Find the intersection of two unsorted arrays - Interview Problem
AfterAcademy Tech
•
01 Oct 2019

Difficulty Level : Medium
Asked in : Google, Facebook
Understanding the Problem
Problem Description: Given two integer arrays A[] and B[] of size m and n, respectively. We need to find the intersection of these two arrays. The intersection of two arrays is a list of distinct numbers which are present in both the arrays. The numbers in the intersection can be in any order.
For example
Input: A[] = {1,4,3,2,5, 8,9} , B[] = {6,3,2,7,5}
Output: {3,2,5}
Input : A[] = {3,4,6,7,10, 12, 5}, B[] = {7,11,15, 18}
Output: {7}
Possible follow-up questions to ask the interviewer:-
- Can you modify the arrays? (Ans: Yes)
- What are the constraints on the length and elements of the array? (Ans: m>n, 1 <= m,n <= 10^5, -10^5 <= A[i], B[i] <= 10^5)
- Can there be repeated elements in the array or between the arrays? (Ans: Yes, the possibility exists)
Designing efficient solutions
We are discussing four ways to solve this problem :
- Brute force: Use nested loops
- Sorting and binary search
- Sorting and two-pointer approach
- Using a Hash Table
1. Brute Force: Use nested loops
For each element in A[], perform a linear search on B[]. Keep on adding the common elements to a list. To make sure the numbers in the list are unique, either check before adding new numbers to list or remove duplicates from the list after adding all numbers.
Pseudo-Code
int[] findIntersection(int A[], int B[], int m, int n)
{
int ans[]
for ( i = 0 to m-1 )
{
for ( j = 0 to n-1 )
{
if ( A[i] == B[j] )
if ( A[i] not in ans)
ans.add(A[i])
}
}
return ans
}
Complexity Analysis
There are two loops in the solution where the outer loop runs n times and the inner loop runs m times. So in the worst case, time complexity = O(m*n).
Space Complexity: worst-case = O(1) (Why? Some space is being consumed by answer list. Why isn't it taken into consideration?)
Critical ideas to think!
- What would be the time and space complexity of removing duplicates from n size array?
- How can we improve the time complexity?
2. Sorting and binary search
In the brute force approach, we select elements from array A[] and linearly search for them in array B[]. We could increase the efficiency of searching the elements if we sort B[] and apply binary search to search for the elements. Binary Search takes O(logn) time complexity.
Solution Steps
- Declare answer list.
- Sort B[] array in increasing order.
- Search for each element in A[] in the sorted array B[]
- If the element if found, add it to the answer list
- Return answer list
Pseudo-Code
bool binary_search(int B[], int n, int K)
{
int low = 0, high = n
while( low <= high )
{
int mid = low + ( high - low ) / 2
if( B[mid] == K )
return True
else if( B[mid] > K )
high = mid - 1
else
low = mid + 1
}
return false
}
int[] findIntersection(int A[], int B[], int m, int n)
{
int ans[]
sort(B,n)
for(i = 0 to m-1)
{
if(binary_search(B, n, A[i]))
ans.add(A[i])
}
return ans
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: Sorting array B[] + Searching for all elements of A[] in B[] = O(nlogn) + O(mlogn) = O(nlogn + mlogn)
Space Complexity: If we use merge sort, then space complexity is O(n), else if we use heap sort, space complexity is O(1).
Critical ideas to think!
- Here, we sorted the smaller array. What if we sort the bigger array for the solution? How does the time complexity changes?
- What would be the time and space complexity if we use quicksort? Compare different sorting algorithms
- What would be the space complexity if we use recursive binary search for the implementation?
- Prepare a list of problems where you can apply the idea of sorting and binary search.
