Merge Two Sorted Arrays
AfterAcademy Tech
•
17 Aug 2020

Difficulty: Medium
Asked in: Microsoft, Adobe
Understanding The Problem
Problem Description
You are given two sorted arrays arr1[] and arr2[] of sizes m and n respectively. Write a program to merge them in such a way that the resultant array is sorted too.
Problem Note:
- The size of the resultant array should be
m+n. - You are expected to solve this question in
O(m+n)time. - Your final array should be the first array i.e. array
arr1[].
Example 1
Input: arr1[] = [3, 9, 10, 18, 23], arr2[] = [5, 12, 15, 20, 21, 25]
m = 5, n = 6
Output: [3, 5, 9, 10, 12, 15, 18, 20, 21, 23, 25]
Explanation: The resultant array i.e. arr1[] has all the elements of arr1[] and arr2[], sorted in increasing order. The size of resultant array is m + n = 5 + 6 = 11
Example 2
Input: arr1[] = [2, 5, 9], arr2[] = [12, 19, 23], m = 3, n = 3
Output: [2, 5, 9, 12, 19, 23]
Explanation: The resultant array i.e. arr1[] has all the elements of arr1[] and arr2[], sorted in increasing order. The size of resultant array is m + n = 3 + 3 = 6
Example 3
Input: arr1[] = [2, 20], arr2[] = [5, 9, 14, 16, 19], m = 2, n = 5
Output: [2, 5, 9, 14, 16, 19, 20]
Explanation: The resultant array i.e. arr1[] has all the elements of arr1[] and arr2[], sorted in increasing order. The size of resultant array is m + n = 2 + 5 = 7
Solutions
We will be discussing two different solutions to this problem:-
- Merge Function of merge sort: Auxiliary array of n+m size storing values as merge function in merge sort.
- Two pointers: Compare the two values from the end of
ar1andar2and store inar1while decrementing pointers accordingly.
You should try to solve the problem here.
1. Merge Function of Merge Sort
The two given array is sorted, so we can directly use the merge function of merge sort. We create an auxiliary array of size m+n and then follow the merge function of the merge sort.
