Median in a Row-wise Sorted Matrix-Interview Problem
AfterAcademy Tech
•
06 Apr 2020

Difficulty: Medium
Asked in: Amazon
Understanding the Problem: →
Given a N*M matrix which is sorted row-wise, you task is to find the median of the given matrix.
Median: The median of a group of ordered number is the middle number that will separate the highest half with lowest half of numbers. If there are two middle numbers the, the median is the mean of the numbers.
For example:
Input: 2 3 3
1 5 6
6 6 7
Output: 5
Explanation: The total number of elements is 9(odd), in this case the formula for finding the median is (1+N*M)/2 th smallest element out of the given elements. Here it is 5 which is the 5th smallest element as 1 2 3 and 3 are smaller than it.
Possible questions to ask the interviewer: →
- Can I use extra space for solving this? (Ans: Try to come up with an efficient solution)
- Is the number of elements odd, even or can be both?(Ans: You can consider the numbers to be odd.)
You can first try to solve this problem here.
Solutions
We are going to discuss two different approaches to solve this problem. First, we will look at the Brute Force Solution and then move on to optimize the solution using a better algorithm.
- Brute Force Solution
- Optimized Solution Using Binary Search
Brute Force Solution
Solution idea
Here is it given that the total number of elements is always odd. Now, we have the formula that the (1+N*M)/2 th smallest element in an ordered(sorted) list is the median. Since the number of elements are odd there is no case of having more than one middle elements.We can think of a very simple approach where we will store all the elements of the matrix in a 1-Dimensional array and after sorting we will output the element at [(1+N*M)/2–1]th index.
Solution steps
- First, create an array of size N*M and copy all the elements of the matrix in that array. You can copy either row-wise or column-wise.
- After copying simply sort the entire array.
- Output the element at the [(1+N*M)/2–1]th index as this will be the middle element partitioning the array in lower and upper halves.
Pseudo-code
int medianRowwiseSortedMatrix(int matrix[N][M])
{
int tempArr[N*M]
int desired_index = (1+N*M)/2 -1
int index = 0
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<M; j++)
{
tempArr[index++] = matrix[i][j]
}
}
sort(tempArr, tempArr + N*M)
return tempArr[desired_index]
}
Complexity Analysis
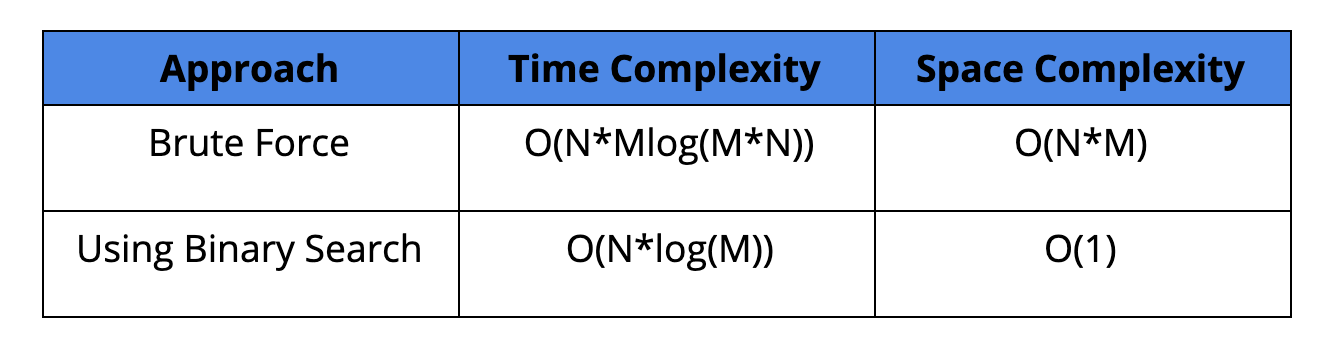
Time Complexity: O(N*M*log(N*M)
Space Complexity: O(N*M)
Critical ideas to think!
- Can we use the given property of this matrix that it is row-wise sorted to improve the complexity?
Optimized Solution Using Binary Search
Solution idea
The idea here is to leverage the binary search algorithm in order to optimize this problem. If you have paid attention to the definition of median, you must have noticed in case of odd elements the median is (1+N*M)/2 th smallest number which basically implies that (1+N*M)/2 is the total number of elements which are smaller or equal to our median.One more thing to analyse is, the median will always lie in the range of minimum and maximum element.Using these observations and applying binary search for elements in the above range (minimum, maximum) and maintaing the counter for smaller or equal numbers for each element in this range, we can find our median(discussed above based on count of smaller or equal elements).
Solution idea
Let us see a step-by-step approach to this solution:
- First, we need to find the minimum and maximum elements from the matrix. The minimum and maximum can be easily found since the rows are sorted so we need to comapare with the first element of each row for minimum and last element of each row for maximum.
- After finding our min and max, we can apply binary search on this range. The mid element can be calculated and number of elements smaller or equal to mid can be calculated, we have used upper_bound() function for this.
- Based on the value of our counter, the min and max can be adjusted accordingly based on what we do for binary search.
Pseudo-code
int medianRowwiseSortedMatrix(int matrix[N][M])
{
int min = INT_MAX;
int max = INT_MIN;
int desired_count = (1+(N*M)/2))
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
if(A[i][0]<min)
min = A[i][0];
if(A[i][M-1]>max)
max = A[i][M-1];
}
int counter =0;
while(min<max)
{
counter=0;
int mid = (max+min)/2;
for(int i= 0;i<N;i++)
{
counter += upper_bound(A[i], A[i]+M, mid) - A[i];
}
if(counter < desired_count)
min = mid+1;
else
max = mid;
}
return min;
}
Note:- The upper_bound function used above is with reference to C++ STL. This basically gives the iterator pointing to the first element strictly greater than its third parameter(mid here). Can read about it here.
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(N*log(M)) (Why?)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Comparison of Different Solutions
Suggested Problems to Solve
- Find the median in a row and column-wise sorted matrix.
- Search an element in a row and column-wise sorted matrix.
- Median of two sorted arrays of different sizes.
- Given a row and column-wise sorted matrix, print all elements in sorted order.
Happy Coding!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Remove Duplicates in a Sorted Array-Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in companies like Google, Microsoft, Amazon. The problem is to remove duplicates from a sorted array or list.
AfterAcademy Tech
Sort a linked list using Insertion Sort - Interview Problem
Sort a linked list using insertion sort and return its head.

AfterAcademy Tech
Remove Duplicates From a Sorted Linked List-Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked by companies like Myntra, Visa, Oracle, Adobe, etc. The problem is to remove the duplicate nodes from the given Linked List so that only unique nodes(with unique data values) are present.

AfterAcademy Tech
Set Matrix Zeros - Interview Problem
Given a matrix, A of size M x N of 0's and 1's. If an element is 0, set its entire row and column to 0
