Maximum Subarray Sum
AfterAcademy Tech
•
16 Oct 2019

Difficulty Level: Hard
Asked in: Facebook, Microsoft, Amazon, Goldman Sachs
Understanding the problem
Problem Description: You are given an array A[] with n elements. You need to find the maximum sum of a subarray among all subarrays of that array. A subarray of array A[] of length n is a contiguous segment from A[i] through A[j] where 0<= i <= j <= n. Some properties of this problem are:
- If the array contains all non-negative numbers, the maximum subarray is the entire array.
- Several different sub-arrays may have the same maximum sum.
For Example :
Input: A[] = {-5, 8, 9, -6, 10, -15, 3}
Output: 21, the subarray {8, 9, -6, 10} has the maximum sum among all subarrays
Input: A[] = { -4, -7, -1, 5,-2}
Output: 4, the subarray {-1, 5} has the maximum sum
Possible follow-up questions to ask the interviewer:-
- What if all elements of the array are negative? (Ans: It is guaranteed that at least one element in the array would be non-negative)
- Is it allowed to modify the array? (Ans: Sure, but a subarray is an ordered contiguous segment of the original array)
Brute force and Efficient solutions
We will be discussing five solutions for this problem:-
- Brute force approach I : Using 3 nested loops
- Brute force approach II : Using 2 nested loops
- Divide and Conquer approach : Similar to merge sort
- Dynamic Programming Approach I : Using an auxiliary array
- Dynamic Programming Approach II : Kadanes's Algorithm
1. Brute force approach I : Using 3 nested loops
We would use nested loops to determine all the possible subarray sums and return the maximum among them. For this, we generate all (i, j): i <= j pairs and calculate the sum between.
Pseudo-Code
int maxSubarraySum ( int A [] , int n)
{
int max_sum = 0
for(i = 0 to n-1)
{
for(j = i to n-1)
{
int sum = 0
for(k = i to j)
sum = sum + A[k]
if(sum > max_sum)
max_sum = sum
}
}
return max_sum
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n^3) (Why?)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical ideas to think!
- Could a subarray which has maximum sum start from a negative number?
- How many subarrays are possible for an array of size n?
2. Brute force approach II : Using 2 nested loops
This is the optimized version of the above approach. The idea is to start at all positions in the array and calculate running sums. The outer loop picks the beginning element, the inner loop finds the maximum possible sum with the first element picked by the outer loop and compares this maximum with the overall maximum.
int max_Subarray_Sum ( int A[] , int n)
{
int max_sum = 0
for ( i = 0 to n-1)
{
sum=0
for( j = i to n-1)
{
sum = sum + A[j]
if (sum > max_sum)
max_sum = sum
}
}
retun max_sum
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n^2) (Why?)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical ideas to think!
- Is it necessary to iterate the inner loop until the end? Could we determine a definitive point, iterating past which wouldn’t lead to the correct answer?
3. Divide and Conquer similar to merge sort
You could divide the array into two equal parts and then recursively find the maximum subarray sum of the left part and the right part. But what if the actual subarray with maximum sum is formed of some elements from the left and some elements from the right? Think!
The sub-array we’re looking for can be in only one of three places:
- On the left part of the array (between 0 and the mid)
- On the right part of the array (between the mid + 1 and the end)
- Somewhere crossing the midpoint.
You could very easily find a cross-sum of elements from the left side and right side which cross the mid-element in linear time.
Solution Steps
- Divide the array into two equal parts
- Recursively calculate the maximum sum for left and right subarray
- To find cross-sum:-
- Iterate from mid to the starting part of the left subarray and at every point, check the maximum possible sum till that point and store in the parameter lsum.
- Iterate from mid+1 to the ending point of right subarray and at every point, check the maximum possible sum till that point and store in the parameter rsum.
- Add lsum and rsum to get the cross-sum
4. Return the maximum among (left, right, cross-sum)
Pseudo-Code
// The original values would be low = 0 and high = n-1
int maxSubarraySum (int A[], int low, int high)
{
if (low == high)
return A[low]
else
{
int mid = low + (high - low)/2
int left_sum = maxSubarraySum (A, low, mid)
int right_sum = maxSubarraySum (A, mid+1, high)
int crossing_Sum = maxCrossingSum(A, low, mid, high)
return max (left_sum, right_sum, crossing_Sum)
}
}
int maxCrossingSum(int A[], int l, int mid, int r)
