What is Data Model in DBMS and what are its types?
AfterAcademy Tech
•
11 Dec 2019
Data Model
Data Model gives us an idea that how the final system will look like after its complete implementation. It defines the data elements and the relationships between the data elements. Data Models are used to show how data is stored, connected, accessed and updated in the database management system. Here, we use a set of symbols and text to represent the information so that members of the organisation can communicate and understand it. Though there are many data models being used nowadays but the Relational model is the most widely used model. Apart from the Relational model, there are many other types of data models about which we will study in details in this blog. Some of the Data Models in DBMS are:
- Hierarchical Model
- Network Model
- Entity-Relationship Model
- Relational Model
- Object-Oriented Data Model
- Object-Relational Data Model
- Flat Data Model
- Semi-Structured Data Model
- Associative Data Model
- Context Data Model
Hierarchical Model
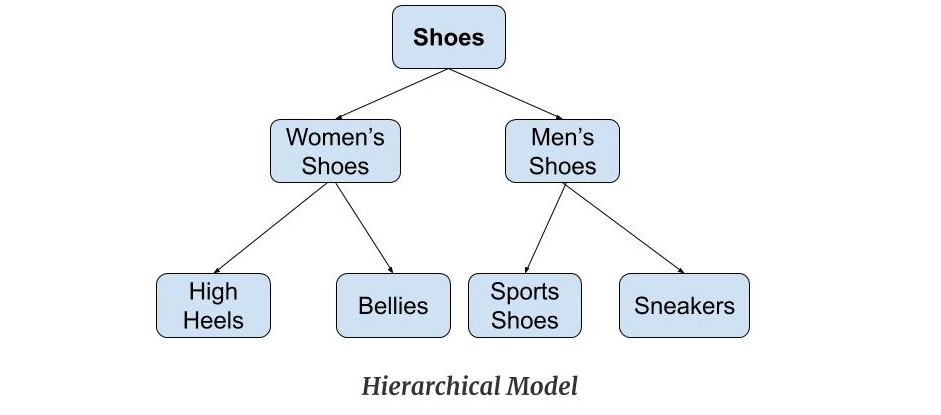
Hierarchical Model was the first DBMS model. This model organises the data in the hierarchical tree structure. The hierarchy starts from the root which has root data and then it expands in the form of a tree adding child node to the parent node. This model easily represents some of the real-world relationships like food recipes, sitemap of a website etc. Example: We can represent the relationship between the shoes present on a shopping website in the following way:
Features of a Hierarchical Model
- One-to-many relationship: The data here is organised in a tree-like structure where the one-to-many relationship is between the datatypes. Also, there can be only one path from parent to any node. Example: In the above example, if we want to go to the node sneakers we only have one path to reach there i.e through men's shoes node.
- Parent-Child Relationship: Each child node has a parent node but a parent node can have more than one child node. Multiple parents are not allowed.
- Deletion Problem: If a parent node is deleted then the child node is automatically deleted.
- Pointers: Pointers are used to link the parent node with the child node and are used to navigate between the stored data. Example: In the above example the 'shoes' node points to the two other nodes 'women shoes' node and 'men's shoes' node.
Advantages of Hierarchical Model
- It is very simple and fast to traverse through a tree-like structure.
- Any change in the parent node is automatically reflected in the child node so, the integrity of data is maintained.
Disadvantages of Hierarchical Model
- Complex relationships are not supported.
- As it does not support more than one parent of the child node so if we have some complex relationship where a child node needs to have two parent node then that can't be represented using this model.
- If a parent node is deleted then the child node is automatically deleted.
