Smallest Multiple With 0s and 1s
AfterAcademy Tech
•
11 Sep 2020

Difficulty: Hard
Asked in: Amazon
Understanding The Problem
Problem Description
You are given an integer n, write a program to find the smallest multiple of n which consists of digits 0 and 1 only.
Problem Note
- The resultant number could be quite large so return it in the form of a string.
- The returned string should not contain any leading zeroes.
Example 1
Input: n = 18
Output: 1111111110
Solutions
We will be discussing two solutions for this problem
- Naive Approach: Iterate on the multiples of
nuntil the multiple is only composed of 0 and 1. - BFS: Starting from string “1”, we can concatenate 0’s or 1’s at the end of the string in search of such a string which is multiple of the given number.
You can try the problem here.
1. Naive Approach
A straight forward approach to this problem is to look for all the multiples of the given number and find the first multiple which is only composed of 0’s and 1's.
However, this approach is not a good approach because you can see from the example that for a small number like 18, the output is a tremendously large number like 1111111110 and finding all the multiples of 18 and checking if it is made of only 0’s and 1’s is computationally very costly.
Solutions Steps
- Iterate over all the multiples of the input
n - For each multiple, check if it is only composed of 0’s and 1’s
- Return the first multiple which is only composed of 0’s and 1’s
Pseudo Code
string smallestMultiple(int n) {
string p = toString(n)
int ctr = 1
while(isNotZerosAndOnes(p)){
ctr = ctr + 1
p = toString(n*ctr)
}
return p
}
// utility function
bool isNotZerosAndOnes(string p){
for(i = 0 to i < p.size){
if(p[i] is not '0' or p[i] is not '1')
return false
}
return true
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(p), where p is the pth multiple of n which is composed of only 0’s and 1’s.
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical Ideas To Think
- Why does this solution is not feasible?
- Why we are iterating over the multiples of n?
- Can you explain the time complexity of this approach?
2. BFS
A faster approach will be a recursive solution where we build all possible numbers consists of digits ones and zeroes only.
For example:
for n = 3
1
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
10 11
/ \ / \
/ \ / \
100 101 110 111
So, we can create such a tree which where each vertex will have two children containing the parent node concatenated with 0 or 1 at the end. For each vertex, we can check if the vertex’s value is a multiple of n or not.
Now, this approach can further be optimized. Let’s define our numbers as type strings. Considering there are N states, where i’th state stores the smallest string which when taken modulo with N gives i. Our aim is to reach state 0 (which basically be the multiple of N). Starting from the state “1” we move forward and at each step, we have two choices, i.e. to append “0” or “1” to the current state. We will explore both options.
Now the point is if we have already visited a state, why would I visit it again? It already stores the smallest string which achieves that state and if I visit it again with a new string it will surely have more characters than the already stored string.
So, this problem boils down to performing BFS on the above-defined states where We will be visiting a state at most once.
Look at the below examples for further clarification.
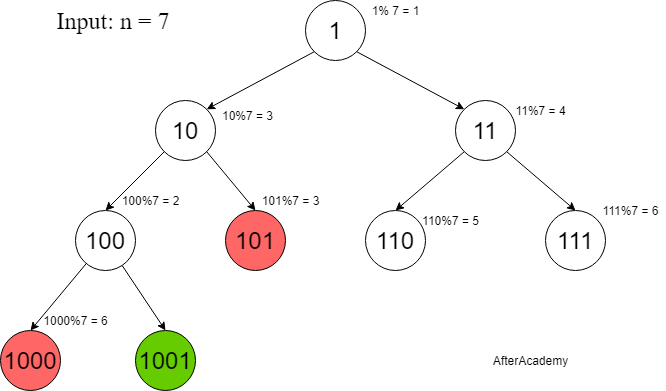
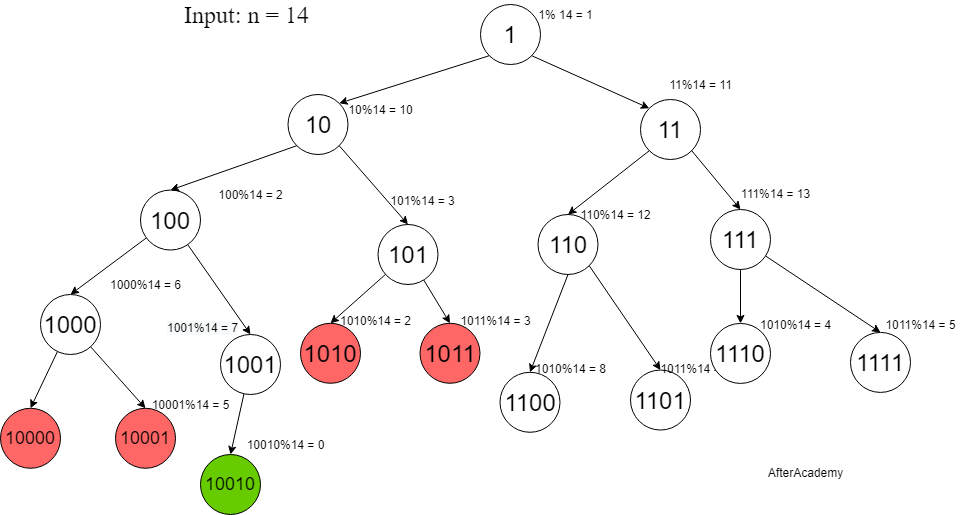
Here, Red nodes represent those states whose remainder state already existed in the tree.
