What is RIP(Routing Information Protocol)?
AfterAcademy Tech
•
10 Feb 2020
Have you ever imagined how you can access the servers in America from India? How are they connected? Our systems are connected to the routers which in turn is connected to many other routers which eventually are connected to the servers. So whenever we want to access any server, the link between our computer and server is established through these routers only. But how the routers are selected so that the distance between our computer and the server is minimum? This is what RIP does. It selects the shortest path between the computer and the remote server. Now, let's get down to the nitty and gritty of the RIP and discuss it in more detail.
RIP
It is a vector routing protocol that uses the hop count as the routing unit for finding the most suitable path between the source and the destination. Now, let us understand the meaning of the terms used in the definition of RIP.
Vector Routing Protocol
In a vector routing protocol, the routers interchange the network accessibility information with the nearest neighbours. They interchange the information of the set of destinations that they can reach and the next-hop address to which the data packet should be sent so that the data reaches the destination.
Hop Count
Hop count is the number of routers that are between the source and the destination in a network. RIP considers the path with the shortest number of hops as the best path to a remote network hence placed in the routing table. RIP allows only 15 hops to reach any network. If the packet does not reach the destination in 15 hop counts then the destination is considered as unreachable.
Routing Table
Every RIP router maintains a routing table. These tables store the information of all the destinations that the router knows it can reach. Each router interchange the information of their routing table to their nearest neighbours. The routers broadcast the routing table information every 30 seconds to their closest neighbours.
Example: If you are the user and you want to reach google.com. There can be many paths through which you can reach the server of Google. In the example below, the user has three paths. RIP will count the number of routers required to reach the destination server from each route. Then it would select that route that has a minimum number of paths.
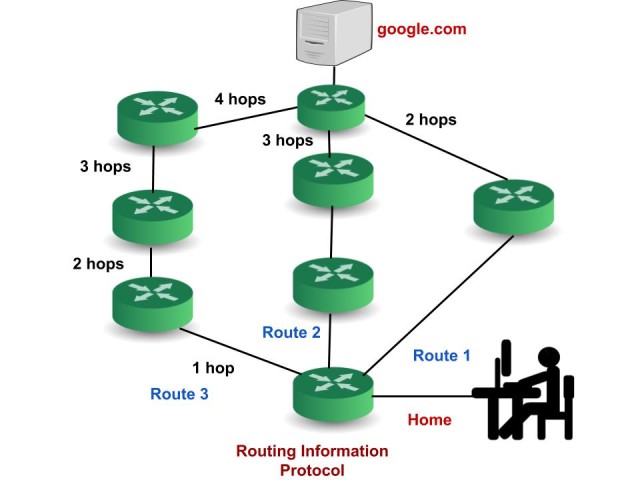
The route 1 has 2 hop counts, route 2 has 3 hop counts and route 3 has 4 hop counts to reach the destination server. So, the RIP will choose Route 1.
We can trace the route of the data packet and know about the router that comes in its path before it reaches the destination. Open the Command Prompt and type → “tracert google.com” (without double quotes) to see the path the data packets would take i.e. the routers that are between your computer and the destination server of google.
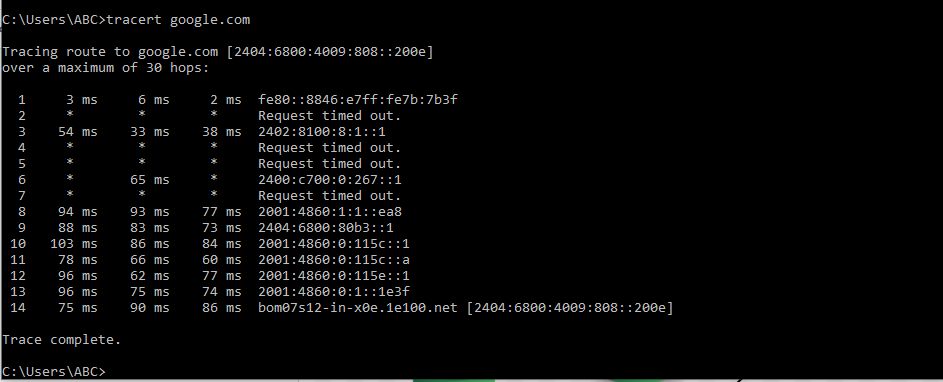
There is a total of 14 hops i.e. the data packet has to go through these routers in order to reach google.com.
Request Timed Out means that the server doesn't respond to the request for the information.
