Detect and Remove Loop In A Linked List
AfterAcademy Tech
•
09 Sep 2020
Difficulty: Hard
Asked in: Amazon, Microsoft
Understanding The Problem
Problem Description
You are given the head of a linked list which probably contains a loop. If the list contains a loop, you need to find the last node of the list which points to one of its previous nodes to create a loop and make it point to NULL, thereby removing the loop.
Problem Note:
- It’s possible that the linked list does not contain a loop
- Do not use extra space
Example 1
Input: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
| |
| |
- - - - - -
Output: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
Explanation: The node 5 at the end of loop points to 3 and creates a loop. We make it point to NULL and remove the loop.
Example 2
Input: 2 -> 20 -> 6 -> 19 -> 13 -> 4
Output: 2 -> 20 -> 6 -> 19 -> 13 -> 4
Explanation: No loop present.
Solutions
We will be discussing two different solutions to this problem.
- Using Hashing: Store each node in a set until there are no new nodes available and the first node which is already in the set will be the start of the loop.
- Using Mathematics: Find total nodes in the loop and then head-start a pointer from that many nodes from the head node. Now, start another pointer from the head node at an equal pace and look for the point where they meet.
The node structure passed to the function will be
class Node {
int data
Node next
}
You can try the problem here.
1. Hashing
This problem asks us to check if there’s a loop inside the linked list and if so, we have to remove the loop without losing any nodes, which means we have to remove the link of the first repeating node.
So, a very simple idea is to use a hash set to store all the nodes of the linked list until there’s a repeating node. We are familiar with the concept that lookup time in a set is of constant time which can help us in optimizing the time complexity.
If the set has all the nodes of the linked list and the head pointer is now pointing to NULL, then obviously that means there is no loop.
Solution Step
- Create a hash set,
nodeSet - Create a reference pointer
ptrpointing tohead. - Move the
ptrforward untilptr.nextis notNULLorptr.nextis not present innodeSet - If we encounter
ptr.nextalready present inhashSetthen setptr.nexttoNULL
Pseudo Code
// driver function
void detectAndRemoveLoop(Node head)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node without loop
if (head == NULL or head.next == NULL)
return
Node ptr1 = head
set hashSet
hashSet.add(ptr1)
while(not hashSet.contains(ptr1.next) or ptr1 is not NULL){
hashSet.add(ptr1)
ptr1 = ptr1.next
}
// if ptr1 is not NULL then it ptr1.next must be the start of loop
if(ptr1){
ptr1.next = NULL
}
}
Complexity Analysis
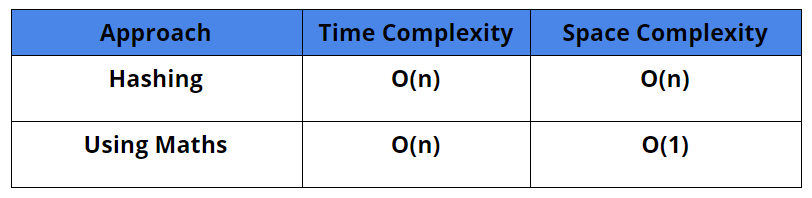
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
Critical Ideas To Think
- How did we make sure that there is a loop inside the linked list or not in this approach?
- Why is the first repeating node already available in the
hashSetrepresent the start of the loop?
2. Using Maths
The previous approach was working in linear time. However, the problem explicitly asked us to solve using constant extra space.
So, We will first have to check if there’s a loop inside the linked list. For that, we can use the concept of the slow and fast pointer or Floyd Cycle Detection algorithm. We will take two pointers, say slow and fast pointing to the head of the linked list. Now ascend slow by one and fast by two in each iteration. If any of the pointers reaches to NULL then there’s no cycle otherwise, at some point slow and fast will point to the same node and that will prove there is a cycle inside the linked list.
Now, Confirming there’s a cycle in the linked list, we will have to identify the node from where the loop first originates. To do that let’s try some maths.
Consider a linked list of some nodes which also contains a loop.
- First, identify the length of the loop. Use slow and fast pointer and move them until they point to the same node. Now keeping slow pointer constant, move the fast pointer by one until it reaches to slow pointer again, thereby giving the length of the loop. Say, the length of the loop is
D