Solution Steps
- Create a string
‘t’and initialize it with‘1’ - Create a queue for performing BFS and insert
‘t’in it. - Create a set that will store the remainders that have been visited.
- Perform BFS over the states as explained above:
- pop the front and store it in
‘t’ - check if
‘t’ % Nis0, if so, then't'is the smallest binary string multiple of N - otherwise, check if the obtained remainder exists in the set or not. If the remainder is a new state, i.e. not present in the visited set, then add it to the visited set and create two new states i.e.
t + ‘0’andt + ‘1’and push them to the Queue.
Pseudo Code
string smallestMultiple(int N) {
Queue(string) q
Set(int) visited_rem
string t = "1"
q.push(t)
while (q is not empty) {
t = q.front()
q.pop()
int rem = mod(t, N)
// solution found if remainder is 0
if (rem == 0)
return t
// If this remainder is not previously seen,
// then push t+'0' and t+'1' in our queue
if(rem not in visited_rem)
{
visited_rem.insert(rem)
q.push(t + "0")
q.push(t + "1")
}
}
}
int mod(string t, int N) {
int rem = 0
for (int i = 0 to i < t.length())
{
rem = rem * 10 + (t[i] - '0')
rem = rem % N
}
return rem
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n)(How?)
Space Complexity: O(n)
Critical Ideas To Think
- Why does the BFS traversal on the above-defined states will always give the smallest multiple binary strings? Answer: BFS proceeds level by level so the first answer we get will be our smallest answer.
- How does the time complexity is O(n)? Answer: Here we are only taking into account those states whose remainder is unique and thus there can be a maximum of n such nodes on which we are performing BFS.
- How did we make sure that the states whose remainder has already existed will not participate in the solution? Answer: If we visit it again with a new string it will surely have more characters than the already stored string.
- Why we are performing BFS? Can we perform DFS instead of BFS here?
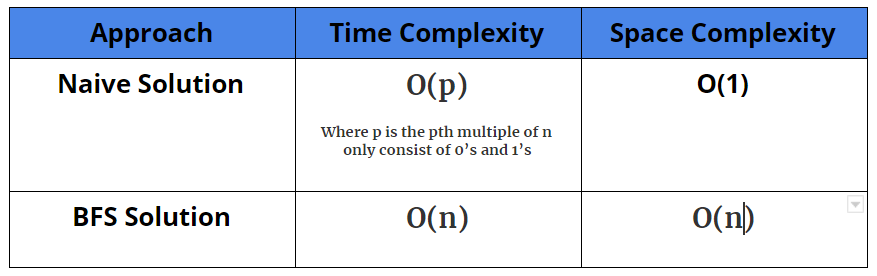
Comparison Of Different Solutions
Suggested Problems To Solve
- Single source shortest path between two cities
- All possible shortest chains to reach the target word
- Check if a knight is unsafe on a chessboard
- Flood fill algorithm
- Min steps to convert N-digit prime number into another by replacing a digit in each step
Please comment down below if you have a better insight in the above approach.
Happy Coding, Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Matrix Chain Multiplication
Given a chain <M1, M2...Mn> of n two-dimensional matrices, write a program to fully parenthesize the product M1×M2×⋯×Mn in a way that minimizes the number of multiplications. It's a famous dynamic programming problem.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find the kth smallest element in an array
Given an array A[] of n elements and a positive integer K, find the Kth smallest element in the array. It is given that all array elements are distinct.

AfterAcademy Tech
Wave Array
You are given an unsorted array of integers(arr) of length n, write a program to sort it in wave form. The array elements in the resultant array must be such that arr[0] >= arr[1] <= arr[2] >= arr[3] <= arr[4] ... and so on. If there are multiple sorted orders in wave-form, return the one which is lexicographically smallest.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find Missing Positive - Interview Problem
Given an array, find the smallest missing positive integer.
