Minimum Coin Change-Interview Problem
AfterAcademy Tech
•
02 Jan 2020

Level: Medium
Asked in: Microsoft, Amazon, Oracle
Understanding the Problem
Given a set C of m coins (different denominations) and an amount say A, for which we have to provide the change with the coins in the set C. The problem is to find out the minimum count of coins required to provide the change of ammount A.
Note: We have infinite supply of each of C = { C1, C2, .. , Cm} valued coins.
Example 1
Input: C[] = [2,3,5,6] , A = 10
Output: 2
Explanation: Possible change for 7 are {2,2,2,2,2},{2,2,3,3}, {2,2,6},{2,3,5} and {5,5}. So output will be 2 where we are using two coin of 5 cents to provide the change.
Example 2
Input: C[] = [1, 2, 3], A = 3
Output: 1
Explanation: Possible change for 3 is {1,1,1},{1,2} and {3}. So output will be 1 where we are using one coin of 3 cents to provide the change.
Possible follow-up questions to ask:
- Does the order of the coins matters? (Ans: No, both {1,2} and {2,1} is considered as same.)
- What if the given amount is 0? (Ans: We will take 0 as it’s solution)
Solution Approach
This is an optimization problem and there can be several ways to provide the change. But we need to provide optimal solution only i.e. min no. of coins required to provide the change. We should think about following ideas when we encounter such problem:
- To find optimal solution among all possible ways to provide the change, we can solve the problem recursively i.e. the solution of the problem using the solution of smaller sub-problems.
- There can be a situation when same sub-problems will be solved several times during the recusion and the time complexity of the solution will be of exponential order.
- If both the above observations are correct then we can apply the idea of Dynamic Programming for the solution i.e. time memory tradeoff where we solve the sub-problems only once and store it in extra memory.
Lets move forward step by step and build the recursive solution first.
1. Recursive Solution
For building the recursive solution, initial available choices are important. In this problem, we have m choices to pick the coin in the start i.e. we can pick any coin among m coins. (Think!)
Lets say minCoin(A) represents the minimum number of coins required to make change of amount A. Here are the diiferent smaller sub-problems based on our different initial choices:
- If we select 1st coin in the start (value = C[0]), Now smaller problem is minimum number of coins required to make change of amount (A - C[0]) i.e minCoin(A - C[0]).
- If we select 2nd coin in the start (value = C[1]), Now smaller problem is minimum number of coins required to make change of amount (A - C[1]) i.e. minCoin(A - C[1]).
- Likewise to up to m coin, If we select mth coin in the start (value = C[m-1]), Now smaller problem is minimum number of coins required to make change of amount (A - C[m-1]) i.e. minCoin(A - C[m-1]).
We need to find the minimum number of coins required to make change for A amount, so whichever sub-problem provide the change using the minimum number of coins, we shall add 1 to it (because we have selected one coin) and return the value. Here smaller sub-problems will be solved recursively.
Note: Before selecting any coin, make sure whether value of the coin is less than equal to amount needed i.e. C[i] <= A (Think!)
Base Case
If A == 0, then 0 coins required.
Recursive Structure
If A > 0
minCoin(A) = min { 1 + minCoin(A - C[i]) }
where i varies from 0 to m-1 and C[i] <= A
Pseudo Code
int minCoin(int C[], int m, int A)
{
if(A == 0)
return 0
int min = INT_MAX
for(int i = 0 to m-1)
{
if(C[i] <= A)
{
int curr_min = minCoin(C, m, A-C[i])
if(curr_min != INT_MAX && curr_min + 1 < min)
min = curr_min + 1
}
}
return min
}
Complexity Analysis
Every coin has 2 options, to be selected or not selected. So,
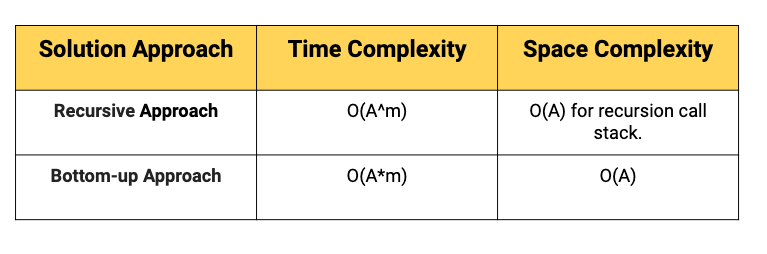
Time Complexity = O(A^m), where m is the number of coins given (Think!)
Space Complexity: O(A) for the recursion call stack.
Critical idea to think!
- Why recursive solution is exponenetial time? Analyse the above recursive code using the recursion tree method.
- Have you noticed any overlapping problems? What if we store the solution of sub-problems, will it help? Think about the top-down approach to solve this problem.
