Sliding Window Maximum
AfterAcademy Tech
•
02 Jun 2020
Difficulty: Hard
Asked in: Amazon, Microsoft
Understanding the Problem
You are given an integer array arr of size n. Assume a sliding window of size k starting from index 0. In each iteration, the sliding window moves to the right by one position till n-k. Write a program to return an array representing the maximum number in all sliding windows.
Problem Note
- The first element of the resultant array is
max(arr[0...k]), then the second element ismax(arr[1...k+1])and so on. - The size of the resultant array will be
n-k+1. - You are expected to solve this question in
O(n)time complexity
Example 1
Input: arr[] = [4, 3, 8, 9, 0, 1], k = 3
Output: [8, 9, 9, 9]
Explanation: The window size is 3 and the maximum at different iterations are as follows:
max(4, 3, 8) = 8
max(3, 8, 9) = 9
max(8, 9, 0) = 9
max(9, 0, 1) = 9
Hence, we get arr = [8, 9, 9, 9] as output.
Example 2
Input: arr[] = [9, 8, 6, 4, 3, 1], k = 4
Output: [9, 8, 6]
Explanation: The window size is 4 and the maximum at different iterations are as follows:
max(9, 8, 6, 4) = 9
max(8, 6, 4, 3) = 8
max(6, 4, 3, 1) = 6
Hence, we get arr = [9, 8, 6] as output.
Example 3
Input: arr[] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 10, 6, 9, 8, 7, 5], k = 3
Output: [3, 4, 10, 10, 10, 9, 9, 8]
Explanation: The window size is 3 and the maximum at different iterations are as follows:
max(1, 2, 3) = 3
max(2, 3, 4) = 4
max(3, 4, 10) = 10
max(4, 10, 6) = 10
max(10, 6, 9) = 10
max(6, 9, 8) = 9
max(9, 8, 7) = 9
max(8, 7, 5) = 8
Hence, we get arr = [3, 4, 10, 10, 10, 9, 9, 8] as output.
Solutions
We will be discussing 4 solutions
- Naive Approach: Iterating through the elements for all windows separately.
- Using a Self-balancing tree: Use the tree to store the elements of the window and do all operations at
log(n)time. - Using Heap Data Structure: Use a max-heap data structure to find the maximum element in the window at constant time.
- Using Deque: Use a double-ended queue to store the elements of the window.
Before moving on to the solutions, you can try this question here.
Naive Approach
The naive approach to this problem will be to “examine” window of size k starting at each element of the array. We iterate through the whole array and calculate maximum among the window of next k elements from each element of the array till the last element of the window and array coincide.
Solution steps
1. Traverse all the N elements of the array (Outer loop)
2. At each step, calculate maximum element among next k elements (Inner loop)
3. Store the maximum element of each window in the answer array
4. Return the answer array
Pseudo Code
int[] slidingWindowMaximum(int arr[], int n, int k)
{
ans = []
// there are N-k+1 windows
for (i = 0 to N-k)
{
max = arr[i]
for(j = i to i+k-1)
{
if(arr[j] > max)
max = arr[j]
}
ans.append(max)
}
return ans
}
Complexity
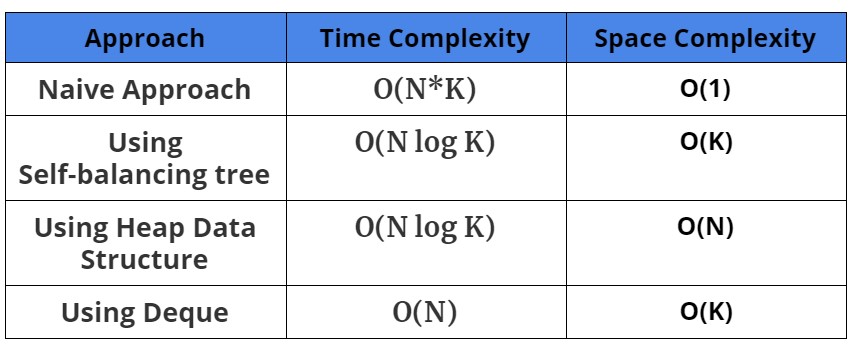
Time Complexity: O(N*K)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Using self-balancing BST
The self-balancing BST like Red-Black Tree, AVL tree, etc. adjust their height automatically for every insertion and deletion, taking O(log N) time on an average.
The idea is to make a BST of size K and at each sliding, we will insert the next element and delete the least-recent added element in O(log N).
Solution steps
- Create a self-balancing BST for the first
Kelements. - Get the maximum element from the BST and store it in the solution array.
- Move the window (having
Kelements) forward. This step needs “dropping” the first element (arr[i]) in the window and “adding” the element after the last element (arr[i+k]) to the window. - Iterate through the whole array from 0 to N-K and repeat the above steps.
- Return the solution array.
Pseudo Code
int[] slidingWindowMaximum(int arr[], int n, int k)
{
ans = []
root = Tree() // self-balancing Tree
// insert first K elements
for(i = 0 to K-1)
root.insert(arr[i])
// Now the tree contains the first k elements
d = 0 // to store the elements to be deleted
for(i = k to n-1)
{
// find the maximum element and append it
// to the answer array
ans.append(findMax(root))
root.delete(d)
d += 1 // increase the d for next window
root.insert(arr[i])
}
ans.append(findMax(root))
return ans
}
// The maximum element will be at the rightest in the tree
int findMax(Tree root)
{
if(root.right == NULL)
return root
return findMax(root.right)
}
Complexity
Time Complexity: O(N * log K)
Space Complexity: O(K) (To store the elements in BST).
Using a heap data structure
The intuition of using a max heap for a better solution to the problem can come from finding a maximum of K elements in less than O(K) time. Within every window, we can use a heap to store the K elements of the current and get the maximum element (top of the max heap) in O(log K) time. For sliding the window forward, we need to “drop” the leftmost element of the window from the heap and add the new element to it. We have done this for all the windows in the array. The heap can be implemented using a priority queue.
Note: In various languages like C++, there is no predefined function to remove a particular element from the priority queue. We can overcome this problem by using another priority queue which keeps the record of the leftmost elements only.
