Climbing Stairs - Interview Problem
AfterAcademy Tech
•
20 Dec 2019

Level: Medium
Asked in: Amazon, Intel, Morgan Stanley, LinkedIn, Snapdeal
Understanding the Problem
Problem Description: There is a staircase of N steps and you can climb either 1 or 2 steps at a time. You need to count and return the total number of unique ways to climb the staircase. The order of steps taken matters.
For Example,
Input: N = 3
Output: 3
Explanation: There are 3 unique ways of climbing a staircase of 3 steps :{1,1,1}, {2,1} and {1,2}
Input: N = 5
Output: 8
Explanation: There are 8 unique ways of climbing a staircase of 5 steps: {1,1,1,1,1}, {1,1,1,2}, {1,1,2,1}, {1,2,1,1}, {2,1,1,1}, {1,2,2}, {2,1,2}, {2,2,1}
Possible questions to ask the interviewer:-
- Do I need to return the order of steps taken as well? (Ans: No, just count and return the total number of unique ways)
- How many unique ways exist if N = 0? (Ans: Conventionally, we assume that as 1)
- Are {1,1,2} and {1,2,1} considered unique or same? The order of steps if different but numbers are the same. (Ans: Yes, these two will be considered unique)
Brute force and efficient solutions
We will be discussing three possible solutions for this problem:-
- Recursive Solution (Brute force approach): Retrieving answer for current step using answers of previous smaller steps
- The Bottom-up approach of Dynamic Programming: Using the concept of memoization to avoid recalculation of the subproblems
- Matrix Exponentiation: A mathematical technique to achieve the result in O(logn) time
1. Recursive Solution (Brute force approach)
Solution Idea
If you see carefully, the answer for N = 1,2,3,4,5 … form a pattern.
For N=1, answer = 1 For N=2, answer = 2
For N=3, answer = 3 For N=4, answer = 5
For N=5, answer = 8 For N=6, answer = 13
{1,2,3,5,8,13} -> This is a Fibonacci sequence.It is not just a coincidence that the answers to the climbing stair problem form a Fibonacci sequence. Why?
If you want to reach the nth step in the staircase, what will be your last second step? If would be either the (n-1)th step or the (n-2)th step, because you can jump only 1 or 2 steps at a time.
Total number of ways to reach nth stair = Total number of ways to reach (n-1)th stair + Total number of ways to reach (n-2)th stair
climbStairs(n) = clinmStairs(n-1) + climbStairs(n-2)
This is also the relation followed by the Fibonacci sequence. Now that we know that our solution follows a Fibonacci sequence and we have a defined recursive relation, we just need to figure out the termination case or base case, i.e., when will the recursion end?
The recursion can end if N becomes 0 or 1, the answer in which case will be 1.
Pseudo-code
int climbStairs(int N)
{
if ( N < 2 )
return 1
else
return climbStairs(N-1) + climbStairs(N-2)
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(2^n) (Think)
Space Complexity: O(n), for recursion stack space
Critical ideas to think
- Are you able to notice the overlapping subproblems?
- How would you modify this recursion if you could take upto k steps at a time?
- Think about the top-down approach to solve this problem.
2. Bottom-up approach of Dynamic Programming
If we create a recursion tree for the above approach, we can notice clearly that there are overlapping subproblems.
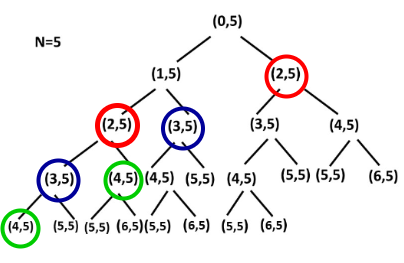
Since overlapping subproblems are present in this scenario and it has optimal substructure property, we could optimize our algorithm using dynamic programming. We could store the results of the already computed subproblems and then retrieve their results in O(1) instead of calculating again.
Elements of Dynamic Programming
Since we have determined that this is a dynamic programming problem, we now need to address some fundamental elements for the implementation using the bottom-up approach of dynamic programming:
1. Define problem variables and decide the states : There is only one parameter on which the state of the problem depends i.e. which is N here.
2. Define Table Structure and Size: To store the solution of smaller sub-problems in bottom-up approach, we need to define the table structure and table size.
- The table structure is defined by the number of problem variables. Since the number of problem variables, in this case, is 1, we can construct a one-dimensional array to store the solution of the sub-problems.
- The size of this table is defined by the number of subproblems. There are a total of (N+1) subproblems for N stairs since we are considering the 0th step as well for our convenience.
3. Table Initialization: We can initialize the table by using the base cases from the recursion. (Think)
- steps[0] = 1
- steps[1] = 1
4. Iterative Structure to fill the table: We can define the iterative structure to fill the table by using the recurrence relation of the recursive solution.
steps[i] = steps[i-1] + steps[i-2]
5. Termination and returning final solution: After filling the table in a bottom-up manner, our final solution gets stored at the last Index of the array i.e. return steps[N].
Solution Steps
- Create a 1D array steps[] of size N+1.
- Assign values for base cases: steps[0] = 1, steps[1] = 1
- Run a for loop from i=2 to N and fill the table
- steps[i] = steps[i-1] + steps[i-2]
4. Return value stored at steps[N].
Pseudo-Code
int climbStairs(int N)
{
int steps[N+1]
steps[0] = 1
steps[1] = 1
for (i = 2 to N)
steps[i] = steps[i-1] + steps[i-2]
return steps[N]
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
Critical ideas to think!
- What if you could take up to k steps at a time? How would the algorithm be modified?
- Can you improve the space complexity here? (Hint: You do not need to use the entire array steps[] at any point, just the last two elements.)
- What if the order of steps you take didn’t matter? {1,1,2}, {1,2,1} and {2,1,1} will be counted as one solution, how will the solution change in this case?
3. Matrix Exponentiation
Matrix Exponentiation is a special technique that is used to find the nth number of a series with a linear recurrence relation in O(logn) time. Since we noticed above that the pattern of numbers follows the Fibonacci sequence, we could apply this technique here.
Solution Steps
- Create the basic 2x2 matrix
mat[2][2] = { {1,1}, {1,0} }
2. Create a function power() which optimally raises a matrix to a power k using a helper function multiply() which multiplies two matrices.
- The trick used here is that mat^N = ( mat^(N/2) ) * ( mat^(N/2) )
3. Store the answer received by power(mat, N) in ans.
4. Return ans[0][0].
Pseudo-Code
int multiply(int A[2][2], int B[2][2])
{
int ans[2][2]
for( i = 0 to 2 )
{
for ( j = 0 to 2 )
{
ans[i][j] = 0
for( k = 0 to 2 )
ans[i][j] += A[i][k] * B[k][j]
}
}
return ans
}
int power(int mat[2][2], int N)
{
if ( N == 0 )
{
int temp[2][2] = { {1,0}, {0,1} }
return temp
}
int half[2][2] = power(M, N/2)
int ans[2][2] = multiply(half,half)
if ( N % 2 == 0 )
ans = multiply(ans, mat)
return ans
}
int climbStairs(int N)
{
int mat[2][2] = { {1,1}, {1,0} }
int ans[2][2] = power(mat,N)
return ans[0][0]
}
Complexity Analysis
Since its only a 2x2 matrix, the time complexity of matrix multiplication is considered to be O(1) and multiply() has been called a total of logN times plus once more if N is odd.
Time Complexity: O(logN) * O(1) = O(logN)
Space Complexity: O(logN)
Critical ideas to think!
- What other kinds of problems have answers as sequences having linear recurrence relations where we can apply this matrix exponentiation technique?
- Can this technique be applied in other variants of this problem, like taking up to k steps at a time?
Comparison between different solutions