3. Sorting and two-pointer approach
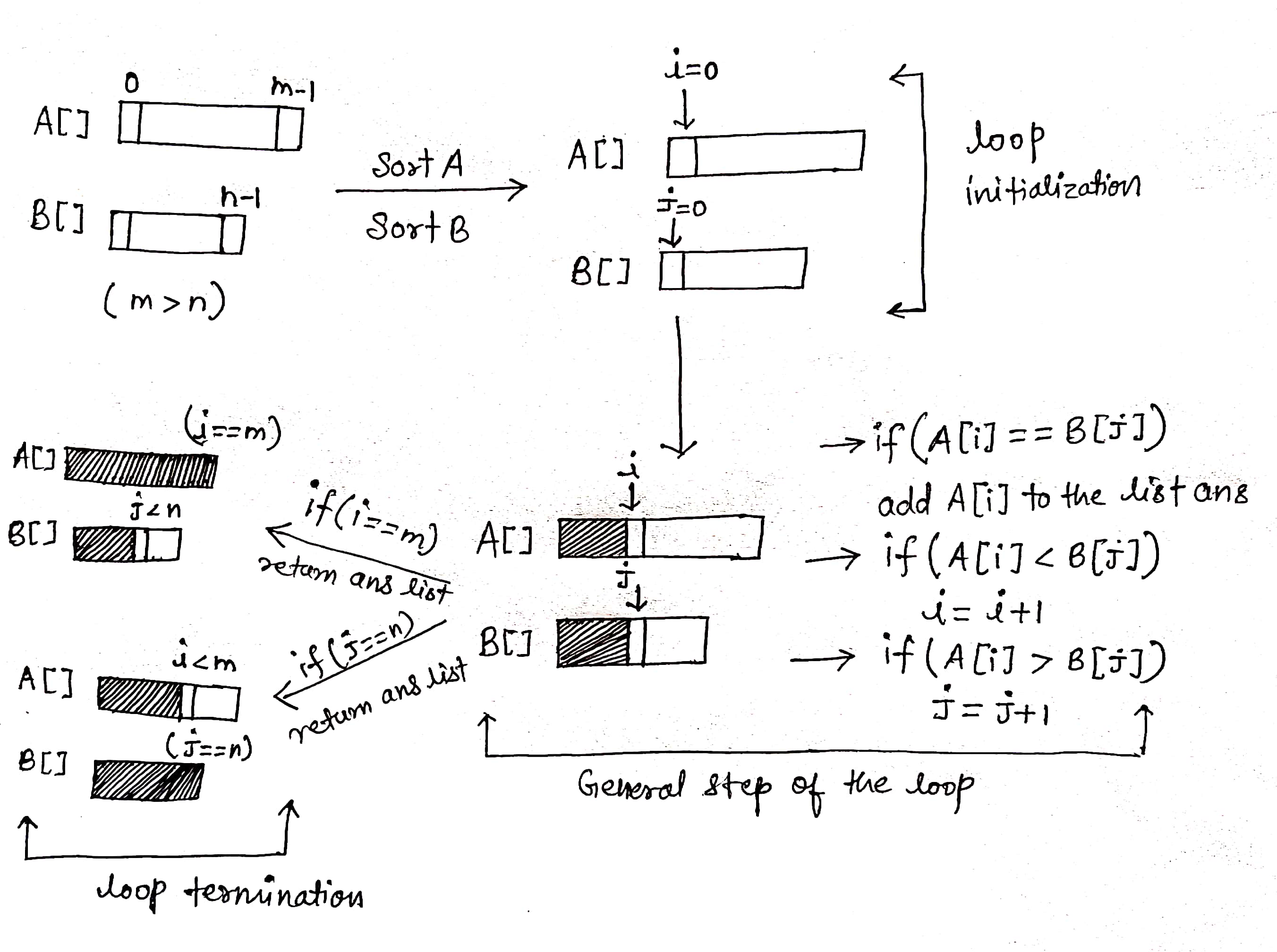
If both A[] and B[] are sorted, we can use a two-pointer approach. At each step, we compare one element of A[] with one element of B[]. If both are equal, we add it to the list, else we move forward.
Solution Steps
- Declare the answer list.
- Sort both the arrays in increasing order.
- Initialize the variables i and j in the sorted array A[] and B[] respectively. i = 0 and j = 0
- Run a loop while i < m and j < n (Why 'and', not 'or'?)