Refer to the below example.
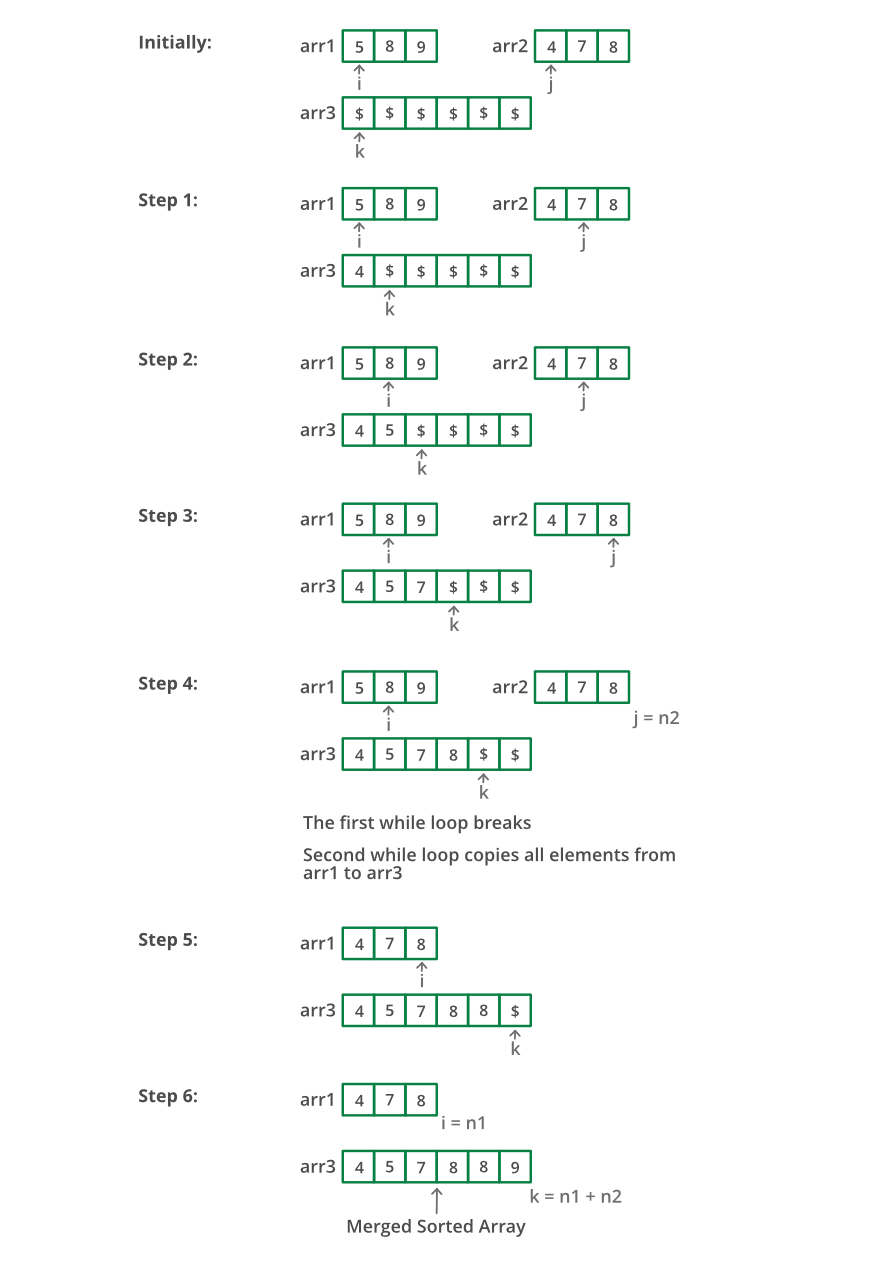
Solution Steps
- Create an auxiliary array of size
m+ nwhere m and n are the sizes ofar1andar2respectively. - While traversing through both the arrays: Pick the smaller of current elements of
arr1andarr2, save the smaller value of both the arrays in the auxiliary array, thereby increment the positions accordingly. - Now copy the auxiliary array to
arr1as the final array should bearr1
Pseudo Code
void mergeArrays(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m) {
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0
int[m+n] arr3
// Traverse both array
while (i < n and j < m) {
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j]) {
arr3[k] = arr1[i]
i = i + 1
}
else{
arr3[k] = arr2[j]
j = j + 1
}
k = k + 1
}
while (i < n){
arr3[k] = arr1[i]
i = i + 1
k = k + 1
}
while (j < m){
arr3[k] = arr2[j]
j = j + 1
k = k + 1
}
// copy arr3 to arr1
i = 0
while(i < (m + n)){
arr1[i] = arr3[i]
i = i + 1
}
return arr1
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n+m)
Space Complexity: O(n+m)
Critical Ideas To Think
- Why did we create an auxiliary array?
- How we are traversing both the array?
- On what basis we are storing the value in the auxiliary array from
arr1andarr2?
2. Two Pointers
The problem statement requires the output after merge operation in arr1 . This states that arr1 has enough space to accommodate the elements of arr1 and arr2.
Now, the two given array are already sorted, so we can put two pointers at the end of each array, say i is pointing arr1[n-1] and j is pointing arr2[m-1]. A third pointer k pointing to arr1[n+m-1]. then we start comparing values at the pointers i and j, the larger value will be stored at the pointer k thereby decreasing the pointer with larger value by 1 and decreasing the pointer k by 1. We can continue comparing the values unless i and j reach to 0th index.