- Our goal is to find X, i.e. distance from head to the beginning of the loop. Such that we can change (X + D)th node’s next from head to NULL and remove the loop.
- Take two-pointers and point them to the head. say
ptr1andptr2
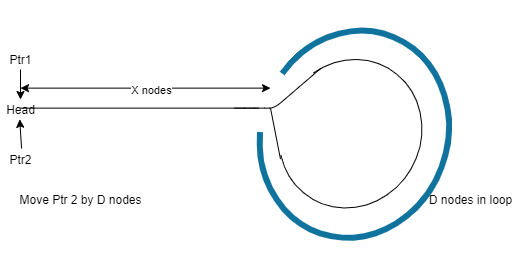
- Now, Move
Ptr2by D nodes. WhereD = length of cycle
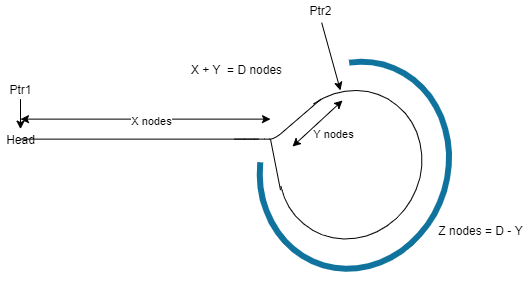
- Let’s do some math
Length of loop is D
Looking at the above diagram, Ptr2 is moved D distance from head.
=> X + Y = D -- eqn 1
and let's assume Ptr2 is Z nodes away from start of loop.
=> Z = D - Y -- eqn 2
Equating eqn 1 and eqn 2
=> X + Y = Z + Y
=> X = Z
- This proves, moving
Ptr1(fromHead) andPtr2(Y dist away from the start of loop) at the same pace will always collide at the node where the loop begins.
Solution Steps
- Take two pointers slow and fast and increment them by one and two respectively until they meet, signifying the existence of a loop.
- Fix the slow pointer and move the fast pointer by one step, such that it visits each node of the loop while stating the total number of nodes(D) inside the loop.
- Take two pointers
ptr1andptr2pointing tohead - Move
ptr2by D nodes. - Now, increment
ptr1andptr2by the equal pace untilptr2.next != ptr1.next - Now, set
Ptr2.nexttoNULL
Pseudo Code
// driver function
void detectAndRemoveLoop(Node head)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node without loop
if (head == NULL or head.next == NULL)
return
Node slow = head, fast = head
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
// Check if loop exists
while (fast and fast.next) {
if (slow == fast)
break
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
}
if(slow == fast) {
int length_of_loop = 1
while(fast.next != slow){
fast = fast.next
length_of_loop = length_of_loop + 1
}
removeLoop(head, length_of_loop)
}
}
// utility function
void removeLoop(Node head, int D) {
Node ptr1 = head
Node ptr2 = head
while(D > 0){
ptr2 = ptr2.next
D = D - 1
}
while(ptr1.next != ptr2.next) {
ptr1 = ptr1.next
ptr2 = ptr2.next
}
// Remove loop
ptr2.next = NULL
return
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical Ideas To Think
- How did we make sure that there is a loop inside the linked list or not in this approach?
- How did we find the number of nodes X in the above diagram?
- How did we make sure that moving ptr2 and ptr1 at the same pace will definitely meet at the beginning of the node?
Comparison of Different Solutions
Suggested Problems To Solve
- Detect loop in a linked list
- Find the first node of the loop in a linked list
- Check linked list with a loop is palindrome or not
- Make a loop at the kth position in a linked list
- Find the length of the loop in a linked list
- Remove every kth node of the linked list
- Remove duplicates from a sorted linked list using recursion
- Count duplicates in a given linked list
Please comment down below if you have a better insight in the above approach.
Happy Coding, Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Types of Linked List and Operation on Linked List
In this blog, we will discuss the types of linked list and basic operations that can be performed on a linked list.

AfterAcademy Tech
Remove Duplicates From a Sorted Linked List-Interview Problem
This is an interview problem asked by companies like Myntra, Visa, Oracle, Adobe, etc. The problem is to remove the duplicate nodes from the given Linked List so that only unique nodes(with unique data values) are present.

AfterAcademy Tech
Reverse a Linked List
The problem is about reversing a Linked List. We are given the head node of the Linked List and we have to return the reversed Linked List's head. This is an interview problem asked in companies like Microsoft, Amazon and Adobe.

AfterAcademy Tech
Remove Nth Node From End of List
You are given a linked list, write a program to remove the nth node from the end of the list and return the head. This problem has been previously asked in Google and Amazon and requires the understanding of the linked list to solve it.