- If A[i] == B[j], add A[i] to the list and increment both i and j
- If A[i] < B[j], increase i by 1
- If A[i] > B[j], increase j by 1
5. Return answer list.
Solution Visualization
Pseudo-Code
int[] findIntersection(int A[], int B[], int m, int n)
{
int ans[]
sort(A, m)
sort(B, n)
i = 0, j = 0
while( i < m and j < n )
{
if ( A[i] == B[j] and A[i] not in ans)
{
ans.add(A[i])
i = i + 1
j = j + 1
}
else if ( A[i] < B[j] )
i = i + 1
else
j = j + 1
}
return ans
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity : Sorting array A[] + Sorting array B[] + Using two pointer approach = O(mlogm) + O(nlogn) + O(n+m) = O(mlogm + nlogn)
Space Complexity: If mergeSort is used, then O(m), else in heapSort, O(1)
Critical ideas to think!
- Why are we incrementing pointers when A[i]>B[j] or A[i]<B[j] ?
- Does this algorithm work fine when elements are repeated? How can you ensure that elements in the answer list are unique?
- The time complexity of while loop is O(m+n) - Why?
- Why the idea of the two pointer works perfectly for a sorted array?
- Prepare a list of problems where you can apply the idea of two pointer approach for the solution.
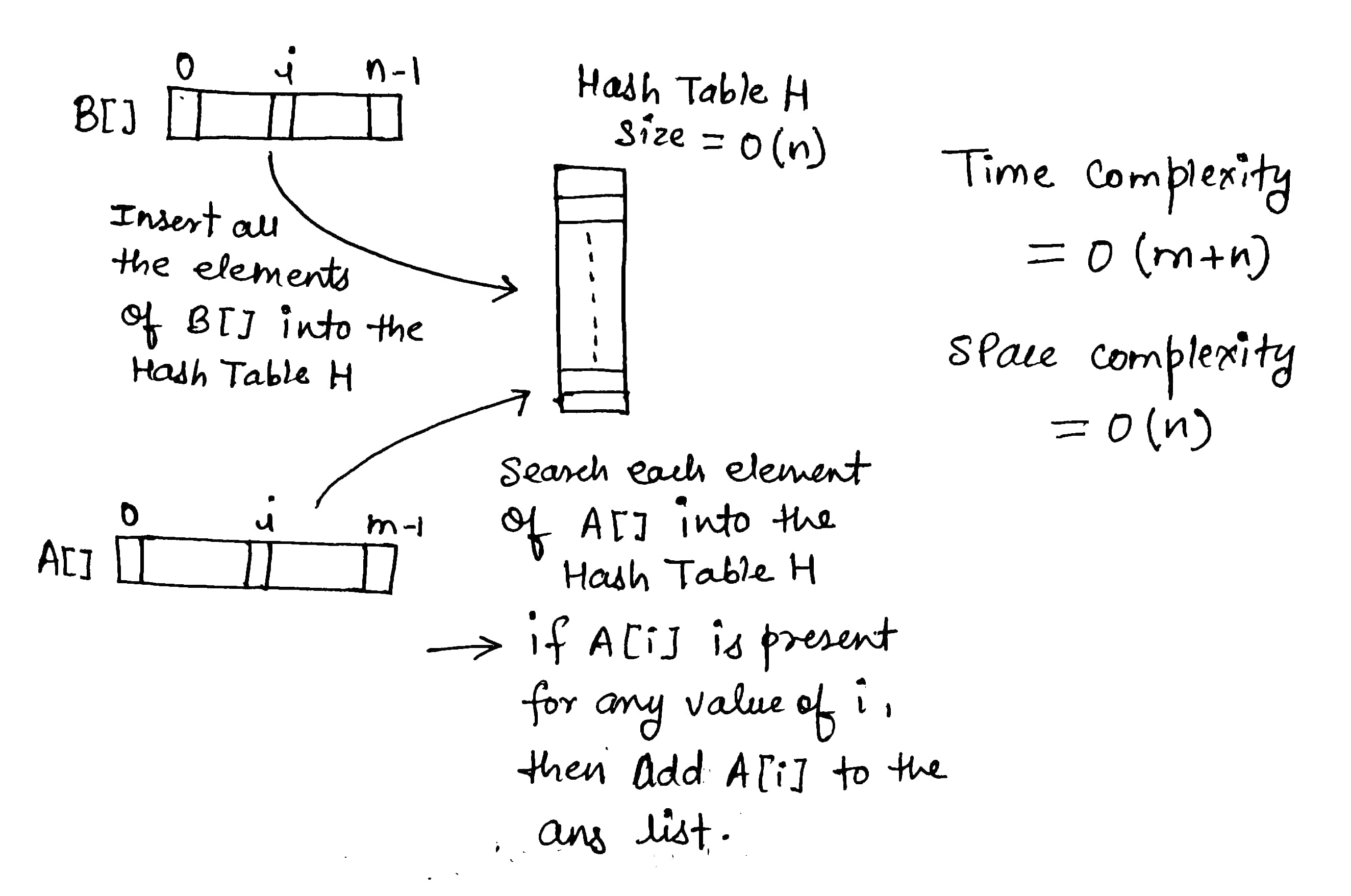
4. Using a Hash Table
We will make a hash table of the smaller array so that our searching becomes faster and all elements appear only once. Now for each element of the bigger array, we will perform a search operation of that element in the hash table. The search operation in a hash table is, in an average case, O(1).
Solution Steps
- Create a hash table of size n
- Add all elements of array B[] in the hash table
- For each element of A[], search for that element in the hash table. If found, add the element to the answer list
- Return answer list
Solution Visualization
Pseudo-Code
int findIntersection(int A[], int B[], int m, int n)
{
int ans[]
Take HashTable H of Size n
for(i = 0 to n-1)
{
H.insert(B[i])
}
for( i = 0 to m-1)
{
if(H.Search(A[i]) is true)
ans.add(A[i])
}
return ans
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity = Inserting n elements of A[] in hash table + Time complexity of searching m elements of B[] in the hash table
= m* O(1) + n * O(1)) = O(m+n)
