What is Process Synchronization in Operating System?
AfterAcademy Tech
•
13 Nov 2019
In the Operating System, there are a number of processes present in a particular state. At the same time, we have a limited amount of resources present, so those resources need to be shared among various processes. But you should make sure that no two processes are using the same resource at the same time because this may lead to data inconsistency. So, synchronization of process should be there in the Operating System. These processes that are sharing resources between each other are called Cooperative Processes and the processes whose execution does not affect the execution of other processes are called Independent Processes.
In this blog, we will learn about Process Synchronization in Operating System. We will learn the two important concepts that are related to process synchronization i.e. Race Condition and Critical Section. So, let's get started.
Race Condition
In an Operating System, we have a number of processes and these processes require a number of resources. Now, think of a situation where we have two processes and these processes are using the same variable "a". They are reading the variable and then updating the value of the variable and finally writing the data in the memory.
SomeProcess(){
...
read(a) //instruction 1
a = a + 5 //instruction 2
write(a) //instruction 3
...
}
In the above, you can see that a process after doing some operations will have to read the value of "a", then increment the value of "a" by 5 and at last write the value of "a" in the memory. Now, we have two processes P1 and P2 that needs to be executed. Let's take the following two cases and also assume that the value of "a" is 10 initially.
- In this case, process P1 will be executed fully (i.e. all the three instructions) and after that, the process P2 will be executed. So, the process P1 will first read the value of "a" to be 10 and then increment the value by 5 and make it to 15. Lastly, this value will be updated in the memory. So, the current value of "a" is 15. Now, the process P2 will read the value i.e. 15, increment with 5(15+5 = 20) and finally write it to the memory i.e. the new value of "a" is 20. Here, in this case, the final value of "a" is 20.
- In this case, let's assume that the process P1 starts executing. So, it reads the value of "a" from the memory and that value is 10(initial value of "a" is taken to be 10). Now, at this time, context switching happens between process P1 and P2(learn more about context switching from here). Now, P2 will be in the running state and P1 will be in the waiting state and the context of the P1 process will be saved. As the process P1 didn't change the value of "a", so, P2 will also read the value of "a" to be 10. It will then increment the value of "a" by 5 and make it to 15 and then save it to the memory. After the execution of the process P2, the process P1 will be resumed and the context of the P1 will be read. So, the process P1 is having the value of "a" as 10(because P1 has already executed the instruction 1). It will then increment the value of "a" by 5 and write the final value of "a" in the memory i.e. a = 15. Here, the final value of "a" is 15.
In the above two cases, after the execution of the two processes P1 and P2, the final value of "a" is different i.e. in 1st case it is 20 and in 2nd case, it is 15. What's the reason behind this?
The processes are using the same resource here i.e. the variable "a". In the first approach, the process P1 executes first and then the process P2 starts executing. But in the second case, the process P1 was stopped after executing one instruction and after that the process P2 starts executing. And here both the processes are dealing on the same resource i.e. variable "a" at the same time.
Here, the order of execution of processes changes the output. All these processes are in a race to say that their output is correct. This is called a race condition.
Critical Section
The code in the above part is accessed by all the process and this can lead to data inconsistency. So, this code should be placed in the critical section. The critical section code can be accessed by only one process at a time and no other process can access that critical section code. All the shared variables or resources are placed in the critical section that can lead to data inconsistency.
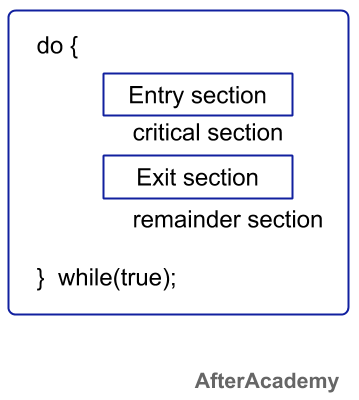
All the Critical Section problems need to satisfy the following three conditions:
- Mutual Exclusion: If a process is in the critical section, then other processes shouldn't be allowed to enter into the critical section at that time i.e. there must be some mutual exclusion between processes.
- Progress: If in the critical section, there is no process that is being executed, then other processes that need to go in the critical section and have a finite time can enter into the critical section.
- Bounded Waiting: There must be some limit to the number of times a process can go into the critical section i.e. there must be some upper bound. If no upper bound is there then the same process will be allowed to go into the critical section again and again and other processes will never get a chance to get into the critical section.
So, in order to remove the problem of race condition, there must be synchronization between various processes present in the system for its execution otherwise, it may lead to data inconsistency i.e. a proper order should be defined in which the processes can execute.
That's it for this blog. Hope you learned something new today. You can learn how to achieve process synchronization using semaphore by reading the blog from here.
Do share this blog with your friends to spread the knowledge. Visit our YouTube channel for more content. You can read more blogs from here.
Keep Learning 🙂
Team AfterAcademy!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
What is a Process in Operating System and what are the different states of a Process?
In this blog, we will learn about Process in Operating System and we will also learn about the various states of a Process during its life cycle.

AfterAcademy Tech
What is an Operating System and what are the goals and functions of an Operating System?
In this blog, we will learn what an Operating System is and what are the goals of an Operating System. We will also learn the functionalities of an Operating System that helps in achieving the goal of the OS.

AfterAcademy Tech
Process scheduling algorithms in the Operating System
In this blog, we will learn about various process scheduling algorithms used in Operating System. We will learn about FCFS, SJF, SRTF, Round-Robin, Priority-based, Highest Response Ratio Next, Multilevel Queue, and Multilevel Feedback Queue scheduling.
AfterAcademy Tech
Process Control Block in Operating System
In this blog, we will learn about Process Control Block also known as PCB and we will see various attributes that are present in the Process Control Block.