Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List
AfterAcademy Tech
•
24 Dec 2019

Asked in: Amazon, Microsoft, Adobe
Difficulty: Medium
Understanding the Problem
Problem Description: Given a binary tree, flatten it to a linked list in-place. After flattening, the left of each node should point to NULL and right should contain the next node in pre-order so that it resembles a singly linked list.
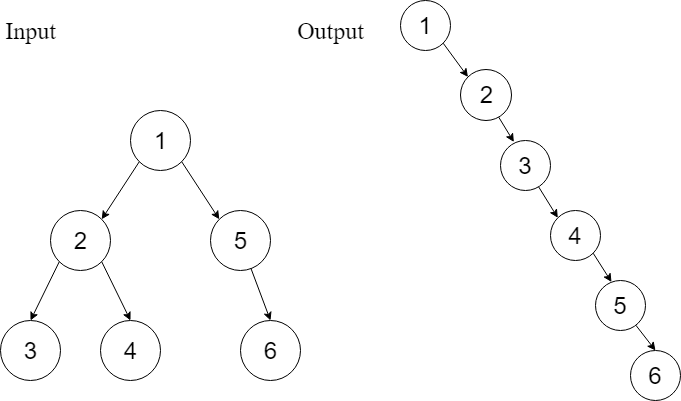
Example 1
Example 2
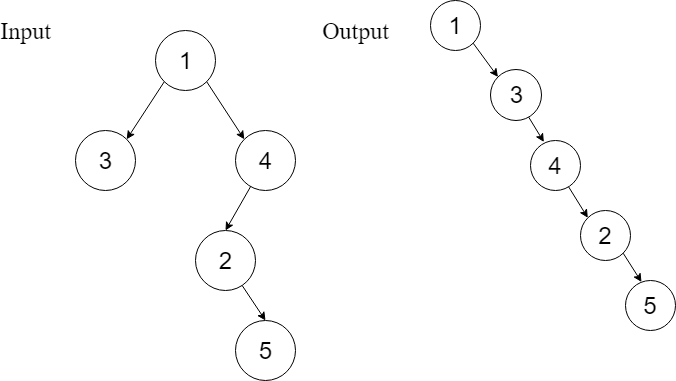
By looking at the example shown, it is very obvious that the head of the output linked list is the root of the tree node, followed by a flattened left subtree, which is followed by a flattened right subtree.
The node structure passed to your function will be
class TreeNode
{
int data
TreeNode left
TreeNode right
}
Possible follow up questions to ask the interviewer —
- Can I use extra space? (Ans: You can but try to optimize if possible.)
- What to return if we are given an empty tree? (Ans: Just return null in this case.)
Hint → If you notice carefully in the flattened tree, each node’s right child points to the next node of a pre-order traversal.
Solutions
We will see three different approaches to solve this problem →
- Reverse preorder traversal— Recursively flatten the right and left children and concatenate them.
- Iterative using Stack — Find the right-most leaf of the current left subtree, and append the subtree there.
- Iterative without using auxiliary space— use while-loop to find the right-most leaf of the current left subtree and append it to the root’s right.
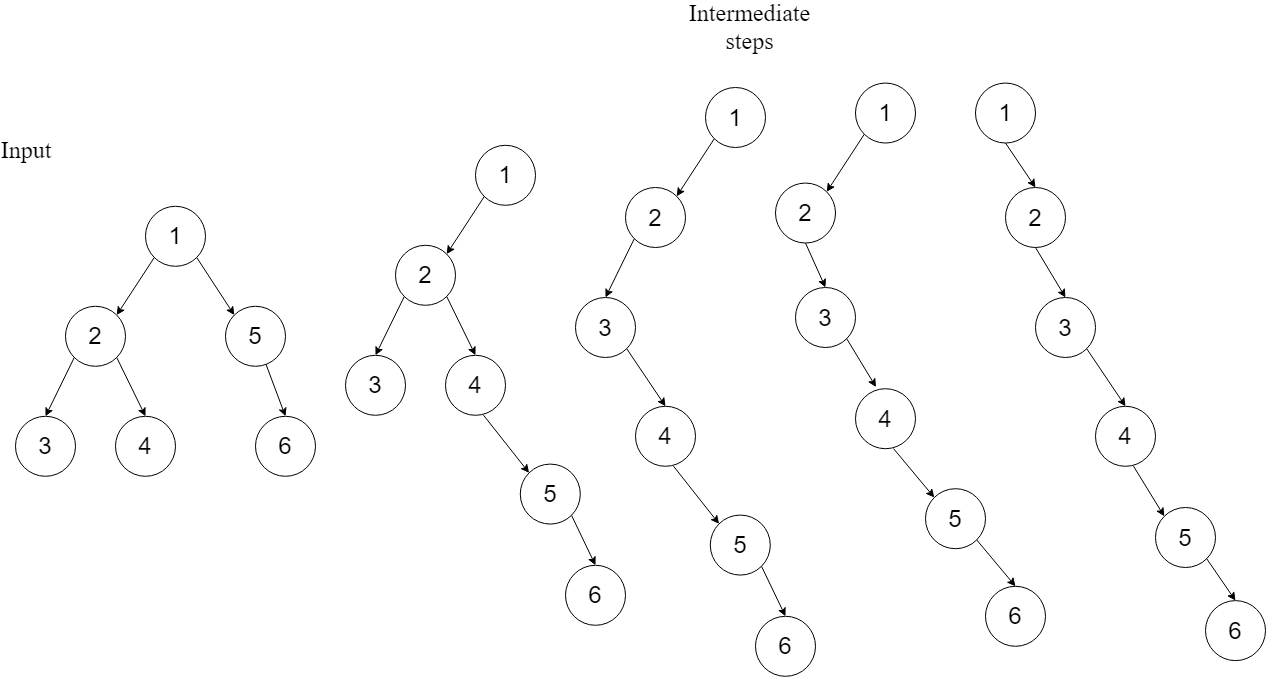
1. Reverse Preorder traversal
If you observe how the tree gets flatten then it is clear that for each subtree’s root node
- Root’s left tree became the right tree
- New right tree’s rightmost node points to root’s right tree
Solution steps —
- Process right sub-tree
- Process left sub-tree
- Process root
- Make the left node as a right node of the root
- Set right node as a right node of the new right sub-tree
- Set left node to NULL
Pseudo Code
void flatten(TreeNode root)
{
// reference temporary variable
TreeNode temp = {0, NULL, NULL}
reverse_preorder(root, temp);
delete temp
}
void reverse_preorder(TreeNode root, TreeNode &temp)
{
if(root is NULL)
return
// process right sub-tree
reverse_preorder(root.right, temp)
// process left sub-tree
reverse_preorder(root.left, temp)
// set the right child of root with the left flattened tree
root.right = temp
// set the left child with null
root.left = NULL
// set the temp variable with the current node
temp = root
}
Complexity analysis
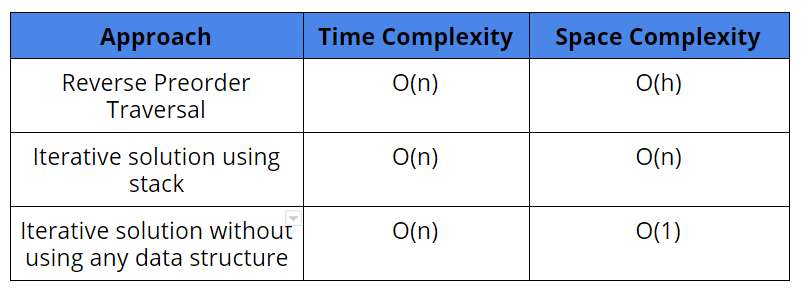
Time Complexity: O(n) Each node is visited exactly once and the operation performed on each node is of constant time.
Space Complexity: O(h), where h is the height of the tree
Critical ideas to think
- Why we used a reversed preorder approach instead of preorder?
- Why the temporary TreeNode is passed in reference?
- How did we set the right child of root with the left flattened tree?
2. Iterative Solution using Stack
The recursive solution could be solved iteratively using stack where at any instant the top of the stack will represent the root of a subtree.
Solution steps —
- Check if the root is not NULL
