What are Paging and Segmentation?
AfterAcademy Tech
•
22 Apr 2020

External fragmentation occurs because we allocate memory continuously to the processes. Due to this space is left and memory remains unused hence, cause external fragmentation. So to tackle this problem the concept of paging was introduced where we divide the process into small pages and these pages are allocated memory non-contiguously into the RAM. So, let’s get started and learn more about it.
Non-Contiguous Memory Allocation Technique
In the non-contiguous memory allocation technique, different parts of the same process are stored in different places of the main memory. Types:
- Paging
- Segmentation
Paging
Paging is a non-contiguous memory allocation technique in which secondary memory and the main memory is divided into equal size partitions. The partitions of the secondary memory are called pages while the partitions of the main memory are called frames. They are divided into equal size partitions to have maximum utilization of the main memory and avoid external fragmentation.
Example: We have a process P having process size as 4B, page size as 1B. Therefore there will we four pages(say, P0, P1, P2, P3) each of size 1B. Also, when this process goes into the main memory for execution then depending upon the availability, it may be stored in non-contiguous fashion in the main memory frame as shown below:
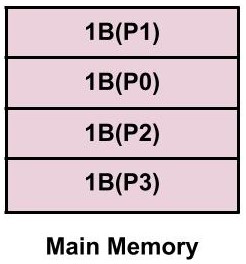
This is how paging is done.
Translation of logical Address into physical Address
As a CPU always generates a logical address and we need a physical address for accessing the main memory. This mapping is done by the MMU(memory management Unit) with the help of the page table. Lets first understand some of the basic terms then we will see how this translation is done.
- Logical Address: The logical address consists of two parts page number and page offset.
1. Page Number: It tells the exact page of the process which the CPU wants to access.
2. Page Offset: It tells the exact word on that page which the CPU wants to read.
Logical Address = Page Number + Page Offset
- Physical Address: The physical address consists of two parts frame number and page offset.
1. Frame Number: It tells the exact frame where the page is stored in physical memory.
2. Page Offset: It tells the exact word on that page which the CPU wants to read. It requires no translation as the page size is the same as the frame size so the place of the word which CPU wants access will not change.
Physical Address = Frame Number + Page Offset
- Page table: A page stable contains the frame number corresponding to the page number of some specific process. So, each process will have its own page table. A register called Page Table Base Register(PTBR) which holds the base value of the page table.
Now, let's see how the translation is done.
How is the translation done?
The CPU generates the logical address which contains the page number and the page offset. The PTBR register contains the address of the page table. Now, the page table helps in determining the frame number corresponding to the page number. Now, with the help of frame number and the page offset the physical address is determined and the page is accessed in the main memory.
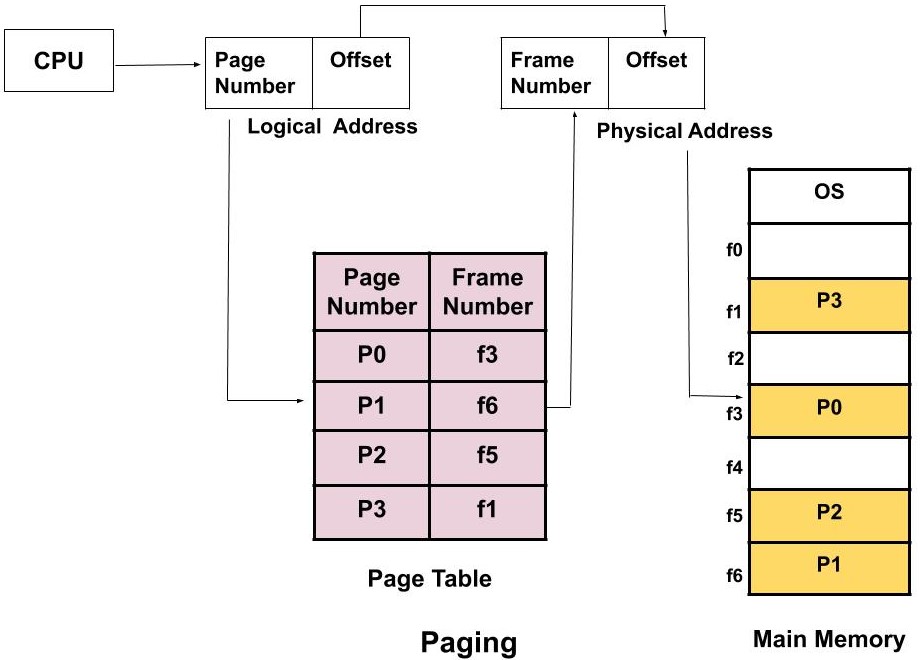
Advantages of Paging
- There is no external fragmentation as it allows us to store the data in a non-contiguous way.
- Swapping is easy between equal-sized pages and frames.
Disadvantages of Paging
- As the size of the frame is fixed, so it may suffer from internal fragmentation. It may happen that the process is too small and it may not acquire the entire frame size.
- The access time increases because of paging as the main memory has to be now accessed two times. First, we need to access the page table which is also stored in the main memory and second, combine the frame number with the page offset and then get the physical address of the page which is again stored in the main memory.
- For every process, we have an independent page table and maintaining the page table is extra overhead.