2. Bottom-up Approach of Dynamic Programming
When we draw the recursion tree of the above problem for say A=5 and C ={1,2,3}, the tree comes up with same sub-problems again and again (Look at the below tree, here the colored eclipse is shown for such sub-problems). If we increase the amount A and draw the recursion tree, the number of overlapping problems will also increase.
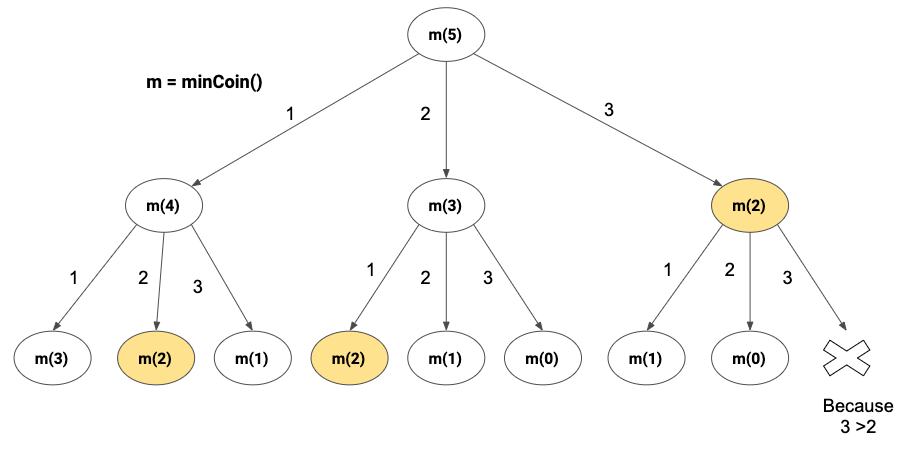
Since it is clear now that this problem has overlapping subproblems, we will see how to improve the performance and solve it using the bottom-up approach of dynamic programming.
Elements of Dynamic Programming
1. Define problem variables and decide the states : There is only one parameter on which the state of the problem depends i.e. which is A here. In the recursive solution, the value of A is decreasing after every recursive call.
2. Define Table Structure and Size: To store the solution of smaller sub-problems in bottom-up approach, we need to define the table structure and table size.
- The table structure is defined by the number of problem variables. Since the number of problem variables, in this case is A i.e. only one, we can construct a one-dimensional array to store the solution of the sub-problems.
- The size of this table is defined by the total number of different subproblems. If we observe the recursion tree, there can be total (A+1) different sub-problems for providing the change for ammount A . (Think!)
3. Table Initialization: We can initialize the table by using the base cases from the recursion. coinChange[0] = 0
4. Iterative Structure to fill the table: We can define the iterative structure to fill the table by using the recurrence relation of the recursive solution.
coinChange[i] = min { 1 + coinChange[i - C[i]) }
where i varies from 0 to m-1 and C[i] <= A
5. Termination and returning final solution: After filling the table in the bottom-up manner, our final solution gets stored at the last Index of the array i.e. return coinChange[A].
Pseudo-code
int minCoin(int C[], int m, int A)
{
int coinChange[A+1]
// Table Initialization or base case
coinChange[0] = 0
// Initialize all table values
for(int i= 1 to A)
coinChange[i] = INT_MAX
// Calculate minimum coins required
for(int i= 1 to A)
{
// Go through all coins smaller than ammount i
for(int j= 0 to m-1)
{
if(C[j] <= i)
{
int curr_min = coinChange[i- C[j]]
if(sub_res != INT_MAX && curr_min + 1 < coinChange[i])
coinChange[i] = curr_min + 1
}
}
}
return coinChange[A]
}
Complexity Analysis
There is two nested loop in the code. The first loop is iterating from 1 to n and the second is iterating from 1 to k. Time Complexity = O(A*m), where m is the number of coins. (Think!)
Space Complexity = O(A)
Critical ideas to think
- Do we require the entire array of size equal to amount or we can optimize the space? Think about the case when the amount is too high.
- How can we modify the code to find the coins which are the part of the optimal solution?
- Think about the problems which can solved using the similar idea.
Comparison of different solutions
Suggested Problems to Solve
- Find the number of ways in which you can change an amount with given coins of different denominations.
- Greedy Algorithm to find minimum coin count.
- Rod Cutting Problem
- 0-1 Knapsack Problem
- Weighted Job Scheduling
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Minimum Absolute Difference in a BST-Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in Google technical interview. Given a BST(Binary Search Tree) with non-negative values, write a program to find the minimum absolute difference between values of any two nodes.

AfterAcademy Tech
Minimum Cost Path - Interview Problem
This is a famous interview problem based on dynamic Programming. This question has been asked in big companies like Amazon. Here we need to find the path between the given source and destination that gives the minimum cost.

AfterAcademy Tech
Minimum Depth of Binary Tree - Interview Problem
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth. The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find minimum and maximum value in an array - Interview Problem
Given an array A[] of size n, you need to find the maximum and minimum element present in the array.Your algorithm should make minimum number of comparisons.
