Binary Tree Zig Zag Level Order Traversal
AfterAcademy Tech
•
04 May 2020

Difficulty: Medium
Asked in: Amazon, Microsoft
Understanding the Problem
Given a binary tree, return the zigzag level order traversal of its nodes’ values. (i.e, from left to right, then right to left for the next level and alternate between).
Example
Input: Given binary tree [5,8,2,null,null,6,4]
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
Output: Return its zigzag level order traversal as:
[
[3],
[20,9],
[15,7]
]
The node structure passed to your function will be
class TreeNode
{
int val
TreeNode left
TreeNode right
}
Solutions
- Recursive Depth-first search approach: Make a DFS search from the root and for even levels reverse the list values at that level.
- Iterative Level Order Traversal approach: Follow an iterative Level order traversal and for each level, poll the visited element from the Queue maintaining a boolean flag to toggle traversals.
You may try to solve this problem here.
1. Recursive Depth-First Search(DFS) Approach
If you will think about the problem, you will realize that this problem is basically a preorder or postorder traversal with the only difference that for each level, the traversal toggles between left to right and right to left.
However, the problems require to return a two-dimensional array that will contain the zig-zag traversal of the tree in a level order fashion.
So, We could create a res array and make a DFS or preorder tree traversal, while passing another argument called level. If the level is even, then we will add the root value in the res array in the end of the res[level] otherwise, at the beginning of res[level]. To reduce the time complexity of shifting, we can use an array of a doubly linked list and before returning, convert all the doubly linked lists into an array.
Example:
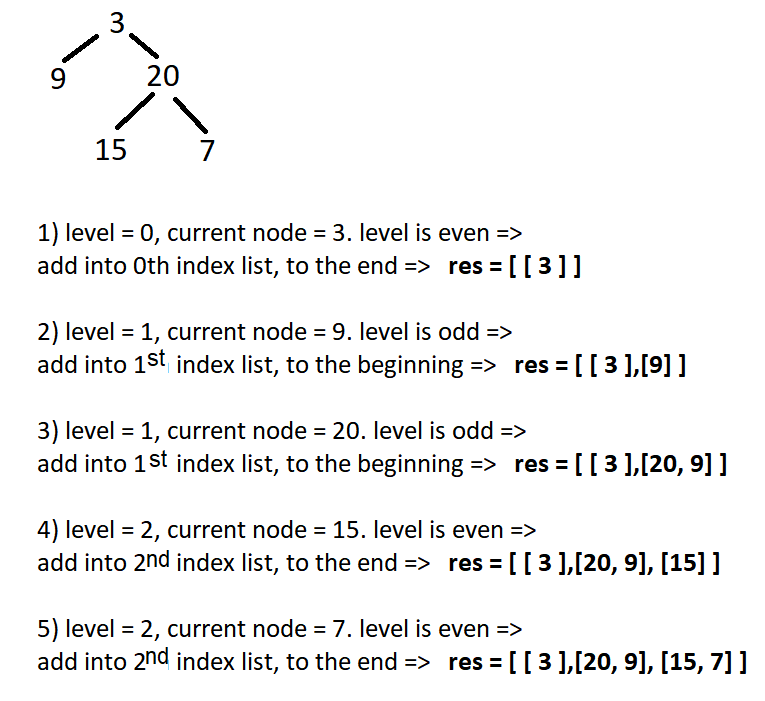
Solution step
- Create an array of lists (this will be our output)
- Call recursively DFS function that adds current node value to the output by level.
- In your recursive call, use the level of this node in the tree as an argument.
- If it’s even → Insert into the end of the list with
index = level - if it’s odd → Insert into the beginning of list with
index = level
int[][] zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
int[][] res
zigzagLevelOrder(root, res, 0)
return res
}
void zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root, int[][] res, int level) {
if (root is not null){
if (res.size() <= level)
res.append([])
if (level%2==0)
res[level].append(root.val) // Inserts at the end of the list
else
res[level].insert(0, root.val) // Inserts at the beginning of the list
zigzagLevelOrder(root.left, res, level+1)
zigzagLevelOrder(root.right, res, level+1)
}
}
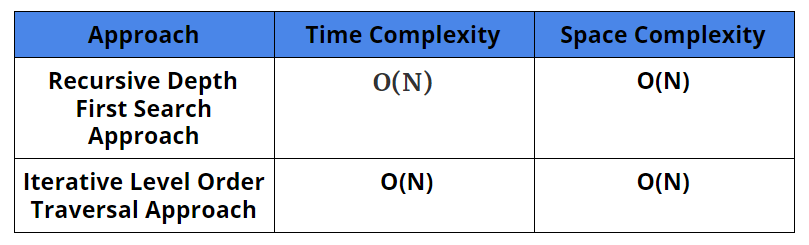
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n), the space complexity is the height of the tree, which in worst-case is n.
Critical Ideas to Think
- How did we toggle from left to right and right to left traversal on each level?
- Do you think that this algorithm could also be implemented by using postorder or inorder traversal? How?
- How does the algorithm work if at any level there is only one node available? Check using a sample test case.
