What is an IP address?
AfterAcademy Tech
•
29 Feb 2020

Every machine in the network has a unique identifier to identify it. Just as your house has an address so that you receive all the parcels, similarly, the computer uses a unique identifier over the internet to send the data. Without a specific address, information cannot be received. Most of the computers on the internet today use TCP/IP protocol for communication. This unique identifier in the TCP/IP protocol is called IP address. So, let's dive deep into this blog to know more about IP addresses.
IP address
The Internet Protocol(IP) address is a unique identifying number that helps in connecting your device with the devices over the internet or in the same network. This is a unique number for all devices like printer, router, modems, laptop, mobile, etc. An IP address is made of characters or numbers. Example: 203.90.105.206. There are two versions of IP standards that co-exist in the global world.
- IPv4
- IPv6
IPv4
IP version 4 is the older version of IP. It uses 32 bits to create a single uniques address on the internet. IPv4 is limited to 4,294,967,296 addresses i.e. 2³² addresses. It consists of four numbers each of which can contain one to three digits ranging from 0 to 255 separated by a single dot(.). Here, each number is the decimal representation(base-10) for an 8 digit binary number(base-2). These IP addresses pretty much guarantee that our emails will come as go as expected, our google searches would take us to the website which we want.
Example of an IPv4 address: 63.171.234.171
Currently, most of the devices use IPv4 but these IP addresses are running out quickly. IPv6 solved this problem. It can accommodate up to trillions of users.
IPv6
It is the replacement for IPv4. It uses 128 bits to create a uniques address. This means that there can be theoretically 2¹²⁸ uniques address i.e. 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456 and this number will never run out. It consists of eight groups of hexadecimal numbers separated by a colon. The IPV4 version used numerical values, so, IPv6 adopted the hexadecimal numbers to avoid any conflict. If any group contains all zeros then the notation can be shortened by using a colon to replace the zeroes.
Example of an IPv6: adba:1925:0000:0000:0000:0000:8a2e:7334
In the above IP address, four groups contain only zeros. This zero can be replaced by a colon and can be re-written as adba:1925::8a2e:7334.
How does your computer get an IP address?
The IP address is assigned to your computer by the ISP. It can be static or dynamic. In most of the cases, it is a dynamic IP.
Static IP address
This type of IP address is one that is assigned to you by the ISP’s. This is fixed and can't change automatically. This is generally used by the server hosting websites, providing mails, databases, etc. The ISP’s charge an extra amount for static IP’s.
Advantages of Static IP address:
- Better DNS Support: Static IP addresses are easy to manage with DNS Servers as the IP address is fixed for the domain name.
- Server Hosting: It is good for hosting web servers, email servers, and internet servers. Having a static IP address means it's easier for the clients to reach you via DNS more quickly.
Disadvantages of Static IP address
- Security Concern: As the IP address is static it is easier for hackers to attack.
- Higher Cost: The ISP generally charges extra for the static IP’s.
Dynamic IP address
This type of IP address is dynamically assigned to you by the ISP. ISP assigns this IP address by using the DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) which typically runs on routers or dedicated DHCP servers. This dynamic IP address is assigned using a leasing system which means that this IP address would be assigned only for a fixed amount of time. When the lease time gets over then this IP address has to be revived. Mostly, DHCP reassigns the same IP address to the same machine but it may be possible that the DHCP is not able to give the same IP address to you again.
Advantages of Dynamic IP address
- More secure: The changing IP address provides more security.
- Lower fees: It is cheaper than static IP.
- Prevents IP Conflicts: As the IP address is assigned automatically it prevents the IP conflicts.
Disadvantages of Dynamic IP address
- Not suitable for Hosted Services: It is not suitable for hosting web services as the changing IP address can be troublesome for the DNS. DNS does not work well with dynamic IP addresses. However, we have Dynamic DNS which mange this problem which comes with additional complexity and cost.
- Less-accurate Geo-location: As your, IP address keeps on changing so your IP address may not reflect your accurate real-time location. So, sometimes the geo-locations services may fail.
A static IP address is good for business which hosts their own websites whereas a dynamic IP address is good enough for the end customers.
No matter if you are using a static IP address or a dynamic IP address it is always vulnerable to hackers. So you should use a proxy server or a VPN to hide your IP address.
How to find your IP address?
You might not know but you have two IP addresses. First, Public or external IP address and second, Private or internal IP address.
- Public Address: The public address is provided by the ISP and it how the internet recognizes you as a network. It is unique for each user. You can find your public IP address, by typing something like "what is my ip address" in google chrome.
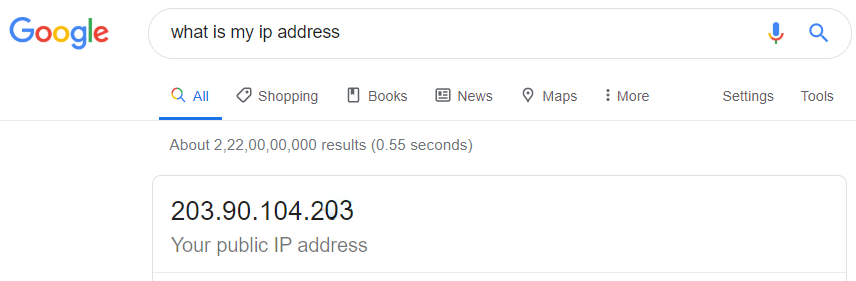
Google shows an IP address:203.90.104.203
This is your external IP address. We can also understand that it is an IP version 4 address.
- Private Address: Every device on a local network has a unique local IP address that is assigned to you by the router of the internal network. You can find your private IP address by going to command prompt and typing "ipconfig"(without double quotes) in it.
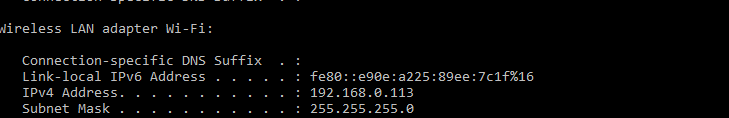
This time your IP address is 192.168.0.113.
This is your Internal IP address.
The internal IP address used in your local internal network whereas the external IP address is used when trying to communicate with the systems on the Intenet.
That’s it for this blog. I hope you enjoyed reading this blog.
Do share this blog with your friends to spread the knowledge. Visit our YouTube channel for more content. You can read more blogs from here.
Keep Learning 🙂
Team AfterAcademy!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
What is the difference between MAC address and IP address?
In this blog, we will first learn about the MAC and IP addresses in brief. And then, we'll see the dissimilarities between the two.
AfterAcademy Tech
What are the classes of IPV4? How to identify IP class from a given IP address?
In this blog, we will learn what are the various types of classes in IPv4 and how we can differentiate among the classes on the basis of the number of bits present the network ID and the host ID of these classes.

AfterAcademy Tech
What is the TCP/IP model and how it works?
In this blog, we will mainly learn about the TCP/IP model and its working in detail. We'll focus on the features and working of each layer of the TCP/IP model.
AfterAcademy Tech
Which model is better, OSI or TCP/IP?
In this blog, we have described the similarities and dissimilarities between the OSI and TCP/IP models. We've also tried to tell which model is better for which scenario.