What is Load Balancing? How does it work?
AfterAcademy Tech
•
29 Apr 2020
Welcome to AfterAcademy!
In this blog, we will learn the concept of Load Balancing in System Design. This is a famous question that is asked in almost every System Design interview. So, we are going to discuss the following in this blog:
- Why there is a need for a solution that Load Balancing provides?
- What is Load Balancing?
- Benefits of Load Balancing
- Load Balancing Algorithms
- Load Balancing using Hashing
- Problems due to normal Hashing
- What next?
So, let's get started with the "Why Load Balancing?" question.
If you are more found of videos than text, you can watch our Load Balancing video:
Why there is a need for a solution that Load Balancing provides?
Suppose a few days back, you made some website, let's say AfterAcademy to provide a one-stop learning solution for everyone i.e. Students, Professionals, learning enthusiasts, etc. Initially, the website was new, so you bought one server than can handle let's say 1000 users at a time.
But when you started putting more good content on the website, then the number of users started growing a lot and now your server is unable to handle the request of so many users. What will you do?
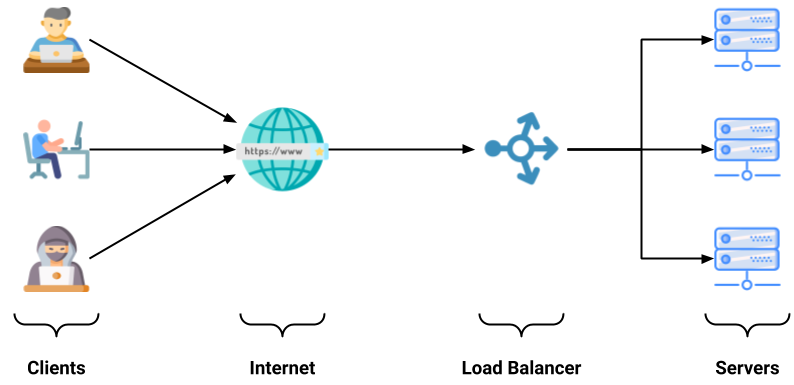
Since your user base is growing, you can plan to buy more servers. So, let's say to give your users a better experience, you are having a total of N servers. So, whenever a user is requesting something from your website, you need to redirect the request to one of your servers and in return, the server will provide some response to the user. The request sent to the server should be such that no server is overloaded and the equal number of requests should be sent to each server. So, here comes the role of Load Balancing.
What is Load Balancing?
Load Balancing is a process that is used to uniformly route the request of users/clients to the different servers that are available for use i.e. to the servers that are currently in working condition. In simpler words, load balancing is a process of balancing the load on different servers.
For example, if you are having 10 servers and 1000 users, then in an ideal situation each server should handle the request of 100 users.
The process of Load Balancing is done with the help of Load Balancers. The following image illustrates the Load Balancing process:
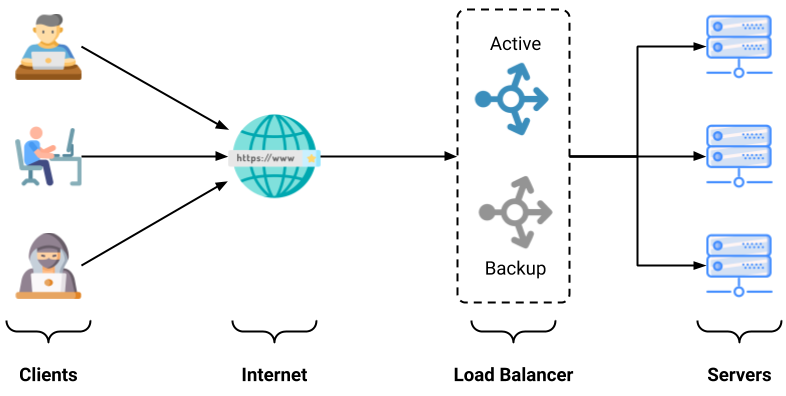
To avoid the case of failure of the Load Balancer, we can add one backup Load Balancer. At a time, only one Load Balancer will be active and the other Load Balancer will keep on watching the status of active Load Balancer. So, in case of failure, the other Load Balancer will take over the charge and do the Load Balancing thing.
To make the most of Load Balancing, we can use Load Balancers in 3 places:
- Between user and web server: Firstly, we can put Load Balancers between users and your web server because the user first interacts with the web server only.
- Between web server and application/cache server: Now, you can put a Load Balancer between the web server and your internal server i.e. backend of your system.
- Between application/cache server and database server: And finally, you can put the Load Balancer between your internal server and the various databases used in your system.
This is how Load Balancing is performed. Apart from the distribution of loads, there are various other benefits of Load Balancing. Let's find.
Benefits of Load Balancing
Some of the benefits of Load Balancing are:
- Uniform load on servers: With the help of Load Balancing, all the requests from the user are uniformly distributed to all the servers.
- Downtime reduction: When Load Balancing is done then all the servers will work properly i.e. all the servers will process only that amount of requests that they are capable of. Even if there is some server failure, then the request of that server will be evenly distributed to the other active servers. So, the downtime of the system will be reduced.
