Check if two strings are anagrams of each other - Interview Problem
AfterAcademy Tech
•
08 Oct 2019

Level: Medium
Asked in: Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Goldman Sachs
Understanding the Problem
Problem Description: Given two strings S1 and S2 of size m and n respectively, you need to check whether the two strings are an anagram of each other or not. S1 is an anagram of S2 if the characters of S1 can be rearranged to form S2.
For Example:
Input: S1 = “admirer” , S2 = “married”
Output: True
Input: S1 = “mindorks”, S2 = “orks”
Output: False
Possible follow up questions to ask the interviewer:-
- Can the string contain duplicate characters? (Ans: Yes)
- What is the range of characters in input strings? (Ans: lowercase English characters)
- Is the size of both strings equal? (Ans: Not necessarily)
Solutions
We will be discussing three possible approaches to this problem:-
- Brute Force: Using nested loops
- Using Sorting: Sort both strings and compare characters at each index
- Using Hashing: Count occurrences of each character in S1 and S2 and compare
1. Brute Force: Using Nested Loops
Iterate over S1 and search for each character in S2. If any character is not found, return false. To avoid bugs due to duplicate characters, we need to mark found characters in S2 so that multiple duplicate characters in S1 do not correspond to the character in the same index in S2.
Pseudo-Code
bool checkAnagram(string S1, int m, string S2, int n)
{
if ( m != n )
return False
for ( i = 0 to m-1 )
{
// search() returns index if element exists, else returns -1
int index = linear_search(S2, n, S1[i])
if ( index == -1 )
return False
else
S2[index] = '\0'
}
return True
}
Complexity Analysis
For each element in S1, we perform a linear search in S2 for that element.
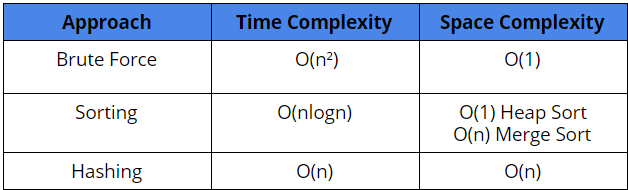
Time Complexity: n*O(n) = O(n²)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical ideas to think!
- Why are found characters in S2 assigned with a null character?
- Why do m and n need to be equal?
- How can you increase the efficiency of the search operation in S2?
2. Using Sorting
Since we just need to check the frequency of characters, we can sort both the strings so that all letters in both strings are ordered for easy comparison.
Pseudo-Code
bool checkAnagram(string S1, int m, string S2, int n)
{
if ( m != n )
return False
sort(S1, m)
sort(S2, n)
for ( i = 0 to n-1 )
if ( S1[i] != S2[i] )
return False
return True
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity = Sorting two strings + Linear Traversal of strings
= 2 * O(nlogn) + O(n) = O(nlogn)
Space Complexity = If we use merge sort, then O(n), else if we use heap sort, its O(1).
Critical ideas to think!
- Do we need to sort both strings or sorting just one would do the trick?
- Does sorting leave anomalies for duplicate characters?
- Can we improve the time complexity of sorting given that the string consists of only lowercase characters?
3. Using Hashing
Since we just need to compare the frequency of characters in both strings, we could create a HashMap for both strings storing the count of characters as value. We can then compare the HashMaps of the two strings with a single traversal to check for the anagram.
Pseudo-Code
bool checkAnagram(string S1, int m, string S2, int n)
{
if ( m != n )
return False
Create two HashMap hash1 and hash2 of size n
for ( i = 0 to n-1 )
hash1[S1[i]] = hash1[S1[i]] + 1
for ( i = 0 to n-1 )
hash2[S2[i]] = hash2[S2[i]] + 1
for ( i = 0 to n-1 )
{
if ( hash1[S1[i]] != hash2[S1[i]] )
return False
}
return True
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity = Adding characters of two strings to HashMap + Traversing the HashMap
= 2* O(n) + O(n) = O(n)
Space Complexity = 2* O(n) = O(n) for storing the HashMap
Critical ideas to think!
- Can this algorithm be implemented using only one HashMap in order to save some space?
- Can space complexity be further optimized without compromising the time complexity?
- What other data structures can be used in the place of HashMap in this algorithm?
Comparison of different solutions
Suggested Problems you could solve
- Find the minimum number of characters that need to be removed to make two strings anagrams
- Given a list of strings, return all groups of strings that are anagrams
- Check if any anagram of a given string is a palindrome or not
- Given a list of elements with each element occurring even no. of times except one, find the element with odd frequency
- Given a string, sort it in decreasing order based on the frequency of characters.
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Merge two Binary Trees - Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in companies like Amazon, Microsoft. The problem is to merge two binary trees. The overlapping nodes are replaced by the sum of corresponding nodes. We are discussing two ways of solving this.

AfterAcademy Tech
Add Two Numbers as Lists - Interview Problem
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.

AfterAcademy Tech
Check if the Singly Linked List is a Palindrome-Interview Problem
Given a Linked List, your task is to find whether the given singly linked list is a palindrome or not. This is an interview problem asked in many companies like Amazon, Microsoft, Adobe, Flipkart and other big companies.
AfterAcademy Tech
Check If Two Arrays Are Equal Or Not
Given two given arrays of equal length, Check if given arrays are equal or not. This is a tricky interview problem as, at first, this looks like problem-related to combinatorics but could be solved quickly upon thinking.