RIP timers
- Update Timers: All the routers configured with RIP send their update(a complete copy of their routing table) every 30 seconds to the neighbouring routers.
- Invalid Timers: If any router gets disconnected from the network then the nearing routers wait for 180 seconds for the update. When it doesn't hear the update until 180 seconds then it will put it into hold-down.
- Hold-Down Timer: Hold-downs ensure that regular update messages do not inappropriately cause a routing loop( A routing loop is a serious network problem in which the data packets continue to be routed within the network in an endless circle). The router doesn’t act on new information(of routing table which it receives after every 30 seconds) for a certain period of time. It is 180 seconds by default.
- Flush Timer: RIP will wait for an additional 60 seconds(total=180+60 =240 seconds) after the route has been declared invalid. Even now if it doesn't hear any update then it removes the route from the routing table.
Versions of RIP
- RIPv1(Routing Information Protocol version 1): It is also called a classful routing protocol because it does not send the information of the subnet mask in the routing update. The routing update is sent as a broadcast( at 255.255.255.255) to every station on the attached network.
- RIPv2(Routing Information Protocol version 2): It is a classless routing protocol because it does send the information of the subnet mask in its routing updates. RIPv2 sends the routing table as multicast (at 224.0.0.9)to reduce the network traffic.
- RIPng(Routing Information Protocol next generation): It is an extended version of RIPV2 that was made to support IPv6. RIPng sends the routing table as multicast (at FF02::9).
Advantages of RIP
- It is easy to configure.
- that it does not require an update every time the topology of network changes.
- Guaranteed to support almost all routers
Disadvantages of RIP
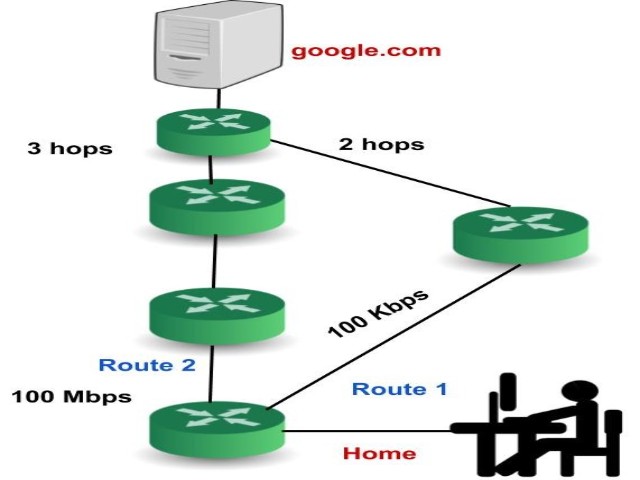
- It is only based on hop count. So, if there is a better route available with better bandwidth then it will not select that route.
Example: Suppose we have two routes, the first route has a bandwidth of 100 Kbps(Kilobits per second) and is there is high traffic in this route whereas the second route has a bandwidth of 100 Mbps (Megabits per second) and is free. Now the RIP will select route 1 though it has high traffic its bandwidth is much less than the bandwidth of route 2. This is one of the biggest disadvantages of RIP.
- Bandwidth utilization in RIP is very high as it broadcasts its updates every 30 seconds.
- RIP supports only 15 hop count so a maximum of 16 routers can be configured in RIP.
- Here the convergence rate is slow. It means that when any link goes down it takes a lot of time to choose alternate routes.
This is all about RIP. Hope you enjoyed reading this blog.
Do share this blog with your friends to spread the knowledge. Visit our YouTube channel for more content. You can read more blogs from here.
Keep Learning 🙂
Team AfterAcademy!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
What are Protocols and what are the key elements of protocols?
In this blog, we will learn about Protocols. We will also learn about the types, key elements, and functionalities of protocols used in computer network and data communication.
AfterAcademy Tech
What are ICMP and IGMP protocols?
In this blog, we will learn about what is ICMP protocols and various messages involved with this protocol. We will also discuss the IGMP protocol of the TCP/IP and various versions of this protocol.
AfterAcademy Tech
What is Stop and Wait protocol?
In this blog, we will learn one of the flow control method i.e Stop and Wait Protocol. We will discuss various situations that can occur while transmitting the data. We will also mathematically derive the efficiency and the throughput of this protocol.

AfterAcademy Tech
What is ARP and how does it work?
In this blog, we will learn what is Address Resolution Protocol and how it helps in communication between two devices. We will also discuss what are the problems that can arise while using this protocol and see sample examples of ARP packets which are captured.
