Print All Subsets of a given set
AfterAcademy Tech
•
31 Dec 2019

Difficulty: Medium
Asked in: Facebook, Microsoft, Amazon
Understanding the Problem
Problem description
Given an array of distinct integers S, return all possible subsets.
Problem Note
- The set is not necessarily sorted.
- The total number of subsets of a given set of size n is equal to 2^n.
Example
Input: S[] = [1,2,3]
Output:
[
[],
[1],
[1,2],
[1,2,3],
[1,3],
[2],
[2,3],
[3]
]
You can try this problem here.
Possible questions to ask the interviewer —
- Could the solution set contain duplicate subsets? (Ans: No)
- Can we print the subset in any order? (Ans: Yes)
Backtracking and Bitmasking solutions
- Backtracking Approach - It's a recursive approach where we backtrack each solution after appending the subset to the resultset.
- BitMasking Approach - The binary representation of a number in range 0 to 2^n is used as a mask where the index of set bit represents the array index to be included in the subset.
1. Backtracking Approach
Solution idea
Why Backtracking? Because the backtracking technique is designed to generate every possible solution once. If we design the algorithm smartly, we can get the backtracking logic to work for us and generate all the possible subsets.
The thought is that if we have N number of elements inside an array, we have exactly two choices for each of them, either we include that element in our subset or we do not include it. So, the take or not take strategy builds a pseudo-binary tree of choices returning only the leaves for each combination resulting in the powerset.
The recursion tree for the above example will look like this:
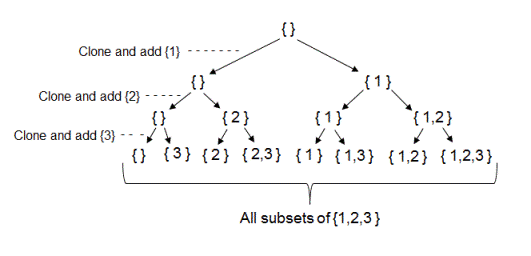
Solution steps
We could just build up the subset of different size in an array i.e. subset[]. Here are the steps to generate it:
- Choose one element from input i.e. subset[len] = S[pos]. We can decide to include it in current subset or not.
- Recursively form subset including it i.e. allSubsets(pos+1, len+1, subset)
- Recursively form subset excluding it i.e. allSubsets(pos+1, len, subset)
- Make sure to generate each set once.
Pseudo Code
int S[N]
void allSubsets(int pos, int len, int[] subset)
{
if(pos == N)
{
print(subset)
return
}
// Try the current element in the subset.
subset[len] = S[pos]
allSubsets(pos+1, len+1, subset)
// Skip the current element.
allSubsets(pos+1, len, subset)
}
Complexity Analysis
Here we are generating every subset using recursion. The total number of subsets of a given set of size n = 2^n.
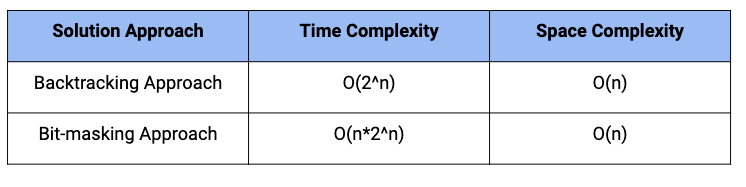
Time Complexity : O( 2^n)
Space Complexity : O(n) for extra array subset.
Critical Ideas to Think
- Why are we keeping track of both the cases when we pick the element and when we don't pick the element?
- Can you write the recurrence relation for the above algorithm?
- Can you think of some different way to implement this solution?
- Can we solve this problem using stack?
- Identify problems which can be solved using similar approach.
2. Bitmasking Approach
Solution Idea
So instead of using an array, we can just use a single integer whose individual bits represent the entries of the array. So the ith bit is 1 or 0 as the ith entry of the array is true or false. This is usually called a bitmasking approach which is really handy to solve other types of problems. (Think!)
Note: n-bit integers are just the numbers from 0 (all n bits zero) to 2^n − 1 (all n bits one).
Set S[] = [1,2,3]
Total number of subsets = pow(2, n) = pow(2, 3) = 8
Value of integer Subsets
000 -> Empty set
001 -> 1
010 -> 2
011 -> 12
100 -> 3
101 -> 13
110 -> 23
111 -> 123
Solution steps
- Get the total number of subsets, subset_size = 2^n
- Loop for index from 0 to subset_size
- Loop for i = 0 to subset_size
- If the ith bit in the index is set then, append ith element from the array for this subset.
Pseudo Code
Void allSubset(int S[], int n)
{
int subset_size = pow(2, n)
int index, i
//Run from index 000..0 to 111..1
for(index from 0 to subset_size)
{
int subset[n]
for(i from 0 to n)
{
// Check if jth bit in the index is set
// If set then add jth element to the subset
if(index & (1 << i))
subset[i] = S[i]
}
print(subset)
}
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity : O(n*2^n)
Space Complexity : O(n)
Critical Ideas to Think
- What does the “<<” operator represent?
- What does each set bit represent in the intermediate iterations?
- Can you explain the time complexity?
- Identify problems which can be solved using similar approach.
Comparison of different approaches
Suggested Problems to Solve
- Partition string such that every string of the partition is a palindrome.
- Sum of subsets of all the subsets of an array
- Given n pairs of parentheses, write a program to generate all combinations of well-formed parentheses.
- Return all possible permutations of collection of distinct integers
- Letter combination of a phone number
- Return all possible combinations of k numbers out of 1 2 3 ... n.
- N Queen Problem
- Rat in a Maze
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Partition Equal Subset Sum
Given a non-empty array of positive integers arr[ ]. Write a program to find if the array can be partitioned into two subsets such that the sum of elements in both subsets is equal.

AfterAcademy Tech
Find whether an array is a subset of another array - Interview Problem
Given two integer array A[] and B[] of size m and n(n <= m) respectively. We have to check whether B[] is a subset of A[] or not. An array B is a subset of another array A if each element of B is present in A. (There are no repeated elements in both the arrays)

AfterAcademy Tech
Set Matrix Zeros - Interview Problem
Given a matrix, A of size M x N of 0's and 1's. If an element is 0, set its entire row and column to 0

AfterAcademy Tech
Check for pair in an array with a given sum - Interview Problem
Write a program that, Given an array of n integers and given a number K, determines whether or not there exist two elements whose sum is exactly K.