Solution steps
- Take two priority queues - one for keeping the heap and other for keeping the elements to be “dropped” from the heap when the window slides forward.
- Push the first
Kelements of the array into the heap. - Store the top of the heap in result array as it is the maximum element in the first window.
- Now, Iterate through the array and at each step we have two cases
- The leftmost element of the window was the maximum element (top of the heap):- For this, remove the top of the heap to slide the window forward.
- The leftmost element of the window was not the maximum element of the window:- For this, keep the leftmost element (
arr[i-k]) in the other heap and keep popping the elements from both the heaps until the top of heaps match.
5. Add that element of array to the heap and store the result.
6. After the iteration, return the array.
Pseudo Code
int[] slidingWindowMaximum(int arr[], int n, int k)
{
heap = PriorityQueue()
toDrop = PriorityQueue()
// Push First K elements in the heap
for(i = 0 to k-1)
heap.push(arr[i])
ans = []
// store the maximum in ans
ans.append(heap.top())
//iterate for rest elements
for(i = k to n)
{
// pop the heap if leftmost element is previous element was maximum
if(arr[i-k] == heap.top())
heap.pop()
else
{
// push the leftmost element to toDrop heap
toDrop.push(arr[i-k])
}
// pop elements from both heap till their top matches
while(!toDrop.isEmpty() and toDrop.top() == heap.top())
{
heap.pop()
toDrop.pop()
}
// push the element to the heap
heap.push(arr[i])
ans.append(heap.top())
}
return ans
}
Complexity
Time Complexity: O(N * log K)
Space Complexity: O(N) (In the worst case, "dropped" priority queue can have size N if the first element in the array is maximum).
Using Deque
We can use a double-ended queue to keep only the indices of those elements which are useful. The use of deque is to add and drop elements from both the ends of a queue. We will slide the window of K elements by “dropping” the first element and “adding” the next element after the window to move it forward.
The deque will keep the index of the maximum element at the front and also at a time, it will delete all the unnecessary elements from the window. You can look at the solution steps for more explanation
- Create a dequeue to store elements.
- Iterate through the array, insert the first K elements in the array. While insertion we will take care of the window such that there are no unnecessary indices. To remove these indices, we will remove all the elements from the back of the queue that is smaller than the current array element.
- After the iteration for the first K element, the maximum element's index is at the front of the queue.
- Now, Iterate through the remaining part of the array and remove the element from the front if they are out of the current window.
- Again, insert the element in the dequeue and before inserting delete those unnecessary indices which are smaller than the current array element.
- Now, after each iteration, you will get the maximum element of the current window.
Pseudo Code
int[] slidingWindowMaximum(int arr[], int n, int k)
{
q = Dequeue()
ans = []
// for First K elements
for( i = 0 to k-1)
{
while(!q.empty() and arr[i] >= arr[q.back()])
{
// Remove the indices of elements that are smaller than the current elements
q.pop_back()
}
q.push_back(i)
}
// the element at the front has index of the highest element in the window
ans.append(arr[q.front()])
// for rest elements
for(i = k to n-1)
{
// drop the elements that are out of window
while(!q.empty() and q.front() <= i-k)
q.pop_front()
// remove those elements smaller than the current element from back
while(!q.empty() and arr[i] >= arr[q.back()])
q.pop_back()
q.push_back(i)
ans.append(arr[q.front()])
}
return ans
}
Complexity
Time Complexity: O(2*N) (Every element is added and removed at most once)
Space Complexity: O(K)
Comparison of different solutions
Suggested problems to solve
- Find Median of sliding window in an array.
- Smallest Window that contains all character of the string itself.
- Count Distinct Elements in every window of size K.
- Maximum and Minimum in the window of a given size in an array
Please comment down below if you find an improvement in the above explanation.
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Maximum Product Of Three Numbers
write a program to find three numbers whose product is maximum and output the maximum product. This is a basic mathematical problem and requires logical skill to solve.

AfterAcademy Tech
Maximum Subarray Sum
You are given an array A[] with n elements. You need to find the maximum sum of a subarray among all subarrays of that array. A subarray of array A[] of length n is a contiguous segment from A[i] through A[j] where 0<= i <= j <= n.

AfterAcademy Tech
Maximum path sum in a binary tree
Given a non-empty binary tree, find maximum path sum. For this problem, a path is defined as any sequence of nodes from some starting node to any node in the tree along with the parent-child connections.

AfterAcademy Tech
What is the maximum segment length of a 100Base-FX network?
In this blog, we will learn what are the pieces of information hidden in the name of the network like 100BaseFX. We will learn about 100baseFX and what is its maximum segment length.