Space Complexity = O(n), for storing the auxiliary hash table
Critical ideas to think!
- Do we need to modify the algorithm if elements are repeated? Is there a possibility of elements being repeated in the answer list?
- What are the changes in time complexity and space complexity if the hash table is created for the bigger array instead of the smaller array? Which is more efficient?
- What is the worst-case time complexity for searching an element in a hash table?
- What other data structures could help efficiently solve this problem? Is self-balancing BST useful?
Comparison of different solutions
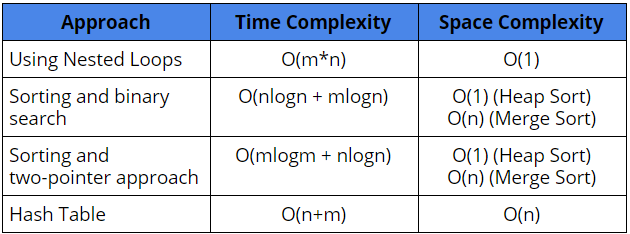
Suggested Problems to solve
- Find the intersection of 3 sorted arrays
- Find the union of two sorted arrays
- Find the intersection of two linked list
- Merge two sorted arrays
- Given an array of integers, and a number K, print all pairs in the array whose sum is equal to K.
- Given an unsorted array of integers, find the length of the longest consecutive sequence
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Find whether an array is a subset of another array - Interview Problem
Given two integer array A[] and B[] of size m and n(n <= m) respectively. We have to check whether B[] is a subset of A[] or not. An array B is a subset of another array A if each element of B is present in A. (There are no repeated elements in both the arrays)

AfterAcademy Tech
Find the most frequent element in an array - Interview Problem
Given an array A[] of size n, find the most frequent element in the array, i.e. the element which occurs the most number of times.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find minimum and maximum value in an array - Interview Problem
Given an array A[] of size n, you need to find the maximum and minimum element present in the array.Your algorithm should make minimum number of comparisons.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find the next greater element for every element in an array - Interview Problem
Given an array A[] of size n, you need to find the next greater element for each element in the array. Return an array that consists of the next greater element of A[i] at index i.
