Minimum Cost Path - Interview Problem
AfterAcademy Tech
•
10 Feb 2020

Difficulty: Medium
Asked in: Amazon, Samsung, MakeMyTrip
Understanding the Problem →
Given a M x N matrix with each cell having a value corresponding to the cost. You are also provided with a position say (m,n), your task is to find the minimum cost path from (0,0) to that position. The total cost is calculated by adding the sum of each cell cost used as a path to the destination(including source and destination). Output the minimum cost associated with the path from source to destination. You can traverse from a cell to its adjacent right cell, adjacent down the cell and diagonally lower-right cell.
For example →
Let us analyze a matrix of 4x3
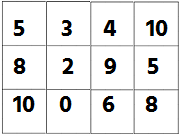
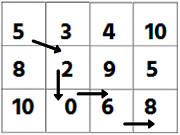
Here it is clear the Minimum Cost Path is 5->2->0->6->8 with cost 21.
Possible follow-up questions to ask→
- Is it possible for the cost to be negative? (Ans: You can assume it to be positive.)
- What if there are more than one minimum cost paths? (Ans: Output any of them.)
Solutions
There can be many possible paths from the source to the destination. However, here we have to choose the path corresponding to the minimum cost. Thus this is an optimization problem.
★ Does this problem follow the greedy choice property? Why or why not?
Approaching the Problem in the right way
- Since it is quite clear that this problem has many different answers possible or there are various ways to reach from the given source to the destination. So to get all possible paths we can use recursion as the path from a particular cell is dependent on the paths from its adjacent cells.
- We are calculating the cost from a cell by calculating the cost of the paths from the adjacent cells. In this process, it is quite obvious that visiting a particular cell can be repeated multiple times. So we can save the cost for the path to destination from a cell already calculated to reduce our calculations and hence time.
- If there is a repetition of the same problems (sub-problems), we can apply Dynamic Programming in such cases. In Dynamic Programming, we save the already calculated value in extra memory for future reference.
Let us first see the recursive solution and analyze it →
1. Recursive Solution
Solution idea
Recursive Solution will use recursion to generate all possible combinations of paths from the given source to destination. Out of all combinations, we will choose the one with the minimum cost associated. Since this is a recursive solution it will create a recursive tree showing all the possible solutions. At any cell, there are three possible options to choose from. For any cell (i,j), we can easily find the cost from this cell to destination if we know the cost of path from (i+1, j) to destination or the cost from the cell (i,j+1) to destination or the cost from the cell(i+1, j+1) to destination.
Solution steps
- We will write the base case(i.e. when the source and the destination both is the same.)
- We will recursively call in all the three adjacent cells to get the cost from those cells.
- We will choose the minimum out of the three costs that we will get from recursion and add the cost of the source cell.
Pseudo-code
int getMinCostPath(int A[M][N], int start_row, int start_col, int end_row, int end_col)
{
if(start_row > end_row or start_col > end_col)
return 0
if(start_row == end_row and start_col == end_col)
return A[start_row][start_col]
//Recursive Calls
int x = getMinCostPath(A, start_row, start_col+1, end_row, end_col)
int y = getMinCostPath(A, start_row+1, start_col, end_row, end_col)
int z = getMinCostPath(A, start_row+1, start_col+1, end_row, end_col)
int minimum = min(x, y, z)
return A[start_row][start_col] + minimum
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: 3^N, where N is the max of M and N (Think!)
Space Complexity: O(N)(Recursive stack space)
Critical ideas to think!
- What do you think about exponential time complexity? Do you think such complexity will work?
- Try drawing the recursion tree of the above program and analyze if there are any repetitive calculations? Do you find anything worth optimizing?
2. Dynamic Programming(Bottom-Up Approach)
Solution idea
