Reverse An Array
AfterAcademy Tech
•
08 Jun 2020

Difficulty: Easy
Understanding The Problem
Problem Description
Given an array, the task is to reverse the array.
Examples →
Input : arr[] = {34, 12, 23}
Output : arr[] = {23, 12, 34}
Input : arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Output : arr[] = {6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1}
Solution
We will be discussing a simple approach to reverse the array in-place. In place means, we will not be using some auxiliary space.
To reverse an array, we will use the concept of swapping. Swapping is a term used for interchanging the values at two different locations with each other.
Look at the below example to get a clear understanding of the array that should be reversed.
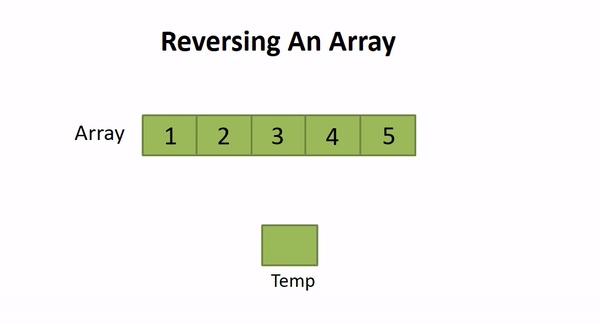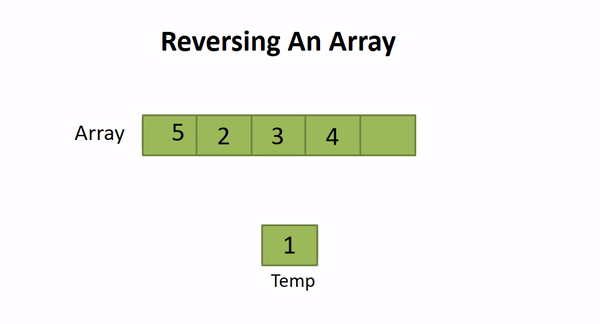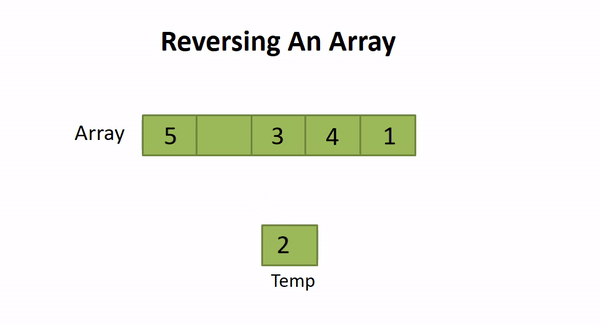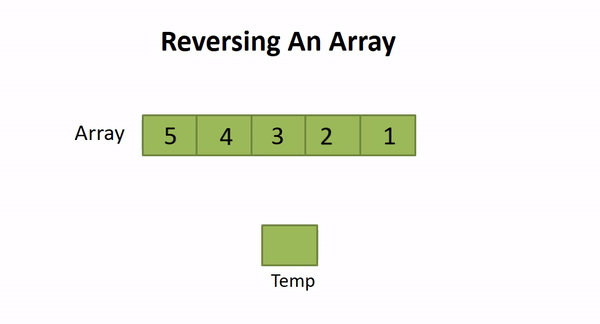
So, we can set two pointers at the start and end of the array and start iterating over it till the (length of array)/2. For every idx , we will swap array[idx] with array[length - idx] . Thus, the array will be reversed in-place.
Solution Steps
- Place the two pointers (let
startandend)at the start and end of the array. - Swap
arr[start]andarr[end] - Increment
startand decrementendwith1 - If
startreached to the valuelength/2orstart ≥ end, then terminate otherwise repeat from step 2.
Pseudo Code
void rvereseArray(int[] arr) {
start = 0
end = arr.length - 1
while (start < end) {
// swap arr[start] and arr[end]
int temp = arr[start]
arr[start] = arr[end]
arr[end] = temp
start = start + 1
end = end - 1
}
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical Ideas to Think
- The loop will run only till
length/2then why the asymptotic time complexity isO(n)instead ofO(n/2)? - How did we perform swapping?
- Why did we iterate until
start < endorstart < (length of array)/2? - What will happen if the while condition would be
start < length of array, instead ofstart < endin pseudocode? Can you dry run the code over some examples?
Suggested Problems To Solve
- Write a program to reverse digits of a number
- Program to reverse a string
- Program to reverse words in a given string.
- Program to reverse the rows in a 2d Array
- Program to Reverse Bits of a Number
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Find whether an array is a subset of another array - Interview Problem
Given two integer array A[] and B[] of size m and n(n <= m) respectively. We have to check whether B[] is a subset of A[] or not. An array B is a subset of another array A if each element of B is present in A. (There are no repeated elements in both the arrays)

AfterAcademy Tech
Introduction to Arrays
The idea of this blog is to discuss the famous data structure called Array. An Array is one of the important data structures that are asked in the interviews. So, we will learn about arrays and we will also discuss about the idea of the dynamic array and its amortized analysis. So let's get started.

AfterAcademy Tech
When to Convert a 2-D DP array to 1-D DP array And How?
In which situation 2 dimensional DP can be dropped to 1 dimension? Is there any principle or regular pattern? This is a very important question when it comes to optimization of DP arrays. Let's find out.
AfterAcademy Tech
Wave Array
You are given an unsorted array of integers(arr) of length n, write a program to sort it in wave form. The array elements in the resultant array must be such that arr[0] >= arr[1] <= arr[2] >= arr[3] <= arr[4] ... and so on. If there are multiple sorted orders in wave-form, return the one which is lexicographically smallest.