2. Iterative Level Order Traversal Approach
Solution steps
- A better idea for ZigZag Level Order Traversal is the Breadth-First Approach that we use in a Level Order Traversal. Add a root node to Queue.
- Iterate until the contents of the queue become empty.
- Reset the
levellist on each level to a new array. On each level, pop the last visited element from the Queue. - A boolean
flagcould be useful that will help in toggle between the left to right and right to left traversal in the tree. A generalization could be for left to right traversal,flagis false, in which case simply add the polled node’s value to thelevellist, used for tracking the list of values on each particular level and vice versa. - Once a visited node’s value has been added to
levellist, explore it’s children if they exist. - If the entire level of nodes has been visited, add the level list to the final result list. Toggle
flagto achieve zig zag level order traversing. Continue to iterate the aforementioned steps until the queue is completely empty.
Pseudo Code
int[][] zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
int[][] res
if(root is null)
return res
//declare queue
Queue(TreeNode) queue
queue.add(root)
boolean zigzag = false
while( queue is not Empty) {
//declare level list and size from q
int[] level
int size = queue.size()
for (int i = 0 to i < size) {
//poll from q
TreeNode node = queue.pop()
if (zigzag) {
level.add(0, node.val)
} else {
level.add(node.val)
}
if (node.left is not null) {
queue.add(node.left)
}
if (node.right is not null) {
queue.add(node.right)
}
}
res.add(level)
zigzag = !zigzag
}
return res
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
Critical Ideas to Think
- Why we are iterating in the inner for loop till the size of the queue?
- What does the statement
zigzag = !zigzagdoes? - What is the use of
levelarray?
Comparison of Solutions
Suggested Problems to Solve
- Iterative Post Order Binary tree Traversal
- Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
- Binary Tree Spiral Traversal
- Flatten Binary Tree in Level Order Traversal
If you have any more approaches or you find an error/bug in the above solutions, please comment down below.
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Average of Levels in Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, write a program to return the average value of the nodes on each level in the form of an array. The range of the node's value is in the range of 32-bit signed integer.

AfterAcademy Tech
How to traverse in a tree?
It is important to know traversal techniques in a tree before solving tree problems. We have discussed the 3 primary traversals in a tree at length in this blog with both recursive and iterative implementations.

AfterAcademy Tech
Path Sum In Binary Tree
Given a binary tree and a sum, write a program to determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals the given sum.Its an easy problem based on Binary tree traversal and a famous interview question

AfterAcademy Tech
Invert a Binary Tree - Interview Problem
Given a binary tree, invert the binary tree and return it. An inverted form of a Binary Tree is another Binary Tree with left and right children of all non-leaf nodes interchanged. You may also call it the mirror of the input tree.
