Sort Characters By Frequency - Interview Problem
AfterAcademy Tech
•
08 Nov 2019

Level: Medium
Asked in: Google, Microsoft, Bloomberg, Paypal
Understanding the problem
Problem Description: You are given a string S and its length n and you need to sort its characters based on their frequency. The characters in the output will be ordered based on their frequency in S, characters with higher frequency come first.
For example,
Input: S = "halalelluejah"
Output: llllaaahheeuj
Input: S = "aaaabeebccccc"
Output: cccccaaaabbee
Possible questions to ask the interviewer:-
- What if two characters have the same frequency, which comes first? (Ans: Whichever occurs earliest in S comes first. In other words, the sorting must be stable)
- Are uppercase and lowercase letters to be treated as equal or not? (Ans: You need to consider uppercase and lowercase different here)
Brute force and efficient solutions
We will be discussing three possible solutions for this problem:-
- Brute Force Approach
- Using BST
- Using Hash Table
1. Brute Force Approach
We could create an auxiliary space where we store the frequency and first indexes of elements and then sort this auxiliary space. We are storing the first index of the element too as this helps in ensuring that there are no duplicate elements in the auxiliary space and it also helps us in stable sorting.
Solution Steps
- Create an auxiliary object array freq_arr[ ] where each element stores the character, its frequency, and its first_index, i.e. its first occurrence.
class elem
{
char ch
int freq
int first_index
}
- For each element, first, check if it already exists in the freq_arr[ ] array.
- If it does, increase the frequency by 1.
- Else, insert this new element with the frequency as 1 and the current index as first_index.
- Sort this array based on the frequency of characters. If the frequency is equal for two elements then we should first process the element with lower first_index (That's why we are storing the indexes instead of elements). You can use a comparator for this. (What’s a comparator?)
- Extract characters from freq_arr[ ] and store in a ans[ ] array.
Pseudo-Code
class elem
{
char ch
int freq
int first_index
}
bool comp(elem a, elem b)
{
if (a.freq != b.freq)
return a.freq > b.freq // Higher frequency comes first
else
return a.first_index < b.first_index // Lower index comes first
}
int[] sortByFrequency(char S[], int n)
{
elem freq_arr[]
for (i = 0 to n-1)
{
bool found = False
for (j = 0 to freq_arr.length - 1)
{
if (freq_arr[j].ch == S[i])
{
freq_arr[j].freq = freq_arr[j].freq + 1
found = True
break
}
}
if (found == False)
{
elem temp
temp.ch = S[i]
temp.freq = 1
temp.first_index = i
freq_arr.append(temp)
}
}
sort(freq_arr, freq_arr.length, comp)
char ans[]
for (i = 0 to freq_arr.length-1)
for(j = 0 to freq_arr[i].freq-1)
ans.append(freq_arr[i].ch)
return ans
}
Complexity Analysis
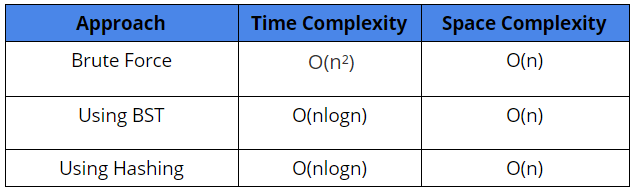
Time Complexity: Storing values in freq_arr[ ] + Sorting freq_arr[ ] + Extracting characters in ans[ ]
= O(n²) (Think!) + O(nlogn) + O(n)
= O(n²)
Space Complexity: freq_arr[] array + Auxiliary space used by sorting + Storing ans[ ] array
= O(n) + ( O(n), if merge sort, else with heap sort, O(1) ) + O(n)
= O(n)
Critical ideas to think!
- Could you improve the time complexity for calculating frequency?
- Can you improve space complexity for this algorithm?
- What if you sort the characters beforehand? How is the time complexity for calculating frequency affected by this? How will you maintain the sorting stable in nature?
2. Using BST
Binary Search Tree(BST) is a useful data structure to run frequent search queries. The time complexity of the search operation in BST depends on the height of the tree.
Although, if we use the idea of Balanced Binary Search Tree such as AVL Tree or Red-Black Tree, the worst-case time complexity for searching would be O(logn). Here we will be assuming a Balanced BST implementation in the pseudo-code.
For solving this problem, we use the following BST node structure which consists of two additional parameter freq and first_index to store the frequency and first occurrence of the character in the input string.
class BSTnode
{
char data
int freq
int first_index
node *left
node *right
}
Solution Steps
1. Create a BST and while creating BST maintain frequency and the first occurrence of each incoming character
2. Before inserting a character in BST, we check if it already exists, if it does, increase the frequency by 1. Else, insert a new node and set frequency as 1.
3. We create an auxiliary object array freq_arr[ ] (like the above solution) and perform in-order traversal of BST to store characters and its frequency to freq_arr[ ]
5. Then we sort the freq_arr[ ] array according to the frequency and if the frequency is equal then use first_index to maintain the stable order.
6. Extract characters to ans[ ] array according to their frequency and return it.
Pseudo-Code
class elem
{
char ch
int freq
int first_index
}
class BSTnode
{
char data
int freq
int first_index
node *left
node *right
}
bool comp(elem a, elem b)
{
if (a.freq != b.freq)
return a.freq > b.freq //Higher frequency comes first
else
return a.first_index < b.first_index //Lower index comes first
}
int[] sortByFrequency(char S[], int n)
{
BSTnode root = NULL
BSTnode temp = NULL
for(i = 0 to n-1)
{
temp = BSTsearch(root, S[i])
if (temp != NULL)
temp.freq = temp.freq + 1