Suggested Problems to solve
- Find the number of ways to climb N stairs by taking at most k leaps
- Write a program to find the Nth Fibonacci Number
- Write a program to count the number of ways to reach the nth stair using steps 1 , 2 or 3.
- Consider a game where a player can score 3 or 5 or 10 points in a move. Given a total score n, write a program to find the number of ways to reach the given score.
- Given N, write a program to count the number of ways to express N as a sum of 1, 3 and 4.
- Write a program to count all palindromic subsequence in a given string.
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
AfterAcademy Data Structure And Algorithms Online Course — Admissions Open
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Greatest Common Divisor-Interview Problem
This is a mathematical problem asked in interviews of Google like companies. For solving such problems you need to have some math skills and also some idea of algorithms like Euclid's GCD algorithm.

AfterAcademy Tech
Remove Duplicates in a Sorted Array-Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in companies like Google, Microsoft, Amazon. The problem is to remove duplicates from a sorted array or list.
AfterAcademy Tech
Merge two Binary Trees - Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in companies like Amazon, Microsoft. The problem is to merge two binary trees. The overlapping nodes are replaced by the sum of corresponding nodes. We are discussing two ways of solving this.

AfterAcademy Tech
Minimum Absolute Difference in a BST-Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in Google technical interview. Given a BST(Binary Search Tree) with non-negative values, write a program to find the minimum absolute difference between values of any two nodes.
