Reverse First K Elements Of A Queue
AfterAcademy Tech
•
05 Oct 2020

Difficulty: Medium
Understanding The Problem
Problem Description
Given an integer k and queue Q of integers. Write a program to reverse the order of the first k elements of the queue. The other elements will be in the same relative order. The following standard operations are allowed on the queue:
- enqueue(x): Insert an item
xto the rear of queue - dequeue(): Remove an item from the front of queue
- size(): Returns the number of items in the queue.
- peek(): Get the front item.
- empty(): Return whether the queue is empty.
Example 1
Input: Q = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
k = 5
Output: Q = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
Explanation: The first 5 elements of Q are reversed.
Example 2
Input: Q = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
k = 4
Output: Q = [4, 3, 2, 1, 5, 6]
Explanation: The first 4 elements of Q are reversed.
Solution
The problem asked us to reverse the first K elements of the queue and we can use the predefined operations given above. To reverse some segment of the queue, we can use an auxiliary stack (How?).
If we insert all the elements of the queue in a stack using the dequeue operation, then we will have a stack that will be seen reversed of the queue.
For example, If we have a queue of numbers sorted in ascending order, then inserting all elements of the queue into a stack one by one, then the top of the resultant stack will have the smallest element, i.e. the stack will be in descending order. We can use this concept here.
We will take an auxiliary empty stack. We will dequeue the first K elements of the queue and push them into the stack one by one. Now, we will pop all elements of the stack and enqueue into the queue one by one. In this way, we will have the input queue with the first K elements in the reversed order at the rear of the queue. We will dequeue (size — k) elements from the front and enqueue in the same queue one by one. Thus, we will have the resultant queue with the first K elements in reversed order.
Look at the below example for clear understanding, Here queue is given to you and K is 4:
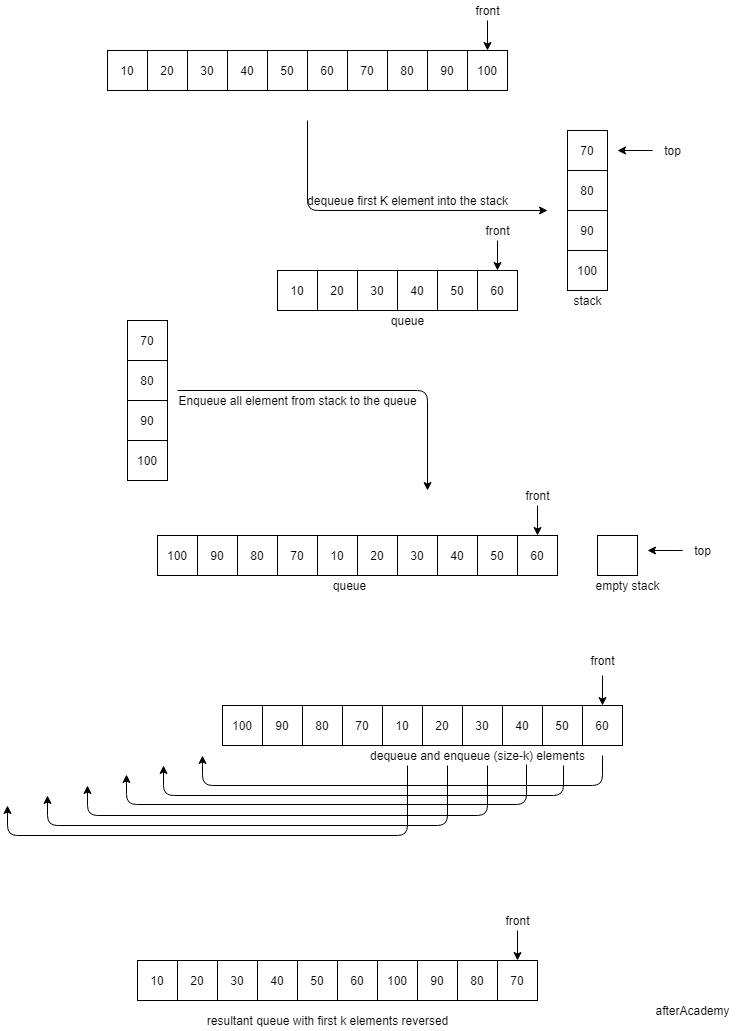
Solution Steps
- Create an empty stack.
- Dequeue K items from the queue and push them into the stack, one by one.
- Enqueue the contents of the stack at the back of the queue
- Dequeue (size-k) elements from the front and enqueue them one by one in the same queue.
Pseudo Code
int[] reverseQueueFirstKElements(queue Q, int k) {
if (queue is Empty or k > queue.size())
return Q
Stack stack
for (int i = 0 to i < k) {
stack.push(queue.peek())
queue.dequeue()
}
while (stack is not empty()) {
queue.enqueue(stack.top())
stack.pop()
}
for (int i = 0 to i < queue.size() - k) {
queue.enqueue(queue.peek())
queue.dequeue()
}
return queue
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n+k)
Where n is the queue size and k is the number of elements to be reversed.
Space Complexity: O(n)
Critical Ideas To Think
- How did we rotate the first K elements?
- Can we solve this problem by using two auxiliary queues instead of one auxiliary stack?
- Why did we enqueue the items from the same queue in the last loop? And why such operation is performed for
size — ktimes only?
Suggested Problems To Solve
- Reversing a Queue using another Queue
- Reversing a queue using recursion
- Check if a queue can be sorted into another queue using a stack
- Queue based approach for the first non-repeating character in a stream
- Reverse a stack using a queue.
Please comment down below if you have a better insight in the above approach.
Happy Coding, Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Priority Queues
Priority Queues are similar to queues where we insert an element from the back and remove an element from the front, but with one difference that the logical order of elements in the priority queue depends on the priority of the elements. In this blog, we will discuss the priority queues, its properties, its various implementations, and its applications. We will also analyze and compare the various implementations of the Priority Queue.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find the next greater element for every element in an array - Interview Problem
Given an array A[] of size n, you need to find the next greater element for each element in the array. Return an array that consists of the next greater element of A[i] at index i.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find an Element In a Bitonic Array
Given a bitonic sequence of n distinct elements, write a program to search a given element k in the bitonic sequence. Bitonic Sequence is a sequence of numbers that is first strictly increasing then after a point strictly decreasing.

AfterAcademy Tech
Search an element in a sorted and infinite array
You are given a sorted and infinite array A and an element K. You need to search for the element K in the array. If found, return the index of the element, else return -1.