Network Model
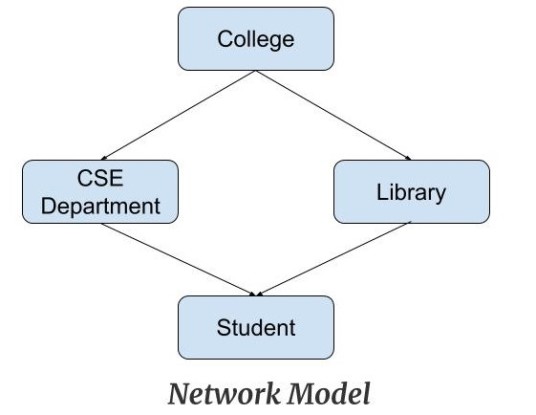
This model is an extension of the hierarchical model. It was the most popular model before the relational model. This model is the same as the hierarchical model, the only difference is that a record can have more than one parent. It replaces the hierarchical tree with a graph. Example: In the example below we can see that node student has two parents i.e. CSE Department and Library. This was earlier not possible in the hierarchical model.
Features of a Network Model
- Ability to Merge more Relationships: In this model, as there are more relationships so data is more related. This model has the ability to manage one-to-one relationships as well as many-to-many relationships.
- Many paths: As there are more relationships so there can be more than one path to the same record. This makes data access fast and simple.
- Circular Linked List: The operations on the network model are done with the help of the circular linked list. The current position is maintained with the help of a program and this position navigates through the records according to the relationship.
Advantages of Network Model
- The data can be accessed faster as compared to the hierarchical model. This is because the data is more related in the network model and there can be more than one path to reach a particular node. So the data can be accessed in many ways.
- As there is a parent-child relationship so data integrity is present. Any change in parent record is reflected in the child record.
Disadvantages of Network Model
- As more and more relationships need to be handled the system might get complex. So, a user must be having detailed knowledge of the model to work with the model.
- Any change like updation, deletion, insertion is very complex.
Entity-Relationship Model
Entity-Relationship Model or simply ER Model is a high-level data model diagram. In this model, we represent the real-world problem in the pictorial form to make it easy for the stakeholders to understand. It is also very easy for the developers to understand the system by just looking at the ER diagram. We use the ER diagram as a visual tool to represent an ER Model. ER diagram has the following three components:
- Entities: Entity is a real-world thing. It can be a person, place, or even a concept. Example: Teachers, Students, Course, Building, Department, etc are some of the entities of a School Management System.
- Attributes: An entity contains a real-world property called attribute. This is the characteristics of that attribute. Example: The entity teacher has the property like teacher id, salary, age, etc.
- Relationship: Relationship tells how two attributes are related. Example: Teacher works for a department.
Example:
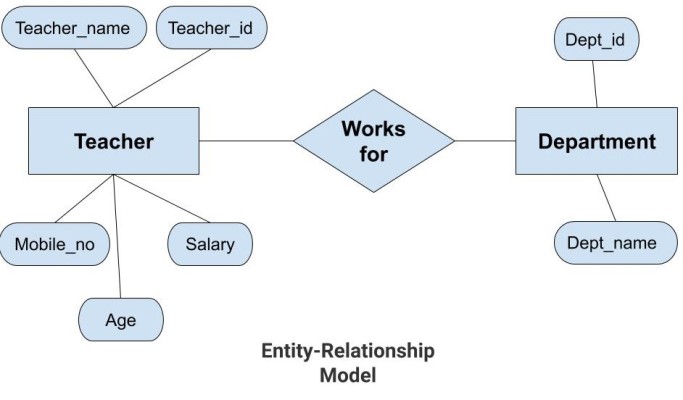
In the above diagram, the entities are Teacher and Department. The attributes of Teacher entity are Teacher_Name, Teacher_id, Age, Salary, Mobile_Number. The attributes of entity Department entity are Dept_id, Dept_name. The two entities are connected using the relationship. Here, each teacher works for a department.
Features of ER Model
- Graphical Representation for Better Understanding: It is very easy and simple to understand so it can be used by the developers to communicate with the stakeholders.
- ER Diagram: ER diagram is used as a visual tool for representing the model.
- Database Design: This model helps the database designers to build the database and is widely used in database design.
Advantages of ER Model
- Simple: Conceptually ER Model is very easy to build. If we know the relationship between the attributes and the entities we can easily build the ER Diagram for the model.
- Effective Communication Tool: This model is used widely by the database designers for communicating their ideas.