- Increase scalability: The scalability of the system will be increased. Whenever we introduce a new server, then the overall load will be balanced.
- Increased flexibility: The flexibility of the whole system will be increased with Load Balancing. Now, adding or removing servers will not lead to some downtime.
Now, let's look at some of the algorithms that are used for Load Balancing.
Load Balancing Algorithms
From the available servers, the Load Balancer will route the request to only those servers which are responding correctly, or in other words, the request will be sent to those servers that are "healthy".
Out of those working servers, the Load Balancers uses various algorithms to route the request. Some of these algorithms are:
- Round Robin: In this algorithm, all the servers can be thought of placed in a circle. The first request will route to the first server, the second request to the second server, and so on until it reaches the last server in the cycle. After this, if some request comes in, then the request will be routed to the first server and again the same process will continue. This algorithm is useful when we have servers of similar configuration.
- Least Connection: In this algorithm, if some request comes from a user, then it will be routed to that server which is having the least active connection at that particular time.
- Least Time: In this algorithm, the request is routed to that server which is having the fastest response time and has the least active connection.
- Hashing: In this algorithm, we route the request based on some key. That key can be the IP address of the user or the request URL or requestId or something else. Hashing is performed on the key and after hashing, the request is directed to the desired server.
- IP Hashing: In this algorithm, the IP address of the client is hashed with some hash function, and the request is directed to the desired server.
Out of these algorithms, Hashing is the most widely used algorithm. Let's learn about it.
Load Balancing using Hashing
Hashing is one of the common methods used in Load Balancing. Here, we have something known as requestId that is uniquely and randomly generated. Each request by the client is uniquely identified by this requestId.
So, along with the request, the requestId will also be sent. With the help of Load Balancer, this requestId will be hashed with a proper Hash Function, and to get the server where the request will be directed, we will find the modulo of the result of the Hash Function with "N" i.e. the total number of active servers available.
If you are not familiar with the Hash Function and Hashing, then learn from here.
Note: The Hash Function should be such that the number generated by it should be uniformly distributed over all servers.
The following is an example of Load Balancing using Hashing:
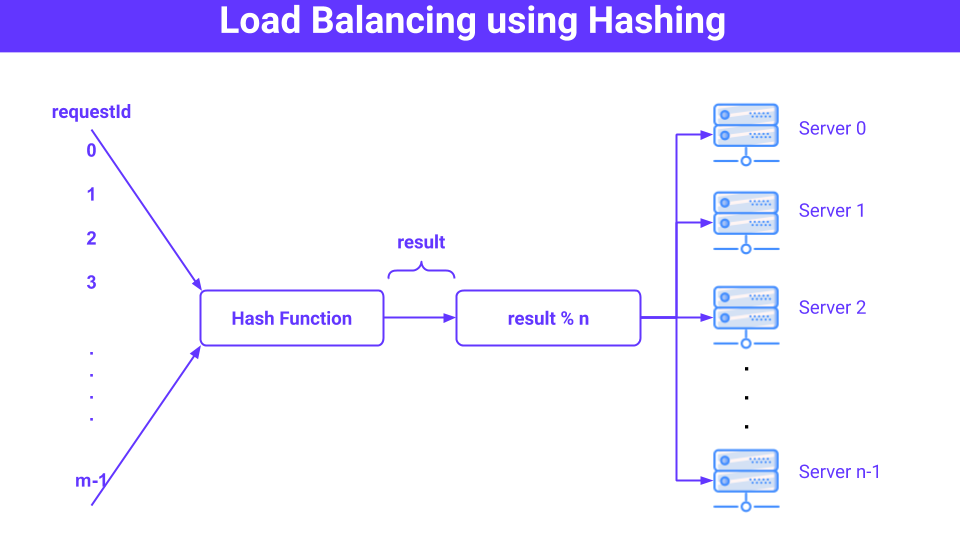
So, for example, if the requestId is 154 and there are 5 servers available. Let's say the Hash Function will give the result as 23. Then the following calculations will be done:
total number of servers = 5
hashFunction(requestId) i.e. hashFunction(154) = 23
so, the assigned server will be: 23 % 5 = 3
therefore, the 3rd server will be assigned
So, by performing the above method the load is uniformly divided i.e. if the total number of requests is R and the total number of active server is N then load on each server is going to be R/N .
Now, let's see if there is some problem with this hashing technique or not.
