Middle Of The Linked List
AfterAcademy Tech
•
10 Aug 2020
Difficulty: Easy
Understanding the Problem
Problem Description
Given a non-empty, singly linked list with head node head, write a program to return a middle node of the linked list. If there are even nodes, then there would be two middle nodes, we need to print the second middle element.
Example 1
Input: 11->2->13->44->5
Output: 13
Explanation: The middle element of the linked list is 13.
Example 2
Input: 10->2->34->24->15->60
Output: 24
Explanation: As there are even number of nodes, return 24 as it is the second node among two middle elements.
Solutions
- Two-Pass: Find the length of the linked list and return the (length/2)th node.
- One-Pass: Use two pointers, the 2nd pointer should traverse twice as fast at the first.
Before moving forward with the question, you must understand the properties of a linked list.
You can try this problem here.
1. Two-Pass
The question demands to find the middle of a singly linked list. We can simply find the total length of the linked list, in this way we can identify which node falls in the middle. To find the middle node, we can traverse again until we reach (length/2)th node.
Solution Steps
- Create a pointer
p, pointing to the head. - Iterate over the linked list until
preaches to the end of the linked list, thereby find the length of the list. - Set
pto head again. Now, incrementplength/2times. Now, thepis at the middle of the linked list node. Return the value atp
Pseudo Code
int middleNode(ListNode head) {
int l=0
ListNode p = head
while (p != null) {
p = p.next
l = l + 1
}
p = head
int c = 0
while (c < l/2) {
p = p.next
c = c + 1
}
return p.data
}
Complexity Analysis
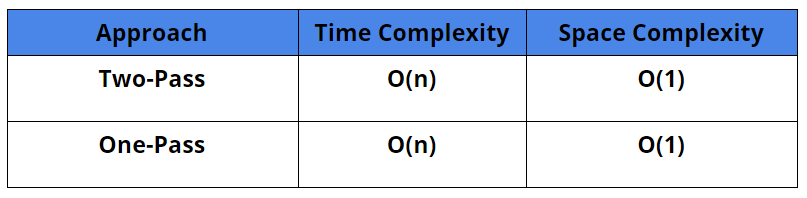
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical Ideas To Think
- Why did we reinitialize
pwith thehead? - Which node will be returned if the length of the linked list is even?
- What if the linked list forms a loop?
2. One-Pass
Another way to solve this problem is to use a little trick. Instead of traversing twice, we can create two-pointers say slow_ptr and fast_ptr.We can make the fast_ptr twice as fast as slow_ptr. So, When the fast_ptr will reach to the end of the linked list, slow_ptr would still be at the middle, thereby pointing to the mid of the linked list.
Solutions Steps
- Create
slow_ptrandfast_ptrpointing to the head initially. - Increment
fast_ptrby2and slow_ptr by1positions untilfast_ptrandfast_ptr.nextis notNULL - Return the value at
slow_ptr.
Pseudo Code
int middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head
ListNode fast = head
while (fast != null and fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
}
return slow.data
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical Ideas To Think
- Why did we use two pointers?
- Why did we iterate until
fast != nullandfast.next != null? - Do both the discussed approaches affect the running time?
Comparison Of Different Approaches
Suggested Problems To Solve
- Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
- Merge Sort on Linked List
- Check if a singly linked list is a palindrome
- Detect and Remove Loop in a Linked List
- Sort a linked list using insertion sort
- Remove Nth Node from List End
Happy coding!
Enjoy Algorithms.
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Types of Linked List and Operation on Linked List
In this blog, we will discuss the types of linked list and basic operations that can be performed on a linked list.

AfterAcademy Tech
Reverse a Linked List
The problem is about reversing a Linked List. We are given the head node of the Linked List and we have to return the reversed Linked List's head. This is an interview problem asked in companies like Microsoft, Amazon and Adobe.

AfterAcademy Tech
Array vs Linked List
Array and Linked List are the two most used data structures. It's really important to understand and compare the advantages and disadvantages of both array and linked list. In this blog, we will compare these two linear data structures. So let's get started.
AfterAcademy Tech
Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
Given a binary tree, flatten it to a linked list in-place. After flattening, the left of each node should point to NULL and right should contain the next node in level order so that it resembles a singly linked list.