Segmentation
In paging, we were blindly diving the process into pages of fixed sizes but in segmentation, we divide the process into modules for better visualization of the process. Here each segment or module consists of the same type of functions. For example, the main function is included in one segment, library function is kept in other segments, and so on. As the size of segments may vary, so memory is divided into variable size parts.
Translation of logical Address into physical Address
As a CPU always generates a logical address and we need a physical address for accessing the main memory. This mapping is done by the MMU(memory management Unit) with the help of the segment table.
Lets first understand some of the basic terms then we will see how this translation is done.
- Logical Address: The logical address consists of two parts segment number and page offset.
1. Segment Number: It tells the specific segment of the process from which the CPU wants to read the data.
2. Segment Offset: It tells the exact word in that segment which the CPU wants to read.
Logical Address = Segment Number + Segment Offset
- Physical Address: The physical address is obtained by adding the base address of the segment to the segment offset.
- Segment table: A segment table stores the base address of each segment in the main memory. It has two parts i.e. Base and Limit. Here, base indicates the base address or starting address of the segment in the main memory. Limit tells the size of that segment. A register called Segment Table Base Register(STBR) which holds the base value of the segment table. The segment table is also stored in the main memory itself.
How is the translation done?
The CPU generates the logical address which contains the segment number and the segment offset. STBR register contains the address of the segment table. Now, the segment table helps in determining the base address of the segment corresponding to the page number. Now, the segment offset is compared with the limit corresponding to the Base. If the segment offset is greater than the limit then it is an invalid address. This is because the CPU is trying to access a word in the segment and this value is greater than the size of the segment itself which is not possible. If the segment offset is less than or equal to the limit then only the request is accepted. The physical address is generated by adding the base address of the segment to the segment offset.
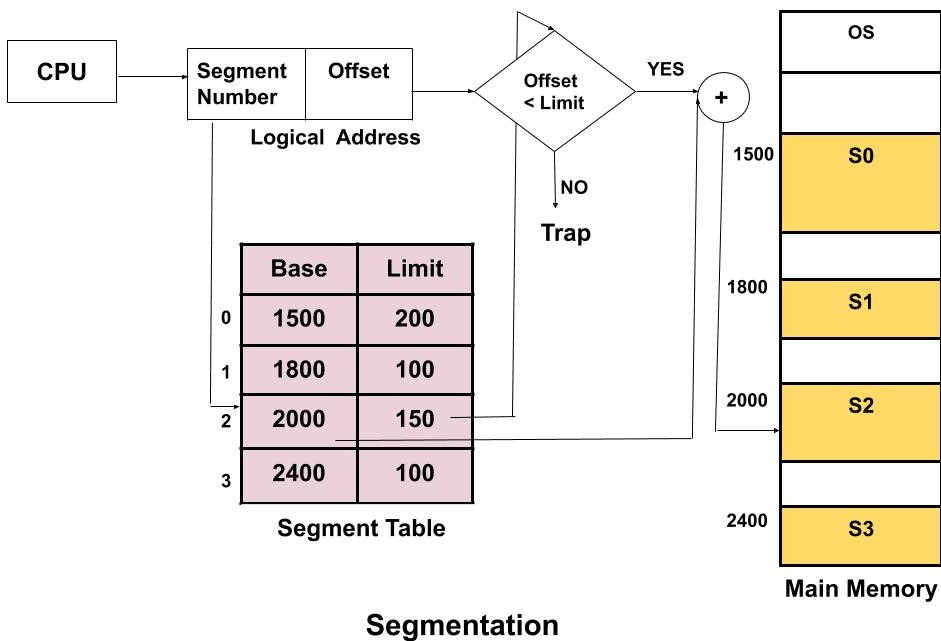
Advantages of Segmentation
- The size of the segment table is less compared to the size of the page table.
- There is no internal fragmentation.
Disadvantages of Segmentation
- When the processes are loaded and removed ( during swapping ) from the main memory then free memory spaces are broken into smaller pieces and this causes external fragmentation.
- Here also the time to access the data increases as due to segmentation the main memory has to be now accessed two times. First, we need to access the segment table which is also stored in the main memory and second, combine the base address of the segment with the segment offset and then get the physical address which is again stored in the main memory.
This is was about paging and segmentation. Hope you learned something new today.
Do share this blog with your friends to spread the knowledge. Visit our YouTube channel for more content. You can read more blogs from here.
Keep Learning 🙂
Team AfterAcademy!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
What are demand-paging and pre-paging?
In this blog, we will learn how pages are brought into the main memory in virtual memory systems. We will see two ways of doing this i.e. demand paging and pre-paging.
AfterAcademy Tech
What are the Page Replacement Algorithms?
In this blog, we will learn about various Page Replacement Algorithms that are used in memory management in OS. We will learn about FIFO, LRU, and Optimal page replacement.
AfterAcademy Tech
What is the maximum segment length of a 100Base-FX network?
In this blog, we will learn what are the pieces of information hidden in the name of the network like 100BaseFX. We will learn about 100baseFX and what is its maximum segment length.
AfterAcademy Tech
Maximum Subarray Sum
You are given an array A[] with n elements. You need to find the maximum sum of a subarray among all subarrays of that array. A subarray of array A[] of length n is a contiguous segment from A[i] through A[j] where 0<= i <= j <= n.
