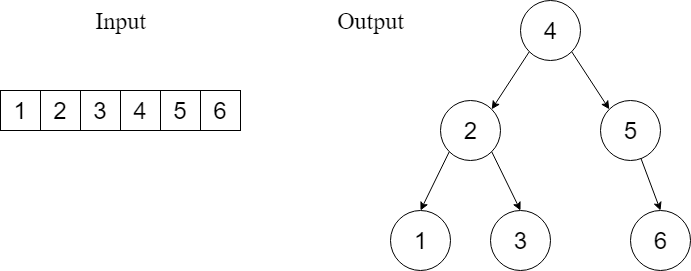
Sorted Array to Balanced BST
AfterAcademy Tech
•
24 Dec 2019

Asked in: VMWare, Amazon
Difficulty: Easy
Understanding the problem
Given an array where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST. For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differs by more than one.
Example 1

Example 2
The node structure for the BST returned from your function will be —
class TreeNode
{
int val
TreeNode left
TreeNode right
}
Recursive and iterative solutions
We will be discussing two approaches to solve this problem:
- Using divide & conquer approach: Choose the middle element as the root and recursively build balanced BST for the left and right part of the array.
- Iterative solution: Similar to level order traversal, keep track of middle elements of the array for each level using the stack.
1. Recursive Solution
Here we use the sorted property of the array to ensure the construction of balanced BST where we divide the array into two equal parts and assign the mid value as a root node. To be in alignment with the definition of a Binary Search Tree, the elements in the array to the left of the mid value, would contribute to the left subtree while the elements in the array to the right of the mid value, would contribute to the right subtree.
The steps to be followed are :
- Get the Middle of the array and make it root.
- Recursively do the steps for the left half and right half.
- Get the middle of the left half and make it the left child of the root.
- Get the middle of the right half and make it the right child of the.
TreeNode sortedArrayToBST_helper(int A[], int start, int end)
{
// continue while this branch has values to process
if(start > end)
return NULL
// Get the middle element and make it root
int mid = start + (end - start)/2
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(A[mid])
// Recursively construct the left subtree
// and make it left child of root
root.left = sortedArrayToBST_helper(A, start, mid - 1)
// Recursively construct the right subtree
// and make it right child of root
root.right = sortedArrayToBST_helper(A, mid + 1, end)
return root
}
TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int A[], int n)
{
TreeNode root = sortedArrayToBST_helper(A, 0, n)
return root
}
Complexity Analysis
In the above approach, we are traversing each index of the array only once. Time complexity: O(n), where n is the length of the array.
Space Complexity of this algorithm is proportional to the maximum depth of recursion tree generated which is equal to the height of the tree (h). Here the tree will be balanced, So the maximum height will be log(n) where n is the length of the array.
Space complexity: O(h) for recursion call stack, where h is the height of the tree.
Critical ideas to think
- How the height of the tree is balanced using the above approach?
- Can you write the recurrence relation for this approach?
- Explore different types of balanced BST structure like AVL tree, red black tree, 2-3 tree etc.
2. Iterative Solution
- The recursive solution is very intuitive. To reformat it as iterative, the overall idea is to create a stack that keeps track of tuples of information of child nodes we need to create.
- Each tuple keeps track of the child's parent and the side of the parent that the child will become.
- We only push child tuples to the stack after their parents are created, the process will create the children until we reach the base case, whereby that branch has exhausted its corresponding chunk of the original nums.
Pseudo Code
struct T {
int low_idx
int high_idx
TreeNode node
Tree(int low, int high, TreeNode _node) {
low_idx = low
high_idx = high
node = _node
}
}
TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int A[], int n) {
// return if the length of array is 0
if (n is 0)
return null
// create stack and push the node with middle element of array
stack S
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(A[(n - 1)/2])
T tree = new T(0, n - 1, root)
S.push(tree)
while (S is not empty) {
// pop the top node and assign the left and right child to it
T tmp = S.top()
S.pop()
int mid = tmp.low_idx + (tmp.high_idx - tmp.low_idx) / 2
if (tmp.low_idx < mid) {
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(A[tmp.low_idx + (mid - 1 - tmp.low_idx) / 2])
tmp.node.left_idx = node
tree = new T(tmp.low_idx, mid - 1, node)
S.push(tree)
}
if (mid < tmp.high_idx) {
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(A[mid + 1 + (tmp.high_idx - mid - 1)/2])
tmp.node.right_idx = node
tree = new T(mid + 1, tmp.high_idx, node)
S.push(tree)
}
}
return root
}
Complexity Analysis
For each node in the tree, we are performing push() and pop() operation only once.
Total no of stack operations = 2n (Think!)
Time complexity: O(n), where n is the total number of nodes.
Space Complexity: O(n)(Think!)
Critical Ideas to think
- Visualize the stack operations via simple examples.
- Why the stack is augmented with low and high index values?
- How we are deciding a node to be the left or right child of the root?
Comparison of different approaches

Suggested Problems to Solve
- Sorted Linked List to Balanced BST
- Sorted order printing of a given array that represents a BST
- Find kth smallest element in BST
- Determine if a tree is a height-balanced tree or not
- Construct a complete binary tree from the given array
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Minimum in a Sorted and Rotated array
You have a sorted and rotated array where elements are sorted and rotated circularly. Write a program to find the minimum element in the array.
AfterAcademy Tech
Merge Two Sorted Arrays
You are given two sorted arrays arr1[ ] and arr2[ ] of sizes m and n respectively. Write a program to merge them in such a way that the resultant array is sorted too.

AfterAcademy Tech
Median of the Two Sorted Array of Same Size
There are two sorted arrays nums1 and nums2 of size n. Find the median of the two sorted arrays.
AfterAcademy Tech
Search For A Range In Sorted Array
Given a sorted array A[] with possibly duplicate elements, write a program to find indexes of first and last occurrences of an element k in the given array. This question will clear your concept of Binary Search