- Easy Conversion to any Model: This model maps well to the relational model and can be easily converted relational model by converting the ER model to the table. This model can also be converted to any other model like network model, hierarchical model etc.
Disadvatages of ER Model
- No industry standard for notation: There is no industry standard for developing an ER model. So one developer might use notations which are not understood by other developers.
- Hidden information: Some information might be lost or hidden in the ER model. As it is a high-level view so there are chances that some details of information might be hidden.
Relational Model
Relational Model is the most widely used model. In this model, the data is maintained in the form of a two-dimensional table. All the information is stored in the form of row and columns. The basic structure of a relational model is tables. So, the tables are also called relations in the relational model. Example: In this example, we have an Employee table.
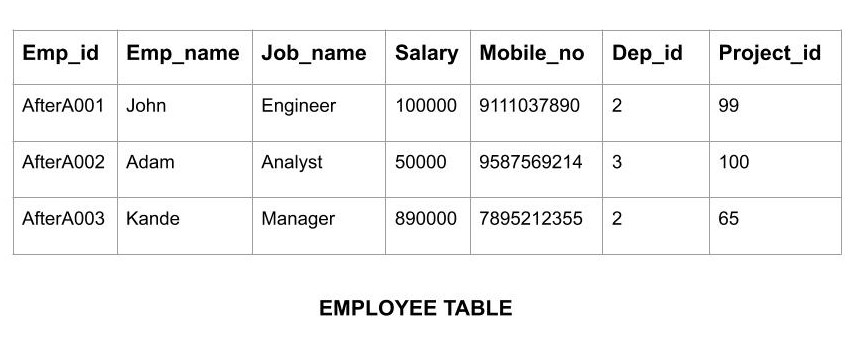
Features of Relational Model
- Tuples: Each row in the table is called tuple. A row contains all the information about any instance of the object. In the above example, each row has all the information about any specific individual like the first row has information about John.
- Attribute or field: Attributes are the property which defines the table or relation. The values of the attribute should be from the same domain. In the above example, we have different attributes of the employee like Salary, Mobile_no, etc.
Advnatages of Relational Model
- Simple: This model is more simple as compared to the network and hierarchical model.
- Scalable: This model can be easily scaled as we can add as many rows and columns we want.
- Structural Independence: We can make changes in database structure without changing the way to access the data. When we can make changes to the database structure without affecting the capability to DBMS to access the data we can say that structural independence has been achieved.
Disadvantages of Relatinal Model
- Hardware Overheads: For hiding the complexities and making things easier for the user this model requires more powerful hardware computers and data storage devices.
- Bad Design: As the relational model is very easy to design and use. So the users don't need to know how the data is stored in order to access it. This ease of design can lead to the development of a poor database which would slow down if the database grows.
But all these disadvantages are minor as compared to the advantages of the relational model. These problems can be avoided with the help of proper implementation and organisation.
Object-Oriented Data Model
The real-world problems are more closely represented through the object-oriented data model. In this model, both the data and relationship are present in a single structure known as an object. We can store audio, video, images, etc in the database which was not possible in the relational model(although you can store audio and video in relational database, it is adviced not to store in the relational database). In this model, two are more objects are connected through links. We use this link to relate one object to other objects. This can be understood by the example given below.
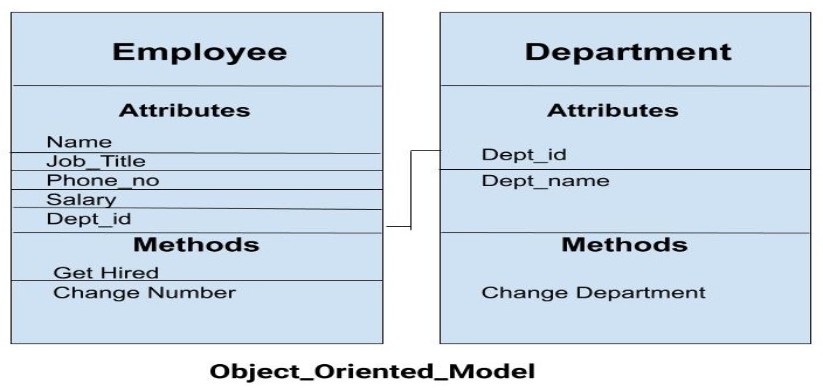
In the above example, we have two objects Employee and Department. All the data and relationships of each object are contained as a single unit. The attributes like Name, Job_title of the employee and the methods which will be performed by that object are stored as a single object. The two objects are connected through a common attribute i.e the Department_id and the communication between these two will be done with the help of this common id.
