Find an Element In a Bitonic Array
AfterAcademy Tech
•
23 Mar 2020

Difficulty : Easy
Asked in: Amazon
Understanding the problem
Problem Description
Given a bitonic sequence of n distinct elements, write a program to search a given element k in the bitonic sequence.
Problem Note →
- A Bitonic Sequence is a sequence of numbers that is first strictly increasing then after a point strictly decreasing.
- It is guaranteed that there are no duplicates in the input array.
- If the element is found then return the index otherwise return -1.
- You are expected to solve this problem in O(log N) time complexity.
Example 1
Input: nums[] = [-3, 8, 9, 20, 17, 5, 1], k = 20
Output: 3
Explanation: Element k Found at index 3
Example 2
Input: nums[] = [5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 3, 2, 1], k = 30
Output: -1
Solutions
- Linear Search — Scan each element from left to right.
- Binary Search — Find peak element and then perform a binary search on one of the halves of the array.
1. Linear Search
In this approach, we make use of the fact that two consecutive numbers nums[i] and nums[i+1] are never equal. Thus, we can traverse over the nums array from the beginning while comparing each element with the key. If the ith element is equal to the k value, then we will return the index of the element. If the element is not found, we will simply return -1.
Psudo Code
// size is the size of the nums array
int findBitonic(int[] nums, int size, int k) {
for (i = 0 to i < size ) {
if (nums[i] == k)
return i
}
return -1
}
Complexity Analysis
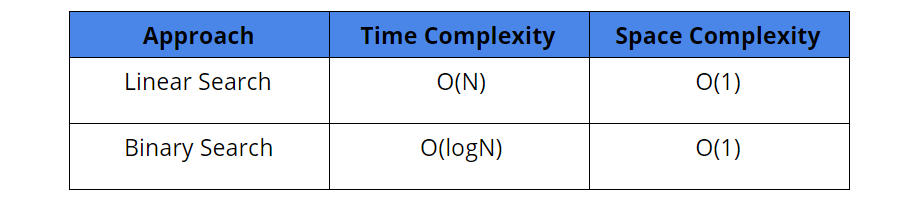
- Time complexity: O(n). We traverse the nums array of size n once only.
- Space complexity: O(1). Constant extra space is used.
Critical Ideas to Think
- Does the property of the bitonic array used in this approach?
- Why does the time complexity in this approach is O(n)?
2. Binary Search
A more efficient way to solve this problem is by using a binary search as the input nums array is Bitonic, i.e strictly increasing and then after a certain point it is strictly decreasing, so we may find the peak element of the array by using binary search. The peak element of the bitonic array could divide the array into two parts, the first part would be increasing array and the second part would be decreasing array. Then we could easily perform binary search on any of the sub-part of the nums array depending on the peak value and the value k.
Example —
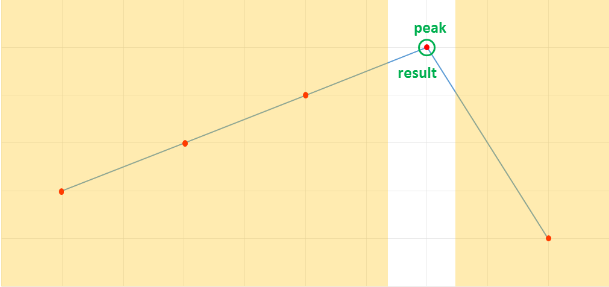
In the above figure, the peak element divides the array into two parts. Now, you can separately apply binary search on the increasing subarray and decreasing subarray and return the index of the element if found. Otherwise, just return -1.
But we first need to find the peak element using binary search →
- We start off by finding the middle element,
midfrom the givennumsarray. If this element happens to be lying in a descending sequence of numbers or a local falling slope(found by comparingnums[i]to its right neighbor), it means that the peak will always lie towards the left of this element. Thus, we reduce the search space to the left ofmid(including itself) and perform the same process on the left subarray. - If the middle element,
midlies in an ascending sequence of numbers, or a rising slope(found by comparingnums[i]to its right neighbor), it obviously implies that the peak lies towards the right of this element. Thus, we reduce the search space to the right ofmidand perform the same process on the right subarray. - In this way, we keep on reducing the search space until we eventually reach a state where only one element is remaining in the search space. This single element is the peak element.