Before going for the bottom-up approach let us first see the recursive tree and analyze it for better understanding of sub-problems:
Recursive Tree
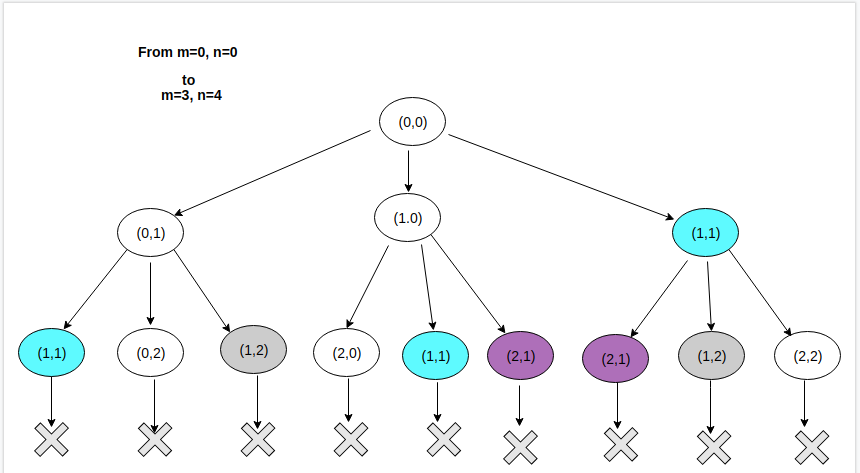
The above tree is for the source S(0,0) and the Destination D(2,3). We can easily see there are various cells for which the cost C is being calculated many times. In order to avoid this redundancy of calculations, we can use some extra memory for storing the result and retrieving it later in O(1) time. This is how we will try improving the efficiency of the above problem.
Elements of Dynamic Programming
- Define problem variables and decide the states: Here the state of the problem is defined by two variables M and N which represents the cell of the matrix. In every recursive call, cost from the three adjacent cells i.e. (M+1, N), (M, N+1), (M+1, N+1) of the corresponding (M, N) cell is recursively calculated.
- Define Table Structure and Size: To store the solutions of smaller sub-problems in the bottom-up approach we need to define the table structure and table size.
- The table structure is defined by the number of problem variables which are participating to define the problem state. Here there are two variables
- M and N, so we need to have a 2-dimensional space for storage.
- The size of this table is defined by the total number of unique calculations involved. If we observe the recursion tree, we can get to know there are at max (M)*(N) calculations. (Think!)
3. Table Initialization: We can initialize our table using the base case from our recursive solution i.e. A[i][j]=0.
4. Iterative Structure to fill the table: We have to define the iterative structure to fill in the table. We can easily derive the iterative structure using the recurrence relation of the recursive solution.
getMinCostPath(M,N) = min(getMinCostPath(M+1, N), getMinCostPath(M,N+1), getMinCostPath(M+1, N+1)) + A[M][N]
5. Termination and returning final output: At any cell A[i][j] we are storing the min path from (i,j) to the destination. Thus, our final output will be stored at cell(0,0). Simply return A[0][0] as final result.
Pseudo-code
int getMinCostPath(int A[M][N], int m, int n)
{
int dp[m][n]
//Fill the last cell that is destination
dp[m-1][n-1] = A[m-1][n-1] //Base Case in recursive solution
//Fill the last row from right to left as their dependencies are
//resolved
for(int j=n-2 to j>=0;j=j-1)
dp[m-1][j] = dp[m-1][j+1] + A[m-1][j]
//Fill the last column (bottom to top)
for(int i=m-2 to i>=0i=i-1)
dp[i][n-1]=dp[i+1][n-1]+input[i][n-1]
//Fill the remaining cells
for(int i=m-2 to i>=0;i=i-1)
for(int j=n-2 to j>=0;j=j-1)
dp[i][j]=min(dp[i+1][j], min(dp[i][j+1], dp[i+1][j+1]))
return dp[0][0]
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(M*N)(Why?)
Space Complexity: O(M*N)(Extra Memory)
Critical ideas to think
- Analyze more why we have started filling the dp matrix from last row(right to left).
- What if you want to save the results in a recursive solution? How would you do that?
- Dry run the filling of the dp table to actually know how the dependencies are being resolved.
Suggested Problems to Solve
- Minimize the cost to fill given weight in a bag.
- Minimum cost to make two strings identical.
- Find the minimum adjustment cost of an array.
- Longest Common Sub-sequence.
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Minimum Absolute Difference in a BST-Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in Google technical interview. Given a BST(Binary Search Tree) with non-negative values, write a program to find the minimum absolute difference between values of any two nodes.

AfterAcademy Tech
Minimum Depth of Binary Tree - Interview Problem
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth. The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.

AfterAcademy Tech
Minimum Coin Change-Interview Problem
This is an interview problem based on the concept of dynamic programming. This question has been asked in various companies. We are dealing with solutions based on recursion, memorization and dynamic programming.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find minimum and maximum value in an array - Interview Problem
Given an array A[] of size n, you need to find the maximum and minimum element present in the array.Your algorithm should make minimum number of comparisons.
