What are demand-paging and pre-paging?
AfterAcademy Tech
•
22 Apr 2020
According to concepts of virtual memory, in order to execute any process, it not necessary that the whole process should present in the main memory at the given time. The process can also be executed if only some pages are present in the main memory at any given time. But, how can we decide beforehand which page should be present in the main memory at a particular time and which should not be there?
To resolve this problem Demand paging concept came into play. This concept says we should not load any page into the main memory until required or we should keep all the pages in secondary memory until demanded. In contrast, in Pre-Paging, the OS guesses in advance which page the process will require and pre-loads them into the memory.
So, welcome to AfterAcademy. In this blog, we will learn about the concept of Demand Paging and Pre-paging that is used in OS.
Demand Paging
Demand paging is a technique used in virtual memory systems where the pages are brought in the main memory only when required or demanded by the CPU. Hence, it is also named as lazy swapper because the swapping of pages is done only when required by the CPU.
How does demand paging work?
Lets us understand this with the help of an example. Suppose we have to execute a process P having four pages as P0, P1, P2, and P3. Currently, in the page table, we have page P1 and P3.
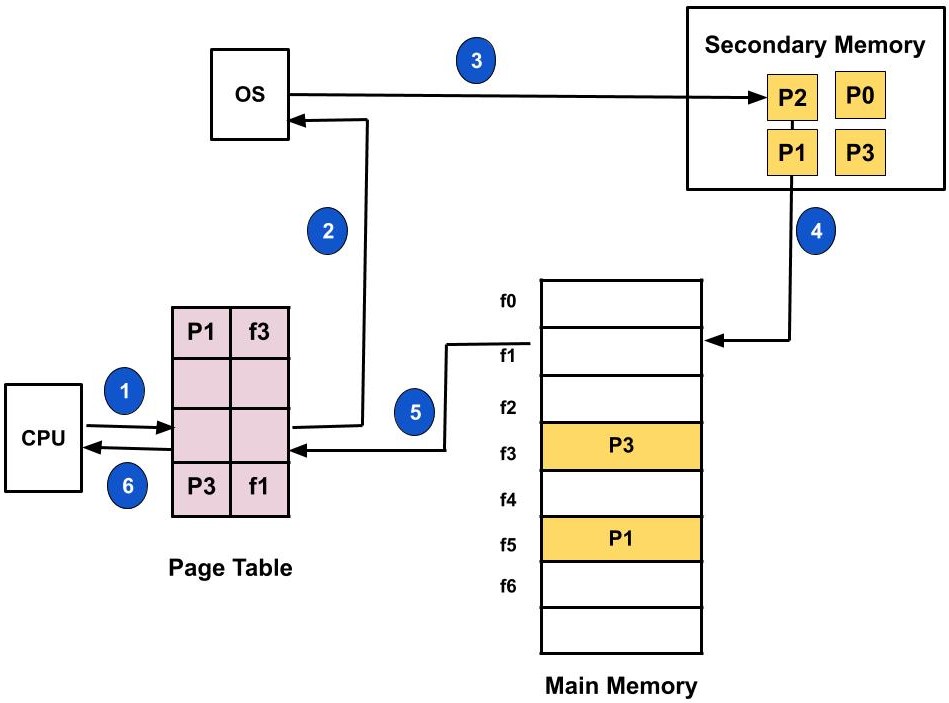
- Now, if the CPU wants to access page P2 of a process P, first it will search the page in the page table.
- As the page table does not contain this page so it will be a trap or page fault. As soon as the trap is generated and context switching happens and the control goes to the operating system.
- The OS system will put the process in a waiting/ blocked state. The OS system will now search that page in the backing store or secondary memory.
- The OS will then read the page from the backing store and load it to the main memory.
- Next, the OS system will update the page table entry accordingly.
- Finally, the control is taken back from the OS and the execution of the process is resumed.
Hence whenever a page fault occurs these steps are followed by the operating system and the required page is brought into memory.
Page Fault Service time
So whenever a page fault occurs all the above steps(2–6) are performed. This time taken to service the page fault is called the Page fault service time.
Effective Memory Access time
When the page fault rate is ‘p’ while executing any process then the effective memory access time is calculated as follows:
Effective Memory Access time = (p)*(s) + (1-p)*(m)
where p is the page fault rate.
s is the page fault service time.
m is the main memory access time.
Advantages
- It increases the degree of multiprogramming as many processes can be present in the main memory at the same time.
- There is a more efficient use of memory as processes having size more than the size of the main memory can also be executed using this mechanism because we are not loading the whole page at a time.
Disadvantages
- The amount of processor overhead and the number of tables used for handling the page faults is greater than in simple page management techniques.
PrePaging
In demand paging, that page is brought to the main memory which is actually demanded during the execution of the process. But, in pre-paging pages other than the demanded by the CPU are also brought in. The OS guesses in advance which page the process will require and pre-loads them into the memory.
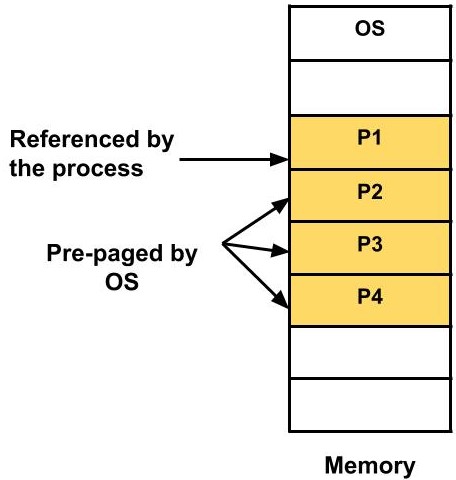
The diagram above shows that only one page was referenced or demanded by the CPU but three more pages were pre-paged by the OS. The OS tries to predict which page would be next required by the processor and brings that page proactively into the main memory.
Advantages
- It saves time when large contiguous structures are used. Consider an example where the process requests consecutive addresses. So, in such cases, the operating system can guess the next pages. And, if the guesses are right, fewer page faults will occur and the effective memory access time will increase.
Disadvantages
- There is a wastage of time and memory if those pre-paged pages are unused.
This was about demand paging and pre-paging. Hope you learned something new today.
Do share this blog with your friends to spread the knowledge. Visit our YouTube channel for more content. You can read more blogs from here.
Keep Learning 🙂
Team AfterAcademy!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
What are the Page Replacement Algorithms?
In this blog, we will learn about various Page Replacement Algorithms that are used in memory management in OS. We will learn about FIFO, LRU, and Optimal page replacement.
AfterAcademy Tech
What are Paging and Segmentation?
In this blog, we will learn about two non-contiguous memory allocation technique i.e. paging and segmentation. We will also learn how the logical address is converted into the physical address in both the techniques. Further, we will analyze the advantages and disadvantages of each technique.
