Remove Duplicates from an unsorted arrray
AfterAcademy Tech
•
21 Oct 2019

Difficulty Level: Medium
Asked in: Amazon, Google, Microsoft
Understanding the Problem
Problem Description: An unsorted array A[] consisting of n elements is given and we need to remove all the duplicate elements from the array. All the elements in the final array must be unique and the order of elements does not matter.
For example,
Input: A[] = { 2, 3, 1, 9, 3, 1, 3, 9 }
Output: { 2, 3, 1, 9 }
Input: A[] = { 4, 3, 9, 2, 4, 1, 10, 89, 34}
Output: { 3, 4, 9, 2, 1, 10, 34, 89}
Possible questions to ask the interviewer:-
- Can negative elements be present in the array? (Ans: Yes, sure)
- Can the elements in the resultant array be in sorted order irrespective of their order in the original array? (Ans: Yes, that’s allowed)
- Does the algorithm need to be in-place? (Ans: No, it doesn’t need to be in-place)
Brute force and efficient Solutions
We will be discussing 5 possible approach to solve this problem:-
- Brute Force approach I: Using 3 nested loops
- Brute Force approach II: Using 2 nested loops
- Sorting approach I: Using extra space
- Sorting approach II: Using constant extra space
- Using Hash-Table
1. Brute Force approach I : Using 3 nested loops
To remove duplicates, first, we need to find them. The idea is to iterate over array A[] till the end, find the duplicates and remove it. How will we maintain the loop variable if we keep on deleting elements?(Think!)
Pseudo-Code
int[] removeDuplicates(int A[], int n)
{
int i = 0
while (i < n)
{
int j = i + 1
while (j < n)
{
if (A[i] == A[j])
{
// Shifting elements one to the left,
// hence, deleting element at pos j
for (k = j to n-2)
A[k] = A[k+1]
n = n-1
}
else
j = j + 1
}
i = i + 1
}
// Reduce the size of array A to now accomodate only initial n elements.
// Here you are required to perform the resize operation any way you see fit according to the language you choose
A.resize(n)
return A
}
Complexity Analysis
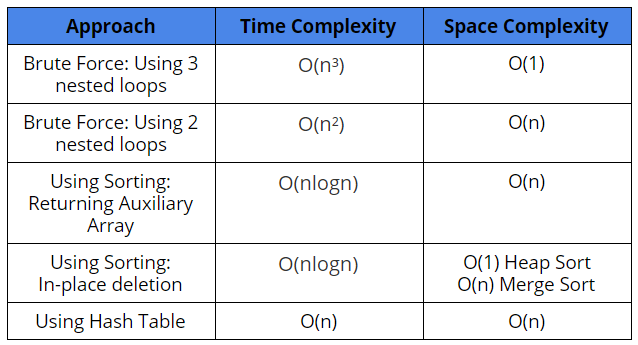
Time Complexity: O(n³) (Why?)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical ideas to think!
- Why is j incremented only when A[i] != A[j] ?
- Deleting a duplicate element in the above approach took O(n) time in the worst-case. How could we optimize the deletion further?
- Why are we resizing array A[] in the end?
- How we solve this if the input is provided in the form of a linked list instead of an array?
2. Brute Force approach II: Using 2 nested loops
We could use an auxiliary array to store the non-duplicates and return the auxiliary array. But how will we know which elements are non-duplicates now? (Think!)
Well, one way is to use another auxiliary array, a boolean array. At every corresponding index for each element, True will mean that the element is unique and False will mean that its a duplicate.
Pseudo-Code
int[] removeDuplicates(int A[], int n)
{
int ans[]
boolean mark[n]
// We can initialize the boolean array mark[n] by True
// assuming that all elements are unique
for (i = 0 to n-1)
mark[i] = True
for (i = 0 to n-1)
{
if (mark[i] == True)
{
for(j = i+1 to n-1)
if (A[i] == A[j])
mark[j] = False
}
}
for(i = 0 to n-1)
if (mark[i] == True)
ans.insert(A[i])
return ans
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: Updating the boolean array mark[] + Inserting non-duplicates in the array ans[] = O(n²) + O(n) = O(n²)
Space Complexity: Extra space of mark[] array + Extra space of ans[] array = O(n) + O(n) = O(n)
Critical ideas to think!
- We just increased your space complexity to reduce your time complexity. This is known as a time-space tradeoff. Where and how is it useful?
- Is the order of the unique elements in the ans[] array the same as the original array?
3. Sorting approach I: Using extra space
If we sort the array, all the duplicate elements line up next to each other and it's easier to find them. We could again delete duplicate elements by shifting or just use a new resultant array similar to the above approach. Do we need a boolean array now? (Think!)
Pseudo-Code
int[] removeDuplicates(int A[], int n)
{
sort(A,n)
int ans[]
int i = 0
while (i < n)
{
ans.insert(A[i])
while (A[i] == A[i+1])
i = i + 1
i = i + 1
}
return ans
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: Sorting the array + Linear traversal of array
= O(nlogn) + O(n) = O(nlogn)
