exist only on the left of mid? - Perform recursive binary search over some custom example?
- The 2014 “Catalogue of Life” contains about 1580000 names of species. If these names were sorted in an array, in the worst case, how many comparisons would it take for the binary search to find the name of a particular species in the array?
- Can you list the places where is Binary search algorithm is used?
Suggested Problems To Solve
- Write the code for pow(x, n) function
- Write the code for sqrt(x) function
- Search in a 2D Matrix
- Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array
- Find Peak Element
- Dungeon Game
- Minimum Size Subarray Sum
If you have any more approaches or you find an error/bug in the above solutions, please comment down below.
Happy Coding!
Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Binary Search Tree: Introduction, Operations and Applications
Binary Search Trees is one of the most important variation of binary tree and is extremely useful in practical applications. The blog discusses the operations and applications of this powerful data structure
AfterAcademy Tech
Binary Search Tree vs Hash Table
In this blog, we will see the difference between a binary search tree and a hash table. We will see which data structure should be used when to solve our problems.

AfterAcademy Tech
Recover Binary Search Tree-Interview Problem
Given a Binary Search Tree such that two of the nodes of this tree have been swapped by mistake. You need to write a program that will recover this BST while also maintaining its original structure

AfterAcademy Tech
Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
Given a binary search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the BST. This is a very famous interview problem and previously asked in Microsoft and Amazon.