Problems due to normal Hashing
So we have seen how hashing can be used for the purpose of Load Balancing. Now, let's take an example where we have 100 requestId and 5 servers. So,
- Server 1 will serve the request from
requestId1 to 20 - Server 2 will serve the request from
requestId21 to 40 - Server 3 will serve the request from
requestId41 to 60 - Server 4 will serve the request from
requestId61 to 80 - Server 5 will serve the request from
requestId80 to 100
The following pie-chart describes the same:
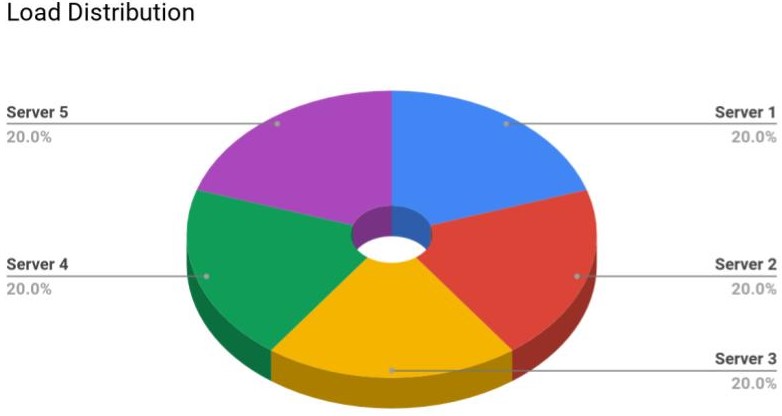
Note: For better performance, the servers keep the data of the users as cache. For example, the server 1 will keep the important or frequently used data ofrequestId1 torequested20.
Now, due to some reasons, the server 5 is down. So, we need to distribute the request from requestId 80 to 100 to all the other 4 servers and now each server will be handling 25 requests each.
So, the new pie-chart will look something like below:
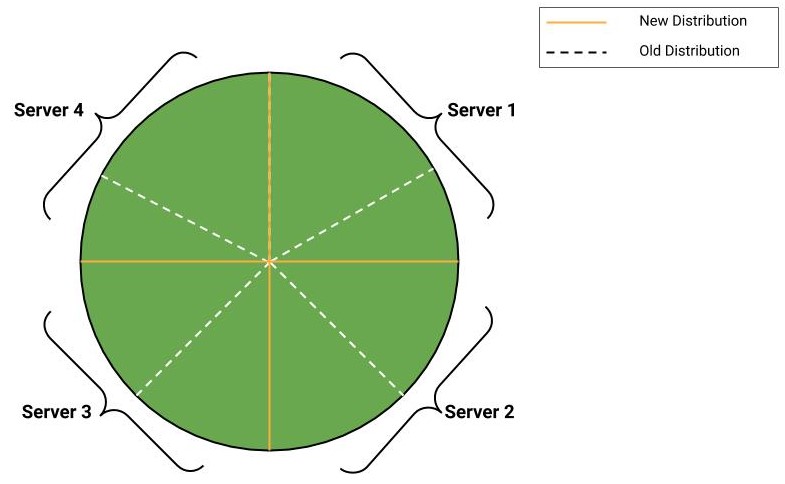
Note: The dotted lines are representing the old distribution and block lines are representing the new distribution.
If you see in the above image, then you will find that there are a lot of operations being performed for migrating the requestId:
- Initially, server 1 was serving 20
requestIds. Now, it is serving 25. So, it is gaining 5requestIds form server 2 i.e. the data of 5 users is migrated to server 1 from server 2. - Initially, server 2 was serving 20
requestIds. Now, it is serving 25. So, it is loosing 5requestIds (given to server 1) and gaining 10requestIds form server 3 i.e. the data of 10 users is migrated to server 2 from server 3. - Initially, server 3 was serving 20
requestIds. Now, it is serving 25. So, it is loosing 10requestIds (given to server 2) and gaining 15requestIds form server 4 i.e. the data of 15 users is migrated to server 3 from server 4. - Initially, server 4 was serving 20
requestIds. Now, it is serving 25. So, it is loosing 15requestIds (given to server 2) and gaining 20requestIds form server 5 i.e. the data of 20 users is migrated to server 4 from server 5. - And server 5 is no more available.
So, if you see the above process, then you will find that there is a lot of data migration operations being performed here i.e. giving and taking of requestIds. This will lead to downtime until all the migrations are not performed and we don't need this situation. Some improvements must be done to this normal Hashing process and this is done with the help of Consistent Hashing.
What next?
We have seen that there is some problem with the normal Hashing approach and this can be removed by using Consistent Hashing.
So up next, you can learn about Consistent Hashing from AfterAcademy video.
Also, you can find the whole playlist of System Design from here.
Know about other Backend technologies by learning from our open-source projects.
Keep Learning 🙂
Team AfterAcademy!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
What is FTP and how does an FTP work?
In this blog, we will learn what is an FTP protocol, how does it works, what are various modes in which it works, what are the advantages and disadvantages of using it.

AfterAcademy Tech
What is the OSI model and how it works?
In this blog, we will mainly learn about the OSI model and its working in detail. We'll focus on the features and working of each layer of the OSI model.
AfterAcademy Tech
What is DHCP and how does it work?
In this blog, we will learn what is DHCP, what are various entities related to DHCP and how does it work. We will also discuss how IP configurations are dynamically done.

AfterAcademy Tech
What is the TCP/IP model and how it works?
In this blog, we will mainly learn about the TCP/IP model and its working in detail. We'll focus on the features and working of each layer of the TCP/IP model.