What is Virtual Memory and how is it implemented?
AfterAcademy Tech
•
09 Nov 2019
We all know that a process is divided into various pages and these pages are used during the execution of the process. The whole process is stored in the secondary memory. But to make the execution of a process faster, we use the main memory of the system and store the process pages into it. But there is a limitation with the main memory. We have limited space and less space in the main memory. So, what if the size of the process is larger than the size of the main memory? Here, the concept of Virtual Memory comes into play.
Virtual Memory is a way of using the secondary memory in such a way that it feels like we are using the main memory.
So, the benefit of using the Virtual Memory is that if we are having some program that is larger than the size of the main memory then instead of loading all the pages we load some important pages.
In general, when we execute a program, then the entire program is not required to be loaded fully in the main memory. This is because only a few portions of the program are being executed at a time. For example, the error handling part of any program is called only when there is some error and we know that the error happens rarely. So, why to load this part of the program in the main memory and fill the memory space? Another example can be a large-sized array. Generally, we have over-sized arrays because we reserve the space for worst-case scenarios. But in reality, only a small part of the array is used regularly. So, why to put the whole array in the main memory?
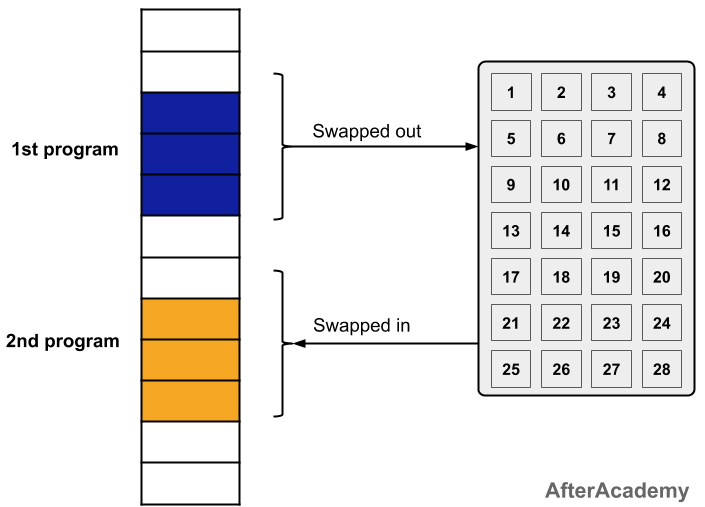
So, what we do is we put the frequently used pages of the program in the main memory and this will result in fast execution of the program because whenever those pages will be needed then it will be served from the main memory only. Other pages are still in the secondary memory. Now, if some request to the page that is not in the main memory comes, then this situation is called a Page Miss or Page Fault. In this situation, we remove one page from the main memory and load the desired page from the secondary memory to the main memory at the run time i.e swapping of pages will be performed here. By doing so, the user feels like he/she is having a lot of memory in its system but in reality, we are just putting that part of the process in the memory that is frequently used. The following figure shows the working in brief:
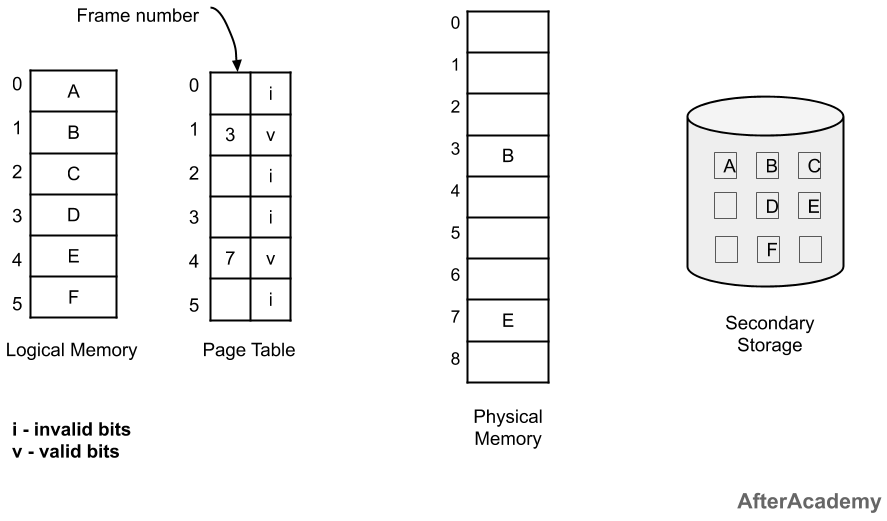
In the above image, we can see that the whole process is divided into 6 pages and out of these 6 pages, 2 pages are frequently used and due to this, these 2 pages are put into the physical memory. If there is some request for the pages present in the physical memory, then it is directly served otherwise if the page is not present in the physical memory then it is called a page fault and whenever page fault occurs, then we load the demanded page in the memory and this process is known as Demand Paging.
Demand Paging
Whenever a page fault occurs, then the process of loading the page into the memory is called demand paging. So, in demand paging, we load the process only when we need it. Initially, when a process comes into execution, then at that time only those pages are loaded which are required for initial execution of the process and no other pages are loaded. But with time, when there is a need for other pages, then the CPU will find that page from the secondary memory and load that page in the main memory.
Following are the steps involved in demand paging:
- The CPU first tries to find the requested page in the main memory and if it is found then it will be provided immediately otherwise an interrupt is generated that indicates memory access fault.
- Now, the process is sent to the blocked/waiting state because, for the execution of the process, we need to find the required page from the secondary memory.
- The logical address of the process will be converted to the physical address because without having the physical address, you can't locate the page in secondary memory.
- Now, we apply some page replacement algorithms that can be used to swap the pages from the main memory to secondary memory and vice-versa.
- Finally, the page table will be updated with the removal of the address of the old page and the addition of the address of the new page.
- At last, the CPU provides the page to the process and the process comes to the running state from the waiting/block state.
So, in this way, we can implement the concept of Virtual Memory with the help of Demand Paging.
That's it for this blog. Hope you enjoyed this blog.
Do share this blog with your friends to spread the knowledge. Visit our YouTube channel for more content.
Keep Learning 🙂
Team AfterAcademy!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
LRU Cache Implementation
Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used(LRU) cache. Your data structure must support two operations: get(key) and put(). The problem expects a constant time solution

AfterAcademy Tech
Implement Queue Using Stack-Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked in companies like Microsoft, Amazon, Adobe, Flipkart, etc. Here, we need to implement Queue data structure using another data structure Stack. This problem is meant for testing the data structure knowledge.

Janishar Ali
Implement JSON Web Token (JWT) Authentication using AccessToken and RefreshToken
Implement JSON Web Token (JWT) Authentication using AccessToken and RefreshToken In this blog, we will learn about the concepts of JsonWebToken (JWT) based authentication in Node.js. We will also cover all the edge cases of the security involved in token handling.
AfterAcademy Tech
What are the operations implemented in tree and what are its applications?
Tree Data Structure supports various operations such as insertion, deletion and searching of elements along with few others. This blogs discussed those operations along with explaining its applications.