Odd Even Linked List
AfterAcademy Tech
•
21 Aug 2020

Difficulty: Medium
Understanding The Problem
Problem Description
Given a singly linked list, write a program to group all odd nodes together followed by the even nodes.
Problem Note
- Please note here we are talking about the node number and not the value in the nodes.
- You should try to do it in place.
- The program should run in O(n) time complexity.
- The relative order inside both the even and odd groups should remain as it was in the input.
- The first node is considered odd, the second node even, and so on.
Example 1
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Output: 1->3->5->2->4->NULL
Explanation: The first group is of elements at odd position (1,3,5) in the linked list and then the ones at the even position(2,4)
Example 2
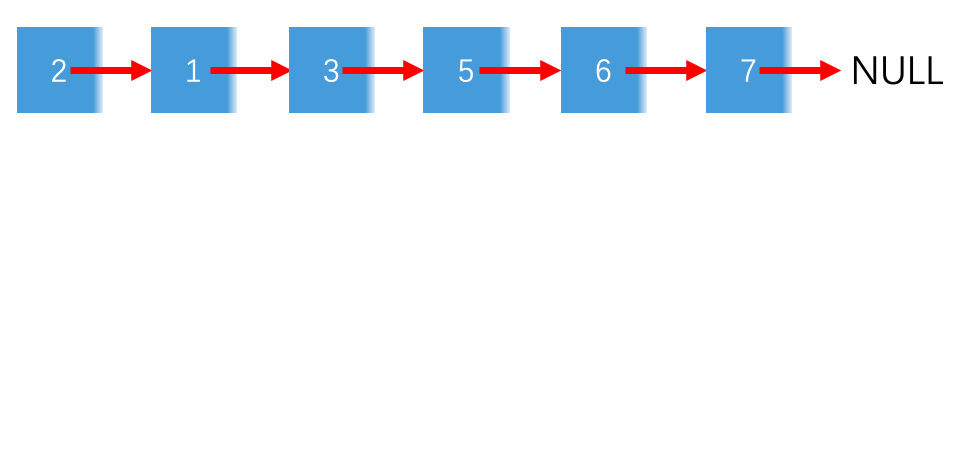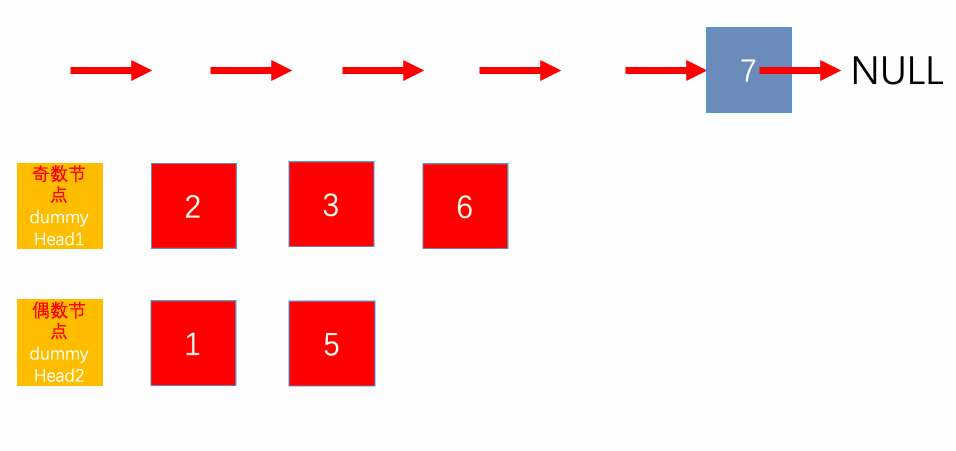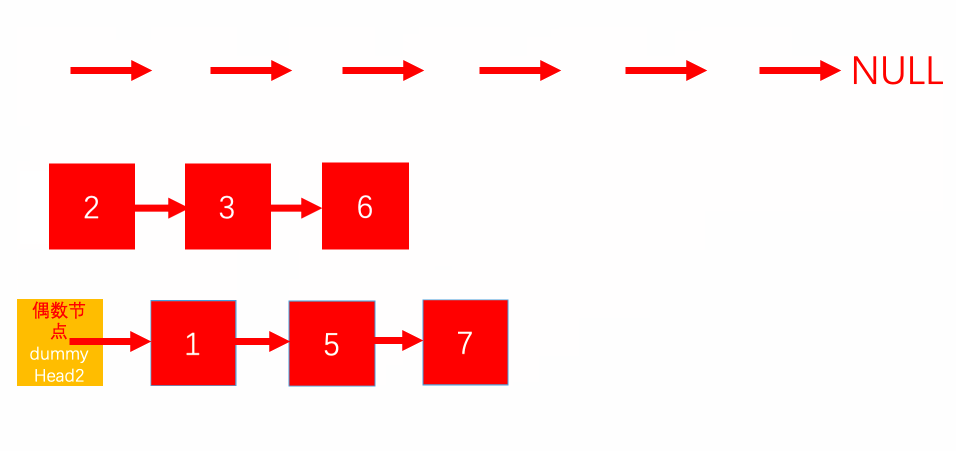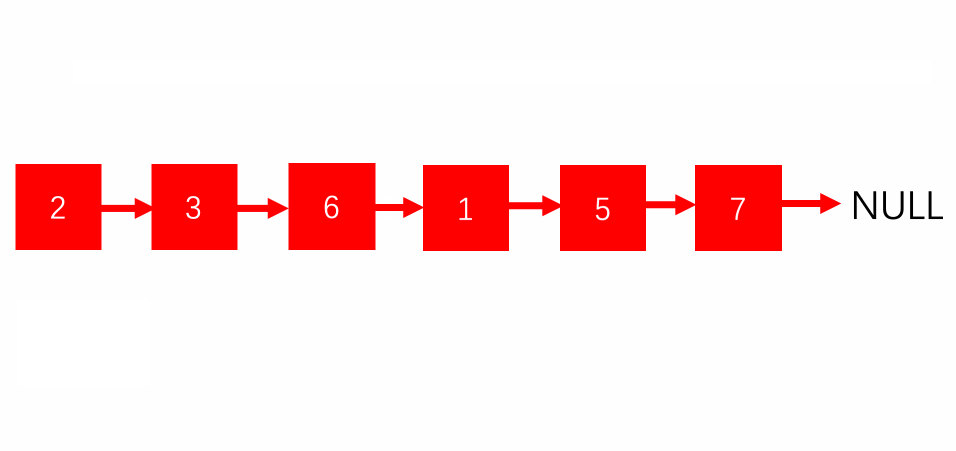
Input: 2->1->3->5->6->4->7->NULL
Output: 2->3->6->7->1->5->4->NULL
Explanation: The first group is of elements at odd position (2,3,6,7) in the linked list and then the ones at the even position(1,5,4)
You should have a clear understanding of a linked list to solve the problem.
You may try to solve this problem here.
Solution
The problem could have various possible solutions in which you can use an auxiliary space to store the numbers in order and recreate a linked list but the question explicitly demands the time complexity to be O(n) and to be solved in-place.
So the basic idea is that we can put all the odd positioned nodes in a linked list and all the even positioned nodes in another linked list, and we can simply join them end to end.
In short, we will have two pointers. The first will point to the head and the second will point to the next of the head. Now in each iteration, each of the pointers will skip one element add the even positioned and odd positioned nodes respectively. This will allow us to use the same linked list and save us from using auxiliary space.
Look at the following diagram of example 1 to get a clear picture of how the linked list is being manipulated.
