Move all the zeroes to the end - Interview Problem
AfterAcademy Tech
•
12 Nov 2019

Level: Easy
Asked in: Facebook, Uber
Understanding the Problem
Problem Description: Given an array A[] of n elements filled with several integers, some of them being zeroes, you need to move all the zeroes to the end.
For example :
Input: A[] = {1, 8, 3, 0, 2, 0, 1, 10, 13, 0}
Output: {1, 8, 3, 2, 1, 10, 13, 0, 0, 0}
Input: A[] = {0, 3, 5, 9, 0, 0, 23, 2}
Output: {3, 5, 9, 23, 2, 0, 0, 0}
Possible questions to ask the interviewer:-
- Can the array consist of negative integers? (Ans: Sure, that’s a possibility)
- Does the relative order of non-zero integers matter in the resultant array? (Ans: Yes, the relative order of non-zero integers needs to remain the same as in original array)
- What if there are no zeroes in the array? (Ans: Less work for you! )
Brute force and Efficient solutions
We will be discussing three possible solutions for this problem:-
- Brute Force Approach: Using an auxiliary space
- Two Pointer Approach I: In-place using two traversals
- Two Pointer Approach II: In-place using one traversal
1. Brute Force Approach : Using an auxiliary space
We can create an auxiliary array B[] of size n which will be used to store all the non-zero elements as we linearly traverse A[]. Let the number of non-zero elements be x. Now fill the remaining n-x elements with zeroes and return B[].
Pseudo-Code
int[] moveZeroes(int A[], int n)
{
int B[n]
int j = 0
for (i = 0 to n-1)
{
if (A[i] != 0)
{
B[j] = A[i]
j = j + 1
}
}
while (j < n)
{
B[j] = 0
j = j + 1
}
return B
}
Complexity Analysis
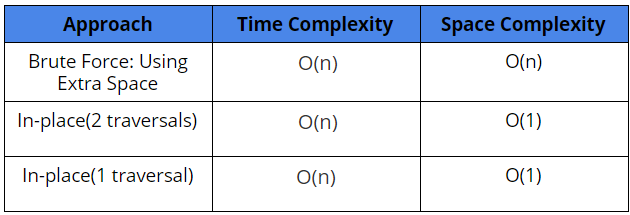
Time Complexity: Filling non-zero elements in B[] + Filling zeroes in B[] = O(n) + O(n) (Why?) = O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n), for storing B[]
Critical ideas to think!
- Can we try and modify this algorithm to make it in-place?
- Is the relative order of non-zero elements maintained in this algorithm?
2. Two pointer approach I: In-place using two traversals
A two-pointer approach could be used for these types of questions. A pointer i to linearly traverse A[] and a pointer j to track the non-zero element. After the whole process, all elements in A[0…j] are non-zero elements.
Solution Steps
- Initialize j = 0.
- Run a for loop from i = 0 to n-1 to traverse A[].
- At any step of iteration, if (A[i] != 0) then update A[j] = A[i] and increment j by 1. Here we are shifting each non-zero element to the start of A[].
- After completing the loop, traverse A[] from j to n-1 and fill it with zeroes. (Think!)
Pseudo-Code
int[] moveZeroes(int A[], int n)
{
int j = 0
for (i = 0 to n-1)
{
if (A[i] != 0)
{
A[j] = A[i]
j = j + 1
}
}
while (j < n)
{
A[j] = 0
j = j + 1
}
return A
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: Traversing A[] for non-zero elements + Traversing A[] again to fill zeroes = O(n) + O(n) = O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical ideas to think!
- Can you optimize the above algorithm so that one does not need to traverse A[] again in the end to fill zeroes?
- How the elements in A[] are stored after first traversal? Try to visualize the steps via an example.
- What other problems could be solved using a similar approach?
3. Two Pointer Approach II : In-place using one traversal
In the above method, every time we encounter a non-zero element, we assign A[j] to A[i]. Instead, if we swap the two elements, we wouldn’t need to fill the rest of the array with zeroes in the end. They will be moved to the end due to swapping. This idea is similar to the partition process in the quick sort.
Solution Steps
- Initialize j = 0.
- Run a for loop from i = 0 to n-1.
- At each iteration, if (A[i] != 0), swap A[j] and A[i] and increment j by 1.
- Return A[].
Pseudo-Code
int[] moveZeroes(int A[], int n)
{
int j = 0
for(i = 0 to n-1)
{
if(A[i]!= 0)
{
swap(A[j], A[i])
j = j + 1
}
}
return A
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: Linear traversal of the array with swap operations = O(n) (Why?)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical ideas to think!
- Could you sort an array containing elements of only two values repeated, again and again, using this approach? What about three values?
- What would be the total swap operation in the worst-case scenario? Compare the number of operations in each approach above.
- Is the relative order of non-zero elements maintained in this algorithm?
Comparison of different solutions
Suggested problems to solve
- Given an array consisting of characters ‘R’, ‘G’ and ‘B’ repeated multiple times shuffled together, sort them by having all ‘R’ at the beginning and all ‘B’ in the end and remaining ‘G’ in the middle
- Remove all instances of element k from array A[] in-place and return the new size of the array
- Find the minimum number of swaps required to sort the array in ascending order.
- Given an array of positive and negative numbers, arrange the array elements so that all negative numbers appear before all positive numbers.
- Given an array of positive and negative numbers, arrange them in an alternate fashion such that every positive number is followed by negative.
- Segregate Even and Odd numbers in an array where all even numbers come first and then odd numbers.
- Given an array of integers greater than zero, find if it is possible to split it into two subarrays such that the sum of the two subarrays is the same.
Please comment down below if you have alternative approaches or find an error/bug in the above approaches.
Happy Coding, Enjoy Algorithms!
AfterAcademy Data Structure And Algorithms Online Course - Admissions Open
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Set Matrix Zeros - Interview Problem
Given a matrix, A of size M x N of 0's and 1's. If an element is 0, set its entire row and column to 0

AfterAcademy Tech
Greatest Common Divisor-Interview Problem
This is a mathematical problem asked in interviews of Google like companies. For solving such problems you need to have some math skills and also some idea of algorithms like Euclid's GCD algorithm.

AfterAcademy Tech
Remove Duplicates in a Sorted Array-Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in companies like Google, Microsoft, Amazon. The problem is to remove duplicates from a sorted array or list.
AfterAcademy Tech
Merge two Binary Trees - Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in companies like Amazon, Microsoft. The problem is to merge two binary trees. The overlapping nodes are replaced by the sum of corresponding nodes. We are discussing two ways of solving this.