else if (temp == NULL)
{
BSTnode node = Newnode()
node.data = S[i]
node.first_index = i
node.freq = 1
node.left = node.right = NULL
BSTinsert(root, node)
}
}
elem freq_arr[]
inorderStore(root, freq_arr) //Extracting Characters from BST to freq_arr[] using in-order traversal
sort(freq_arr, freq_arr.length, comp)
char ans[]
for (i = 0 to freq_arr.length-1)
for(j = 0 to freq_arr[i].freq-1)
ans.append(freq_arr[i].ch)
return ans
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: Building a BST + Extracting Characters to freq_arr[ ] + Sorting freq_arr[ ] + Extracting characters to ans[ ]
= O(nlogn) (Think!) + O(n) + O(nlogn) + O(n)
= O(nlogn)
Space Complexity: Extra space for BST + Storing freq_arr[ ] + Storing ans[ ] + Extra space used by sorting
= O(n) + O(n) + O(n) + ( O(n), if merge sort, else with heap sort, O(1) )
= O(n)
Critical ideas to think!
- Implement and analyze search, Insert and delete operation in BST.
- Why are we extracting elements from BST and storing it in freq_arr[ ] ? Implement inorderStore(root, freq_arr) function.
- Think about the other scenario where we could store extra details in the nodes of BST to solve the problem.
- This is a good example of problems solving via data structure. What other problems could be solved using BST?
- Try to visualize the solution via different examples.
3. Using Hash Table
Given an unsorted array, hashing is the most time-optimal way to find the frequency of each element. But given a HashTable of characters with their frequency, how would you perform a stable sorting on it? (Think!)
For stable sorting, we could use another HashTable which stores the first index or first occurrence of each character.
Solution Steps
- Create a HashTable count to store the frequency of each character as a value.
- Create another HashTable index to store the first indexes of each character as a value.
- Linearly traverse the array, for each character
- If it exists in the count, increase its frequency by 1
- If it does not exist in the count, insert it with frequency 1 and also insert it in index with its index as value
4. Create freq_arr[ ] just like in the algorithm above using count and index Hash Tables
5. Sort the freq_arr[ ] array according to the frequency and if the frequency is equal then use first_index to maintain the stable order.
6. Extract characters to ans[ ] array according to their frequency and return it.
Pseudo-Code
class elem
{
char ch
int freq
int first_index
}
bool comp(elem a, elem b)
{
if ( a.freq != b.freq)
return a.freq > b.freq // Higher frequency comes first
else
return a.first_index < b.first_index // Lower index comes first
}
int[] sortByFrequency(char S[], int n)
{
Create a Hash Table count
Create a Hash Table index
for(i = 0 to n-1)
{
if (S[i] in count)
count[S[i]] = count[S[i]] + 1
else
{
count[S[i]] = 1
index[S[i]] = i
}
}
elem freq_arr[]
for( x : count ) // For each element x in count
{
elem temp
temp.ch = x
temp.freq = count[x]
temp.first_index = index[x]
freq_arr.append(temp)
}
sort(freq_arr, freq_arr.length, comp)
char ans[]
for (i = 0 to freq_arr.length-1)
for(j = 0 to freq_arr[i].freq-1)
ans.append(freq_arr[i].ch)
return ans
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: Storing values in count and index Hash Tables + Creating freq_arr[ ] array + Sorting freq_arr[ ] array + Extracting characters to ans[ ] array
= O(n) + O(n) + O(nlogn) + O(n)
= O(nlogn)
Space Complexity: Extra space of count and index Hash Tables + Storing an freq_arr[ ] array + Storing ans[ ] array + Auxiliary Space used by sorting
= 2*O(n) + O(n) + O(n) + (O(n), if merge sort, else with heap sort, O(1))
= O(n)
Critical ideas to think!
- Could you improve the space complexity of this algorithm?
- Did you find some patterns or similarities in all three approaches?
- Explore some problems where we use two hash tables for the solution.
- Compare the BST and Hash Table. In which scenario we prefer BST over Hash Table.
Comparison of the different solutions
Suggested Problems to solve
- Perform minimum deletion operations such that all elements have a unique frequency
- Find the most frequent element in an array
- Find the sum of all elements with an even frequency
- Sort the array except for elements with frequency k
Please write comments down below if you find any error or bug.
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
AfterAcademy Data Structure And Algorithms Online Course - Admissions Open
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Remove Duplicates in a Sorted Array-Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in companies like Google, Microsoft, Amazon. The problem is to remove duplicates from a sorted array or list.
AfterAcademy Tech
Sort a linked list using Insertion Sort - Interview Problem
Sort a linked list using insertion sort and return its head.

AfterAcademy Tech
Median in a Row-wise Sorted Matrix-Interview Problem
The problem is to find the median in a row-wise sorted matrix. This is an interview problem asked in companies like Amazon. There is a further constraints on extra space. We have discussed two possible solutions.

AfterAcademy Tech
Remove Duplicates From a Sorted Linked List-Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked by companies like Myntra, Visa, Oracle, Adobe, etc. The problem is to remove the duplicate nodes from the given Linked List so that only unique nodes(with unique data values) are present.