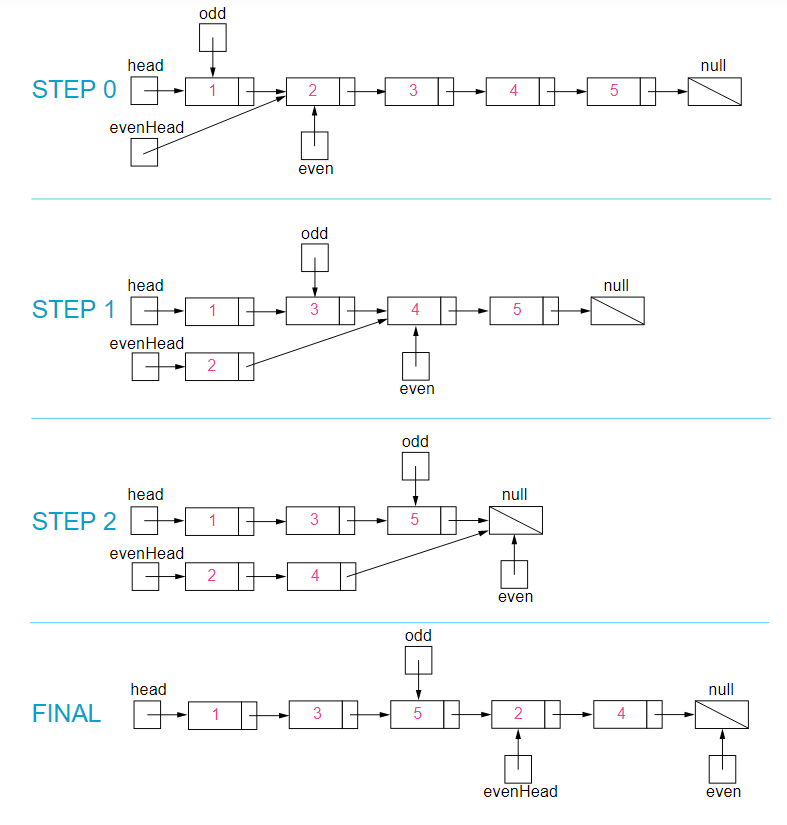
Solution Steps
- Take two pointers oddPointer and evenPointer
and maintain head pointers too. - Now, Do below process until evenPointer becomes null
- Delete one node in the odd list and move two steps forward.
- Delete one node in even list and move two steps forward.
3. Now, merge odd and even lists.
- This can be done by
oddPointer.next = even_head - oddPointer points to the last node in the odd list
- We need to add the even list at the end of the odd list.
4. Return the resultant list.
Pseudo Code
ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {
if(head == nullptr or head->next == nullptr)
return head
ListNode oddPointer = head
ListNode evenPointer = head.next
ListNode even = head.next
while(evenPointer != null and evenPointer.next != null){
oddPointer.next = oddPointer.next.next
oddPointer = oddPointer.next
evenPointer.next = evenPointer.next.next
evenPointer = evenPointer.next
}
oddPointer.next = even
return head
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n) (How?)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical Ideas To Think
- What do
oddPointerandevenPointerrepresent? - Why did we initialize
evenPointerwithhead.next? - We created an
evenvariable to store the head ofevenPointer.How does this help to solve the problem? - The even list has n/2 nodes. Why does the solution have O(1) space complexity? Answer: Since we are not creating any new nodes here, space complexity is O(1). we are just creating three new pointers overall irrespective of the input. So the space remains constant.
- Can we conclude that we are just adding the even nodes at the end of the linked list every time until the original list is over?
Suggested Problems To Solve
- Split the linked list into parts
- Segregate even and odd nodes in a Linked List
- Sum of alternate nodes in a linked list
- Count nodes in a circular linked list.
If you have any more approaches or you find an error/bug in the above solutions, please comment down below.
Happy Coding!
Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Types of Linked List and Operation on Linked List
In this blog, we will discuss the types of linked list and basic operations that can be performed on a linked list.

AfterAcademy Tech
Middle Of The Linked List
Given a non-empty, singly linked list with head node head, write a program to return a middle node of linked list. If there are even nodes, then there would be two middle nodes, we need to print second middle element.
AfterAcademy Tech
Reverse a Linked List
The problem is about reversing a Linked List. We are given the head node of the Linked List and we have to return the reversed Linked List's head. This is an interview problem asked in companies like Microsoft, Amazon and Adobe.

AfterAcademy Tech
Array vs Linked List
Array and Linked List are the two most used data structures. It's really important to understand and compare the advantages and disadvantages of both array and linked list. In this blog, we will compare these two linear data structures. So let's get started.