{
int sum = 0
int lsum = INT_MIN
for(i = mid to l)
{
sum = sum + A[i]
If (sum > lsum)
lsum = sum
}
sum = 0
int rsum = INT_MIN
for(i = mid+1 to r)
{
sum = sum + A[i]
If (sum > rsum)
rsum = sum
}
return (lsum + rsum)
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: The recurrence relation formed for this Divide and Conquer approach is similar to the recurrence relation of Merge Sort
T(n) = 2T(n/2) + O(n) = O(nlogn)
Space Complexity = O(logn), stack space by recursive calls
Critical ideas to think!
- What is the extra O(n) time complexity in recurrence relation for?
- Does this algorithm appropriate hangle negative numbers?
4. Dynamic Programming approach I : Using an auxiliary array
We can store the maximum subarray sum ending at a particular index in an auxiliary array and then traverse the auxiliary array to find the maximum subarray sum.
Solution Steps
- Create an auxiliary array max_ending_here of size n
- Assign max_ending_here[0] = A[0]
- Traverse from i = 1 to n-1, and at each step add the current element to max_ending_here[i-1]
- If max_ending_here[i] < 0 then max_ending_here[i] = A[i]
- Else, max_ending_here[i] = A[i-1] + max_ending_here[i-1]
4. Return the maximum element present in max_ending_here array
Pseudo-Code
int maxSubarraySum(int A[], int n)
{
int max_ending_here[n]
max_ending_here[0] = A[0]
for ( i = 1 to n-1 )
{
if ( A[i] + max_ending_here[i-1] > 0 )
max_ending_here[i] = A[i] + max_ending_here[i-1]
else
max_ending_here[i] = A[i]
}
int ans = 0
for( i = 0 to n-1 )
ans = max(ans, max_ending_here[i])
return ans
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: Traversing array A + Traversing the auxiliary array
= O(n) + O(n) = O(n)
Space Complexity = O(n), for storing the auxiliary array
Critical ideas to think!
- Do you need to store the maximum subarray sum ending at an index for all indices?
- Can the resultant auxiliary array contain negative numbers?
- What could be some other problems where you could apply this logic?
5. Dynamic Programming Approach II : Kadanes's Algorithm
The idea followed in Kadane’s algorithm is to maintain the maximum possible sum of a subarray ending at an index without needing to store the numbers in an auxiliary array. It is an improvement in the previous dynamic programming approach optimizing the space complexity.
Solution Steps
- Declare and initialize max_so_far and max_ending_here with 0.
- Iterate the array and add each element to max_ending_here
- If at any point, max_ending_here becomes negative, reassign it to 0 (Why?)
- Keep on updating max_so_far with maximum values of max_ending_here
- Return max_so_far
Pseudo-Code
int maxSubarraySum(int A[], int n)
{
int max_so_far = 0
int max_ending_here = 0
for ( i = 0 to n-1 )
{
max_ending_here += A[i]
if( max_ending_here < 0 )
max_ending_here = 0
max_so_far = max(max_so_far, max_ending_here)
}
return max_so_far
}
Complexity Analysis
Notice that each element has been visited only once.
Time Complexity = O(n)
Space Complexity = O(1)
Critical ideas to think!
- What is the best time complexity you could manage if you’re provided a sorted array as an input for this problem?
- Could you use the same approach for finding the maximum product subarray as well?
- What other problems could you solve using approaches similar to Kadane’s algorithm?
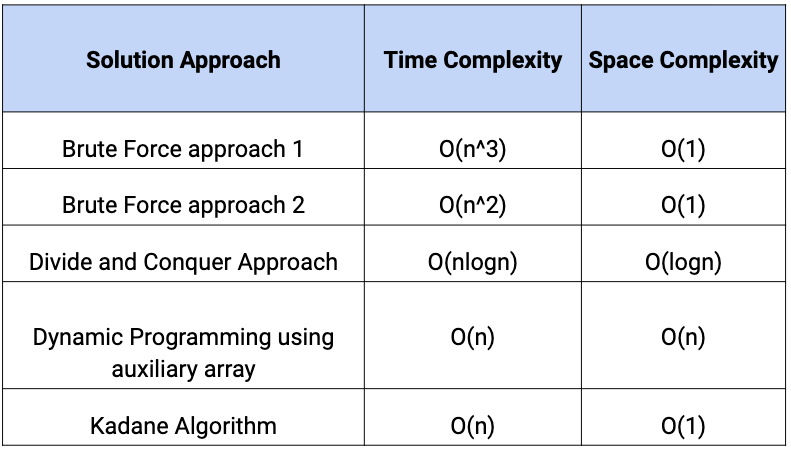
Comparison of solutions
Suggested Problems you could solve
- Find the maximum product subarray
- Find the sum of the maximum elements of every possible sub-array
- Calculate maximum sum submatrix of size k x k in m x n matrix
- Find the longest subarray in a binary array with an equal number of 0s and 1s
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Maximum path sum in a binary tree
Given a non-empty binary tree, find maximum path sum. For this problem, a path is defined as any sequence of nodes from some starting node to any node in the tree along with the parent-child connections.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find the length of largest subarray with 0 sum
Given an array A[] of n integer elements, find the length of the longest subarray with sum equals to 0.

AfterAcademy Tech
Combination Sum
Given an array of integers arr[] and a target number k, write a program to find all unique combinations in arr[] such that the sum of all integers in the combination is equal to k. This famous backtracking problem has previously been asked in Adobe, Amazon, Facebook.

AfterAcademy Tech
Maximum Product Of Three Numbers
write a program to find three numbers whose product is maximum and output the maximum product. This is a basic mathematical problem and requires logical skill to solve.
