Search For A Range In Sorted Array
AfterAcademy Tech
•
01 May 2020

Difficulty: Easy
Asked in: Microsoft, Google
Understanding the Problem
Given a sorted array A[] with possibly duplicate elements, write a program to find indexes of first and last occurrences of an element k in the given array.
Problem Note
- The algorithm’s runtime complexity must be in the order of O(log n).
- If the target is not found in the array, return [-1, -1].
Example 1
Input: A[] = [1, 3, 5, 5, 5, 5 ,28, 37, 42], target = 5
Output: [2, 5]
Explanation: First Occurrence = 2 and Last Occurrence = 5
Example 2
Input: A[] = [1, 3, 5, 5, 5, 5 ,7, 28, 37], target = 7
Output: [6, 6]
Example 3
Input: A[] = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 6
Output: [-1,-1]
Solutions
We will be discussing two different approaches to solve this problem:-
- Linear Search: Iterate over the array and maintain
lower_rangeandupper_rangevariables while comparing the value at each index withtarget. - Binary Search: Perform binary search twice for the
target.
You may try to solve this problem here.
1. Linear Search
We have to search for the start and end indexes for the target value. As the array is sorted then it means that all the target values will be seen together. If we will iterate over the input array, then we could check if the element at any index is equal to the target or not. On the first occurrence of the target element update the lower_range and upper_range with that index. Upon further iteration, on each encounter of the target value, update upper_range .
Solution Steps
- Initialize
lower_boundandupper_boundwith-1. - On the first occurrence of
targetelement update these variables with the index. - For the next occurrence of the
targetelement, update theupper_boundwith the index.
Pseudo Code
int[] searchRange(int[] arr, int target) {
lower_bound = -1
upper_bound = -1
for(i = 0 to i < arr.length){
if(arr[i] == target){
if(lower_bound == -1){
lower_bound = i
}
upper_bound = i
}
}
return [lower_bound, upper_bound]
}
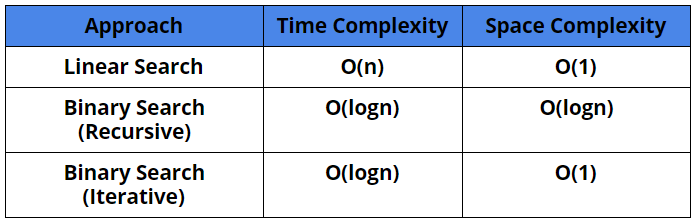
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical Ideas To Think
- Why we are updating
upper_boundat each occurrence oftarget?
2. Binary Search
To find the upper and lower range we could call Binary Search two times for the target value. To get the lower range, we would want to slide to the “Left” of the array overtime (Since it's sorted). A slight modification in the Binary search would give us the left-most value:
while(lower_bound < upper_bound)
mid = (upper_bound + lower_bound)/2
if (target <= arr[mid])
upper_bound = mid
else:
lower_bound = mid+1
(upper_bound + lower_bound)/2 would give us floor value of the integer. So, for every iteration, if arr[mid] is <= the target number, the starting range of the number is either at arr[mid] or is at its left of it.
So, we set the upper bound at mid (not mid-1, as the current element could itself be the upper limit). If the number is greater then the mid, the lower bound should be mid+1 .
Next, we need to find the upper bound, so we need to slide to the right of the array. mid = (upper_bound+lower_bound)/2 + 1
Also, we won’t change the value stored at lower_bound. Since the upper_bound will be at lower_bound index or at the right of it.
while (lower_bound < upper_bound)
mid = (lower_bound+upper_bound)/2 + 1
if target < arr[mid]:
upper_bound = mid-1
else:
lower_bound = mid
So, if the target is lower, upper_bound = mid-1 (it's at the lower part of the array).
If the target element is ≥ arr[mid], we would set the lower_bound as mid (not mid+1, as this index could itself hold the upper range of the number).
Solution Steps
- Find the leftmost index of the target in the array using binary search
- Find the rightmost index of the target in the array using another binary search
- Return the lower and upper index.
Pseudo Code
// Driver function
int[] searchRange(int[] arr, int target) {
int upperLowerBounds[2]
start_index = 0
end_index = arr.length - 1
left_most_index = leftmost(start_index, end_index, target)
right_most_index = rightmost(start_index, end_index, target)
upperLowerBounds[0] = left_most_index
upperLowerBounds[1] = right_most_index
return upperLowerBounds
}
// Binary search function for leftmost target
int leftmost(int min, int max, int target) {
if (min == max)
return min
int mid = (min + max) / 2
if (array[mid] < target)
return leftmost(mid + 1, max, target)
else
return leftmost(min, mid, target)
}
// Binary search function for rightmost target
int rightmost(int min, int max, int target)
{
if (min == max)
return min
int mid = (min + max + 1) / 2
if (array[mid] > target)
return rightmost(min, mid - 1, target)
else
return rightmost(mid, max, target)
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(log n)
Space Complexity: O(log n).
We can reduce the space complexity by using the iterative function for binary search instead of recursive to O(1) space.
// Range search using itarative binary search
public int[] searchRange(int[] arr, int target)
{
int[] upperLowerBounds[2]
int startIndex = 0;
int endIndex = arr.Length - 1
while (startIndex < endIndex) {
int midIndex = (startIndex + endIndex) / 2
if (target <= arr[midIndex]) {
endIndex = midIndex
}
else {
startIndex = midIndex + 1
}
}
// saving startIndex in the result array that will be returned...
upperLowerBounds[0] = startIndex
endIndex = arr.Length - 1
while (startIndex < endIndex) {
int midIndex = (startIndex + endIndex) / 2 + 1
if (target < arr[midIndex]) {
endIndex = midIndex -1
}
else {
startIndex = midIndex;
}
}
upperLowerBounds[1] = endIndex
return upperLowerBounds
}
Critical Ideas to Think
- How do the two binary search functions differ?
- How are we reducing space complexity?
- For what does the upperLowerBounds array is used for?
Comparison of different solutions
Suggested Problems to Solve
- Find the element that appears once in a sorted array
- Find the minimum element in a sorted and rotated array
- Find the only repeating element in a sorted array of size n
- Find the Kth smallest element in the sorted generated array
- Find the missing element in a sorted array of consecutive numbers
If you have any more approaches or you find an error/bug in the above solutions, please comment down below.
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Search an element in a sorted and infinite array
You are given a sorted and infinite array A and an element K. You need to search for the element K in the array. If found, return the index of the element, else return -1.

AfterAcademy Tech
Minimum in a Sorted and Rotated array
You have a sorted and rotated array where elements are sorted and rotated circularly. Write a program to find the minimum element in the array.
AfterAcademy Tech
Merge Two Sorted Arrays
You are given two sorted arrays arr1[ ] and arr2[ ] of sizes m and n respectively. Write a program to merge them in such a way that the resultant array is sorted too.

AfterAcademy Tech
Median of the Two Sorted Array of Same Size
There are two sorted arrays nums1 and nums2 of size n. Find the median of the two sorted arrays.