Considering the above Example1:
step 1)
i k
arr1 = [3, 9, 10, 18, 23, _ , _ , _ , _ , _ , _]
j
arr2 = [5, 12, 15, 20, 21, 25]
step 2) arr1[i] < arr2[j] => arr1[k] = arr2[j], j--, k--
i k
arr1 = [3, 9, 10, 18, 23, _ , _ , _ , _ , _ , 25]
j
arr2 = [5, 12, 15, 20, 21, 25]
step 3) arr1[i] > arr2[j] => arr1[k] = arr1[i], i--, k--
i k
arr1 = [3, 9, 10, 18, 23, _ , _ , _ , _ , 23 , 25]
j
arr2 = [5, 12, 15, 20, 21, 25]
step 4) arr1[i] < arr2[j] => arr1[k] = arr2[j], j--, k--
i k
arr1 = [3, 9, 10, 18, 23, _ , _ , _ , 21 , 23 , 25]
j
arr2 = [5, 12, 15, 20, 21, 25]
step 5) arr1[i] < arr2[j] => arr1[k] = arr2[j], j--, k--
i k
arr1 = [3, 9, 10, 18, 23, _ , _ , 20 , 21 , 23 , 25]
j
arr2 = [5, 12, 15, 20, 21, 25]
.
.
step 10) arr1[i] < arr2[j] => arr1[k] = arr2[j], j--, k--
i k
arr1 = [3, 5, 9, 10, 12, 15 , 18 , 20 , 21 , 23 , 25]
j
arr2 = [5, 12, 15, 20, 21, 25]
Solution Steps
- Create two pointers
i,jpointing at arr1[n] and arr2[m] - While
i ≥ 0andj ≥ 0,the pointer with larger value by one and decreasekby 1. - Return
arr1
Pseudo Code
void mergeArrays(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n, int m) {
int i = n-1
int j = m-1
int k = n+m-1
// Traverse both array
while (i >= 0 and j >= 0) {
if (arr1[i] > arr2[j]) {
arr1[k] = arr1[i]
i = i - 1
}
else{
arr1[k] = arr2[j]
j = j - 1
}
k = k - 1
}
while (i >= 0){
arr1[k] = arr1[i]
i = i - 1
k = k - 1
}
while (j >= 0){
arr1[k] = arr2[j]
j = j - 1
k = k - 1
}
return arr1
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n+m)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical Ideas To Think
- Why did we iterate from backward of
arr1andarr2? - How different is this approach compared to the merge function of the merge sort?
- Why is the space complexity is O(1)?
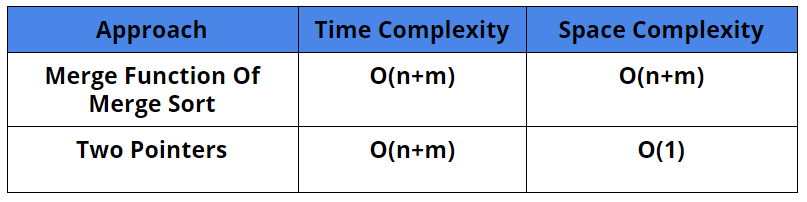
Comparison of Different Approaches
Suggested Problems To Solve
- Merge two sorted linked list.
- Merge K sorted arrays.
- Merge two sorted arrays using a heap.
- Merge two unsorted linked list to get a sorted list.
- Merge K sorted arrays of different sizes.
Please comment down below if you have a better insight in the above approach.
Happy Coding, Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Median of the Two Sorted Array of Same Size
There are two sorted arrays nums1 and nums2 of size n. Find the median of the two sorted arrays.
AfterAcademy Tech
Sort List - Merge Sort
Sort a linked list using Merge Sort. This is a very famous interview problem that demonstrates the concept of recursion. This problem is quite similar to Merge Sort in Arrays.

AfterAcademy Tech
Merge Two Sorted Lists - Interview Problem
Merge two sorted linked lists and return it as a new sorted list. The new list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.

AfterAcademy Tech
Merge Sort
Merge sort is a divide-and-conquer algorithm based on the idea of breaking down a list into several sub-lists until each sublist consists of a single element and merging those sublists in a manner that results into a sorted list.