Linked List and its Properties
AfterAcademy Tech
•
10 Feb 2020

A linked list is a linear data structure as well as a dynamic data structure. A Linked list consists of nodes where each node contains a data field(to store some data values) and a reference to the next node in the list.
Properties of Linked List
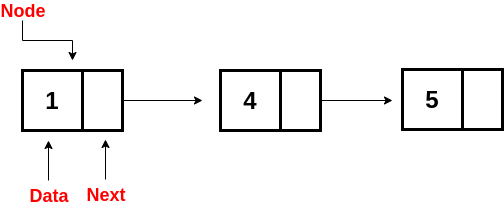
- It can be visualized as a chain of nodes where each node contains the location of the next node. You can see this in the diagram given below:
- The structure of the node is
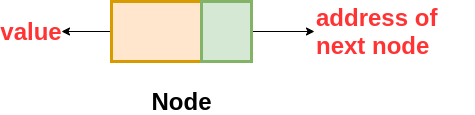
class Node{
int val // variable storing the data of each node
Node next // variable storing the address of the next blog
}
- The first node of the linked list is called the head of the linked list. Through head, we can perform different operations on the linked list. In every linked list question, we will be given the reference of the head node of the linked list.
- The last node of the linked list is pointing to NULL(None) which indicates that it is the last node.
- Unlike arrays, linked list elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations.
- Linked Lists addresses some of the limitations of arrays of having a fixed size because Linked Lists are dynamic in nature.
Advantages and Disadvantage of Linked list
PROS
- They are dynamic in nature which allocates the memory when required.
- Insertion and deletion operations can be easily implemented.
CONS
- The memory is wasted as pointers require extra memory for storage.
- No element can be accessed randomly, it has to access each node sequentially i.e. proper traversal must be done.
- Reverse Traversing is difficult in the linked list(though we can achieve this with the help of Doubly Linked List).
Applications of Linked Lists
- Linked lists are used to implement stacks, queues, graphs, etc.
- Any application which has to deal with an unknown number of objects will need to use a linked list.
Critical Concepts to explore in Linked List
Suggested Problems to solve in Linked List
- Reverse linked list
- Middle of the Linked List
- Odd even linked List
- Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
- Merge Sort on Linked List
- Check if a singly linked list is palindrome
- Detect and Remove Loop in a Linked List
- Sort a linked list using insertion sort
- Remove Nth Node from List End
Happy coding! Enjoy Algorithms.
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Types of Linked List and Operation on Linked List
In this blog, we will discuss the types of linked list and basic operations that can be performed on a linked list.

AfterAcademy Tech
Reverse a Linked List
The problem is about reversing a Linked List. We are given the head node of the Linked List and we have to return the reversed Linked List's head. This is an interview problem asked in companies like Microsoft, Amazon and Adobe.

AfterAcademy Tech
Middle Of The Linked List
Given a non-empty, singly linked list with head node head, write a program to return a middle node of linked list. If there are even nodes, then there would be two middle nodes, we need to print second middle element.
AfterAcademy Tech
Array vs Linked List
Array and Linked List are the two most used data structures. It's really important to understand and compare the advantages and disadvantages of both array and linked list. In this blog, we will compare these two linear data structures. So let's get started.