In short,
- If
midelement is greater than both of its adjacent elements, then mid is the peak element. Example — [1, 3, 5, 7, 6, 4, 2] - If
midelement is greater than its next element and smaller than the previous element then maximum lies on the left side of mid. Example — [1, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3] - If
midelement is smaller than its next element and greater than the previous element then maximum lies on the right side of mid. Example — [2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 3, 1]
Solution steps
- Find the peak point of the bitonic array
- If the element to be searched is equal to the peak element then return its index.
- If the element to be searched is greater than the element at peak point then the element does not exist in the array.
- If the element to be searched is less than the element at peak point then search for that element in both halves of the array using binary search.
Pseudo Code
int findPeakElement(int[] nums, int low, int high) {
if (low == high)
return low
mid = (low + high) / 2
if (nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1])
return findPeakElement(nums, low, mid)
return findPeakElement(nums, mid + 1, high)
}
// Function for binary search in ascending part of array
int ascendingBinarySearch(int arr[], int low, int high, int key) {
while (low <= high) {
mid = low + (high - low) / 2
if (arr[mid] == key)
return mid
if (arr[mid] > key)
high = mid - 1
else
low = mid + 1
}
return -1
}
// Function for binary search in descending part of array
int descendingBinarySearch(int arr[], int low, int high, int key) {
while (low <= high) {
mid = low + (high - low) / 2
if (arr[mid] == key)
return mid
if (arr[mid] < key)
high = mid - 1
else
low = mid + 1
}
return -1
}
// driver function
int findBitonic(int[] nums, int size, int k) {
peak_index = findPeakElement(nums, 0, size-1)
if(k > nums[peak_index])
return -1
else if(key == nums[peak_index])
return peak_index
else {
temp = ascendingBinarySearch(nums, 0, peak_index-1, k)
if (temp != -1) {
return temp
}
// Search in right of k
temp = descendingBinarySearch(nums, peak_index+1, size-1, k)
if(temp != -1){
return temp
}
}
return -1
}
Complexity Analysis
- Time complexity : O(log (n)). We reduce the search space in half at every step.
- Space complexity : O(log(n)). We reduce the search space in half at every step. Thus, the total search space will be consumed in log(n) steps. Thus, the depth of the recursion tree will go up to log(n).
We can reduce the space complexity from O(log n) to O(1) by using an iterative function for finding the peak element instead of a recursive function.
// Pseudo-code for finding the peak element in the bitonic array
int findPeakElement(int[] nums, low, high) {
while (low < high) {
mid = (low + high) / 2
if (nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1])
high = mid
else
low = mid + 1
}
return low
}
Critical Ideas to Think
- Why did we find the peak element first in the above approach?
- Comparing
nums[mid]withnums[mid+1]helps in finding the peak element. How? - Can you convert ascending and descending binary search functions to recursive?
Comparison of solutions
Suggested problems to solve
- Search an element with a sorted and rotated array with duplicates
- Length of Longest Subarray with same elements in atmost K increments
- Maximize the distance between any two consecutive 1’s after flipping M 0’s
- Median of two sorted arrays of same size
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Find the next greater element for every element in an array - Interview Problem
Given an array A[] of size n, you need to find the next greater element for each element in the array. Return an array that consists of the next greater element of A[i] at index i.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find the kth smallest element in an array
Given an array A[] of n elements and a positive integer K, find the Kth smallest element in the array. It is given that all array elements are distinct.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find the most frequent element in an array - Interview Problem
Given an array A[] of size n, find the most frequent element in the array, i.e. the element which occurs the most number of times.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find the majority element in an array - Interview Problem
You are given an array A[] consisting of n elements. You need to find and return the number which appears more than n/2 times.
