Find the kth smallest element in an array
AfterAcademy Tech
•
12 Oct 2019

Difficulty : Medium
Asked in : Amazon, Google
Understanding the Problem
Problem Description: Given an array A[] of n elements and a positive integer K, find the Kth smallest element in the array. It is given that all array elements are distinct.
For Example :
Input : A[] = {10, 3, 6, 9, 2, 4, 15, 23}, K = 4
Output: 6
Input : A[] = {5, -8, 10, 37, 101, 2, 9}, K = 6
Output: 37
Possible follow-up questions to ask the interviewer:-
- Do we know something about the range of the numbers in the array? No, they can be arbitrary integers.
- Are the array elements necessarily positive? No, they can be positive, negative, or zero.
- What if K is greater than the size of the array? (Ans: It is guaranteed that 1 ≤ K ≤ n)
- Can the original array be modified? (Ans: Sure)
Brute force and efficient solutions
We will be discussing four possible solutions for this problem:-
- Brute Force approach : Using sorting
- Using Min-Heap
- Using Max-Heap
- Quick select : Approach similar to quick sort
1. Brute force approach : Using sorting
The idea is to sort the array to arrange the numbers in increasing order and then returning the Kth number from the start.
Pseudo-Code
int kthSmallest(int A[], int n, int K)
{
sort(A,n)
return A[K-1]
}
Complexity Analysis
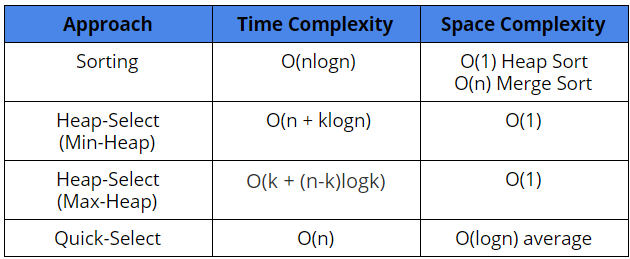
Time Complexity: Sorting the array + Picking Kth element from the start = O(nlogn) + O(1) = O(nlogn)
Space Complexity: If you use merge sort, then O(n), else if you use heap sort, its O(1).
Critical ideas to think!
- Do you need to sort the entire array to find the kth smallest element? Try modifying normal sorting algorithms to extract Kth smallest element. Also, analyze their complexity.
- What is the best sorting algorithm for this problem?
- How can we improve the time complexity?
2. Using Min-Heap
This is a good example of problem-solving via a heap data structure. The basic idea here is to create a min-heap of all n elements and then extract the minimum element K times. The last element to be extracted will be the Kth smallest element.
Solution Steps
- Build a min-heap of size n of all elements
- Extract the minimum elements K-1 times, i.e. delete the root and perform heapify operation K times.
- Return the root of the heap (A[0] would be the root element in the array implementation of the heap)
Pseudo-Code
int kthSmallest(int A[], int n, int K)
{
build_minHeap(A, n)
for( i = 0 to K-1 )
extractMin(A)
return A[0]
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: Building the min heap of n elements + Extracting min element K-1 times = O(n) + (K-1) * log(n) = O( n + Klogn)
Space Complexity: O(1) (Why?)
Critical ideas to think!
- Can we further optimize the above approach using a min-heap?
- Can this problem be solved using Binary Search Tree? What would be the complexity in that case?
- Do you need to change this algorithm to handle duplicates?
- Understand the implementation and time complexity of basic heap operations like heapify, insert, extract min, etc.
- Compare top-down and bottom-up approach of heap building. Which one is a more efficient approach? Do we use extra space in this process?
- Why is Heap preferred over BST for Priority Queue?
3. Using Max-Heap
The idea is to construct a max-heap of the smaller elements. Since the root of the max-heap is the largest element of the heap, you should use this to your advantage to track the top K smallest elements in heap and then returning the root.
Solution Steps
- Create a max-heap of first K elements
- For each element A[i], K onwards till n, compare it with root
- If A[i] < root, replace root with A[i] and heapify the heap.
- If A[i] > root, ignore and move on.
