Check If Two Arrays Are Equal Or Not
AfterAcademy Tech
•
01 May 2020

Difficulty: Easy
Asked in: Amazon, Goldman Sachs
Given two given arrays of equal length, Check if given arrays are equal or not.
Problem Note:
- Two arrays are said to be equal if both of them contain the same set of elements, the permutation of the elements may be different though.
- If there are repetitions, then counts of repeated elements must also be the same for two arrays to be equal.
Example 1
Input: A[] = [3, 8, 9, 1] , B[] = [9, 3, 1, 8]
Output: 1
Example 2
Input: A[] = [1, 2, 5, 2, 1] , B[] = [2, 1, 2, 1, 5]
Output: 1
Example 3
Input: A[] = [1, 2, 2, 7, 1] , B[] = [2, 1, 2, 7, 5]
Output: 0
Example 4
Input: A[] = [0, 5, 0] , B[] = [5, 0, 5]
Output: 0
Solutions
We will be discussing two different solutions for this problem
- Sorting the array: Sort both the arrays and in a single traversal compare their values at each index.
- Using hash: Create a hash table or hash map for both the arrays that will contain the values and their occurrences in the arrays and compare them.
You may now try to solve this problem from here. by applying the above two approach. If stuck, then you can find the solution below:
1. Sorting The Array
To check if two arrays are equal or not, we have to compare the exact occurrence of each of the elements in both of the arrays to be the same.
However, the problem is that the values of the arrays could be in any permutation irrespective of each other.
If we could order them in any way, then it would be easy for us to check their number of occurrences. So, we will sort both the arrays and linearly traverse on it while comparing each element of the arrays. If at any indices after sorting they mismatch then we could return false from there otherwise, we’ll return true.
Solution Steps
- Compare the lengths of
arr1andarr2. If they are equal, then we will continue otherwise returnfalse. - Sort
arr1andarr2either in ascending or descending order. - For each index
iof the array, comparearr1[i]andarr2[i]to be equal. - If at any point the condition fails, then return
Falseotherwise, at the end of the comparison, returnTrue.
Pseudo Code
bool twoArrEqual(int arr1[], int arr2[])
{
// If lengths of array are not equal means
// array are not equal
if (arr1.length != arr2.length)
return false
// Sort both arrays
sort(arr1)
sort(arr2)
// Linearly compare elements
for (int i = 0 to i < arr1.length)
if (arr1[i] != arr2[i])
return false
// If all elements were same.
return true
}
Complexity Analysis
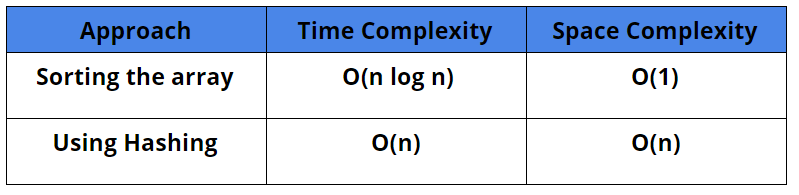
Time Complexity: O(n log n) using merge sort. Using another quadratic sorting algorithm will make the time complexity O(n²)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical Ideas to Think
- Do you think that there could be another approach in which we will take each permutation of elements in the first array and compare it with the second array? If that could be a valid solution, then what would be its complexity?
- Which sorting algorithm should be used here to sort the arrays?(comment down below)
- Can you optimize the time complexity?
2. Using Hash
If we will think again, we could further optimize the time complexity of the previous approach, if you will notice that only the count of occurrence of each element is relevant to us to check the equality of the two arrays.
So, If there exists a value in arr1 then it has to exist in arr2 with the same number of occurrences in each of them.
This reminds me of a data structure called HashMap also known as HashTable or Dictionary. We can use a HashMap to store the elements and their occurrence. Now we can simply iterate over the second array and reduce the count by one for each element.
Solution steps
- Check the size of both the arrays
- Create a HashMap for
arr1and store the count for each element. - Iterate over
arr2and check for each element inarr2there should be a key in HashMap and its value corresponding to the key must be greater than 0. - If such key exists, then decrease the count by one for that key in that particular iteration
- If the value of the key is not greater than 0, return
False - At the end of the code return
True.
Pseudo Code
bool twoArrEqual(int arr1[], int arr2[]) {
// If lengths of arrays are not equal
n = arr1.length
m = arr2.length
if (n != m)
return false;
// Store arr1[] elements and their counts in hash map
HashMap map
for (int i = 0 to i < n)
if(arr1[i] in map.keys())
map[arr1[i]] = map[arr1[i]] + 1
else
map[arr1[i]] = 1
// if all elements of arr2[] are present same number
// of times or not.
for (int i = 0 to i < n ) {
if (arr2[i] not in map.keys())
return false
// If an element of arr2[] appears more
// times than it appears in arr1[]
if (map[arr2[i]] == 0)
return false
map[arr2[i]] = map[arr2[i]] - 1
}
return true
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n). You can use an unordered map. Using Ordered map might land time complexity to O(n log n) for large values of n.
Space Complexity: O(n)
Critical Ideas to Think
- If an element of
arr1appears more than that inarr2, then do you think that this algorithm will work? If yes, How? - Can you think of the case when
map[arr2[i]]become0for anyi? - Instead of sorting and using auxiliary space, can you think of any other approach in O(n²) time complexity?
Comparison of Different Approaches
Suggested Problems to Solve
- Check whether it is possible to make both arrays equal by modifying a single element
- Find sub-arrays from given two arrays such that they have equal sum
- Count sub-arrays which have elements less than or equal to X
- Count pairs from two sorted arrays whose sum is equal to a given value x
If you have any more approaches or you find an error/bug in the above solutions, please comment down below.
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Find the intersection of two unsorted arrays - Interview Problem
Given two integer arrays A[] and B[] of size m and n, respectively. We need to find the intersection of these two arrays. The intersection of two arrays is a list of distinct numbers which are present in both the arrays. The numbers in the intersection can be in any order.

AfterAcademy Tech
Median of the Two Sorted Array of Same Size
There are two sorted arrays nums1 and nums2 of size n. Find the median of the two sorted arrays.
AfterAcademy Tech
Merge Two Sorted Arrays
You are given two sorted arrays arr1[ ] and arr2[ ] of sizes m and n respectively. Write a program to merge them in such a way that the resultant array is sorted too.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find whether an array is a subset of another array - Interview Problem
Given two integer array A[] and B[] of size m and n(n <= m) respectively. We have to check whether B[] is a subset of A[] or not. An array B is a subset of another array A if each element of B is present in A. (There are no repeated elements in both the arrays)