- Create a stack and push the root node to it and iterative the below steps until the stack is empty
- pop the top node from the stack
- push its right child and then its left child
- peek the top node and set it to the right of the popped node
- set the popped node’s left child as NULL
Pseudo Code
void flatten(TreeNode root)
{
if(root is NULL)
return
stack S
S.push(root)
while(S is not empty)
{
TreeNode subroot = S.pop()
if(subroot.right)
S.push(subroot.right)
if(subroot.left)
S.push(subroot.left)
if(S is not empty)
subroot.right = S.peek()
subroot.left = null
}
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
Critical ideas to think
- Why do we check if the stack is empty or not before assigning value to subroot.right?
- Does this approach seem analogous to any famous approach?
- Why do we push the right child and then the left child to the stack?
- Can we optimize the space complexity in the iterative solution?
3. Iterative Without using any other data structure
Each time when we prune a right subtree, we use a while-loop to find the right-most leaf of the current left subtree and append the subtree there.
Pseudo Code
void flatten(TreeNode root)
{
TreeNode cur = root
while (cur != null)
{
if (cur.left != null)
{
// if we need to prune a right subtree
if (cur.right != null)
{
TreeNode next = cur.left
while (next.right != null)
next = next.right
next.right = cur.right
}
cur.right = cur.left
cur.left = null
}
cur = cur.right
}
}
Complexity Analysis
Visit each node at most twice (one for flattening and one for looking for rightmost leaf) and then for each node, cut the right tree and append it to its rightmost node. Overall, access to each node is in constant time.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical ideas to think
- If there exists both the left and right child of the root, then how did we handled the right child?
- How the time complexity is of O(n)?
Comparison of different approaches
Suggested Problems to solve
- Flatten binary tree in order of zig-zag traversal.
- Convert binary tree to a doubly-linked list.
- Convert a binary tree to a circular doubly linked list.
- Flatten a multilevel linked list.
Any feedback or suggestions are welcome in the comment section.
Happy Coding!! Enjoy Algorithms.
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Types of Linked List and Operation on Linked List
In this blog, we will discuss the types of linked list and basic operations that can be performed on a linked list.

AfterAcademy Tech
Reverse a Linked List
The problem is about reversing a Linked List. We are given the head node of the Linked List and we have to return the reversed Linked List's head. This is an interview problem asked in companies like Microsoft, Amazon and Adobe.

AfterAcademy Tech
Invert a Binary Tree - Interview Problem
Given a binary tree, invert the binary tree and return it. An inverted form of a Binary Tree is another Binary Tree with left and right children of all non-leaf nodes interchanged. You may also call it the mirror of the input tree.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find Diameter of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, you need to compute the length of the diameter of the tree. The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two nodes in a tree. This path may or may not pass through the root.