Space Complexity: Storing resultant array + Auxiliary space used by sorting = O(n) + ( O(n), if you use merge sort, else if you use heap sort, O(1) ) = O(n)
Critical ideas to think!
- can we improve the space complexity further?
4. Sorting approach II: Using constant extra space
Earlier, We created an ans[] array that contained the unique elements, but this increased our space complexity. Now we can solve this by manipulating the original array itself to store the unique elements. Here we resize the original array in the end to accommodate only the unique elements.
Pseudo-Code
int[] removeDuplicates(int A[], int n)
{
sort(A,n)
int i = 0, j = 0
while (i < n)
{
A[j] = A[i]
while (A[i] == A[i+1])
i = i + 1
i = i + 1
j = j + 1
}
// Reducing the size of array A to now accomodate only initial j-1 elements. Here you are required to perform the resize operation any way you see fit according to the language you choose
A.resize(j-1)
return A
}
Complexity Analysis
Time complexity = O(nlogn)
Space complexity = O(1) in the case of heapsort and O(n) in case of merge sort.
Critical ideas to think!
- What is the purpose of the inner while loop?
- How many times is each element visited in this algorithm?
- What would be the time and space-complexity if you try deletion by shifting elements one to the left?
- What are some other ways of checking if an element is already present in the array?
4. Using Hash Table
To solve this problem more efficiently, We can use the Hash Table to check duplicate elements in the array. Hash Table performs searching and Insertion efficiently in O(1) average.
Solution steps
- Create an ans[] array to store unique elements
- Create a Hash Table of size n and keep on storing elements in the Hash Table. Before inserting a new element in the hash table, just check if it already exists in the hash table.
- If it does, the current element is duplicate and you need to ignore it.
- Otherwise, the current element is unique, then store it in ans[] array.
4. End of the whole process, return ans[] array.
Pseudo-Code
int[] removeDuplicates(int A[], int n)
{
Create a HashTable H
int ans[]
for(i = 0 to n-1)
{
if(A[i] not in H)
{
ans.insert(A[i])
H.insert(A[i])
}
}
return ans
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: Traversing the array + Searching element in Hash Table + Inserting elements into ans[] array and Hash Table
= O(n) + O(n) + O(n) = O(n)
Space Complexity: Storing Hash Table + Storing ans array
= O(n) + O(n) = O(n)
Critical ideas to think!
- Is the order of elements in ans[] array the same as in the original array?
- Are there some other data structures you could use to solve this problem?
Comparison of different solutions
Suggested Problems to solve
- Recursively remove adjacent duplicates from an array
- Given an array of random numbers, Push all the zero's of a given array to the end of the array.
- Remove duplicates from a given string
- Remove duplicates from an unsorted linked list.
- Find the intersection of two unsorted arrays
- Remove duplicates from an array of size n which contains elements from 0 to n-1
Please write comments if you find any error or bug. Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Remove Duplicates in a Sorted Array-Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in companies like Google, Microsoft, Amazon. The problem is to remove duplicates from a sorted array or list.
AfterAcademy Tech
Remove Duplicates From a Sorted Linked List-Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked by companies like Myntra, Visa, Oracle, Adobe, etc. The problem is to remove the duplicate nodes from the given Linked List so that only unique nodes(with unique data values) are present.

AfterAcademy Tech
Remove Nth Node From End of List
You are given a linked list, write a program to remove the nth node from the end of the list and return the head. This problem has been previously asked in Google and Amazon and requires the understanding of the linked list to solve it.

AfterAcademy Tech
Detect and Remove Loop In A Linked List
You are given the head of a linked list which probably contains a loop. If the list contains a loop, you need to find the last node of the list which points to one of its previous nodes to create a loop and make it point to NULL, thereby removing the loop.