3. Return the root of the heap.
Pseudo-Code
int kthSmallest(int A[], int n, int K)
{
build_maxHeap(A, K)
for ( i = K to n-1 )
{
if ( A[i] < A[0] )
{
A[0] = A[i] // Now A[i] the new root
heapify(A, 0)
}
}
return A[0]
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: Building max-heap of k elements + Inserting n-K elements to the heap = O(K) + O((n-K)logK) = O(K + (n-K)logK)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical ideas to think!
- Do you need to make any changes to handle duplicate elements?
- Why do we ignore elements larger than root in the second part of the algorithm?
- Prepare a list of problems where we can use min or max heap for the solution.
4. Quick-Select : Approach similar to quick sort
This approach is similar to the quick sort algorithm where we use the partition on the input array recursively. But unlike quicksort, which processes both sides of the array recursively, this algorithm works on only one side of the partition. We recur for either the left or right side according to the position of pivot.
Solution Steps
- Partition the array A[left .. right] into two subarrays A[left .. pos] and A[pos + 1 .. right] such that each element of A[left .. pos] is less than each element of A[pos + 1 .. right].
- Computes the number of elements in the subarray A[left .. pos] i.e. count = pos - left + 1
- if (count == K), then A[pos] is the Kth smallest element.
- Otherwise determines in which of the two subarrays A[left .. pos-1] and A[pos + 1 .. right] the Kth smallest element lies.
- If (count > K) then the desired element lies on the left side of the partition
- If (count < K), then the desired element lies on the right side of the partition. Since we already know i values that are smaller than the kth smallest element of A[left .. right], the desired element is the (K - count)th smallest element of A[pos + 1 .. right].
- Base case is the scenario of single element array i.e left ==right. return A[left] or A[right].
Pseudo-Code
// Original value for left = 0 and right = n-1
int kthSmallest(int A[], int left, int right, int K)
{
if (left == right)
return A[left]
int pos = partition(A, left, right)
count = pos - left + 1
if ( count == K )
return A[pos]
else if ( count > K )
return kthSmallest(A, left, pos-1, K)
else
return kthSmallest(A, pos+1, right, K-i)
}
int partition(int A[], int l, int r)
{
int x = A[r]
int i = l-1
for ( j = l to r-1 )
{
if (A[j] <= x)
{
i = i + 1
swap(A[i], A[j])
}
}
swap(A[i+1], A[r])
return i+1
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: The worst-case time complexity for this algorithm is O(n²), but it can be improved if we choose the pivot element randomly. If we randomly select the pivot, the expected time complexity would be linear, O(n).
Space Complexity: O(logn) average for recursion call stack (Think!)
Critical ideas to think!
- What would be the worst-case if we select pivot randomly?
- Median of medians is the ideal pivot selection strategy for the Quick-Select algorithm which works in O(n) time complexity in the worst case. Study about it.
- What other sorting algorithms can be exploited to find the kth largest element by partially sorting it?
- Why a single-element array is the base case of recursion?
- Explore different ways to perform partition of an array
- Visualize all the above approaches via simple examples.
Comparison of solutions
Suggested Problems to solve
- Find the Kth largest element
- Find K smallest elements in an array
- Find the median of an unsorted array
- Median of two sorted arrays of the same size
- The K-th missing element in an unsorted array
- Find the kth largest element in a stream
- Kth Smallest Element in a Sorted Matrix
- K smallest elements in an array
- K-th Element of two sorted Arrays
- Find the top k frequent elements
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Find the next greater element for every element in an array - Interview Problem
Given an array A[] of size n, you need to find the next greater element for each element in the array. Return an array that consists of the next greater element of A[i] at index i.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find the most frequent element in an array - Interview Problem
Given an array A[] of size n, find the most frequent element in the array, i.e. the element which occurs the most number of times.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find the majority element in an array - Interview Problem
You are given an array A[] consisting of n elements. You need to find and return the number which appears more than n/2 times.

AfterAcademy Tech
Largest Element In An Array
Given an array arr[] of size n , write a program to find the largest element in it. To find the largest element we can just traverse the array in one pass and find the largest element by maintaining a max variable.