Object-Relational Model
As the name suggests it is a combination of both the relational model and the object-oriented model. This model was built to fill the gap between object-oriented model and the relational model. We can have many advanced features like we can make complex data types according to our requirements using the existing data types. The problem with this model is that this can get complex and difficult to handle. So, proper understanding of this model is required.
Flat Data Model
It is a simple model in which the database is represented as a table consisting of rows and columns. To access any data, the computer has to read the entire table. This makes the modes slow and inefficient.
Semi-Structured Model
Semi-structured model is an evolved form of the relational model. We cannot differentiate between data and schema in this model. Example: Web-Based data sources which we can't differentiate between the schema and data of the website. In this model, some entities may have missing attributes while others may have an extra attribute. This model gives flexibility in storing the data. It also gives flexibility to the attributes. Example: If we are storing any value in any attribute then that value can be either atomic value or a collection of values.
Associative Data Model
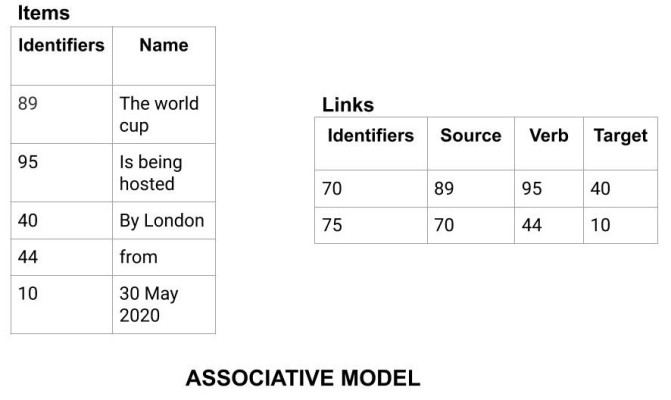
Associative Data Model is a model in which the data is divided into two parts. Everything which has independent existence is called as an entity and the relationship among these entities are called association. The data divided into two parts are called items and links.
- Item: Items contain the name and the identifier(some numeric value).
- Links: Links contain the identifier, source, verb and subject.
Example: Let us say we have a statement "The world cup is being hosted by London from 30 May 2020". In this data two links need to be stored:
- The world cup is being hosted by London. The source here is 'the world cup', the verb 'is being' and the target is 'London'.
- ...from 30 May 2020. The source here is the previous link, the verb is 'from' and the target is '30 May 2020'.
This is represented using the table as follows:
Context Data Model
Context Data Model is a collection of several models. This consists of models like network model, relational models etc. Using this model we can do various types of tasks which are not possible using any model alone.
This is all about the various data model of DBMS. Hope you learned something new today.
Do share this blog with your friends to spread the knowledge. Visit our YouTube channel for more content. You can read more blogs from here.
Keep Learning 🙂
Team AfterAcademy!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
What are the different types of relationships in DBMS?
In this blog, we will study various types of relationships in DBMS which help in defining the association between various entities. Also, we will discuss the types of participation constraints which may exist between the relationship and the entity type.
AfterAcademy Tech
What is Join in DBMS and what are its types?
In this blog, we will learn how to join two tables in DBMS. We will also learn about the various types of joins, mainly the inner and the outer join.
AfterAcademy Tech
What is Data Abstraction in DBMS and what are its three levels?
In this blog, we will learn about data abstraction and how it achieved using its three levels. We will learn the working of all the three levels of data abstraction.
AfterAcademy Tech
What is Data independency?
In this blog, we will learn about data independence and how it helps in doing modification in the database. Further, we will discuss its two types on the basis of levels of abstraction in DBMS.