Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
AfterAcademy Tech
•
03 Mar 2020

Asked in: Amazon, Microsoft
Difficulty: Medium
Understanding the problem
Problem Description: Given a binary search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the BST.
Problem Note
- Lowest Common Ancestor: The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes node1 and node2 as the lowest node in T that has both node1 and node2 as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).
- All of the nodes’ values will be unique.
- node1 and node2 are different and both values will exist in the BST.
- You can use extra memory, helper functions, and can modify the node struct but, you can’t add a parent pointer.
Example 1
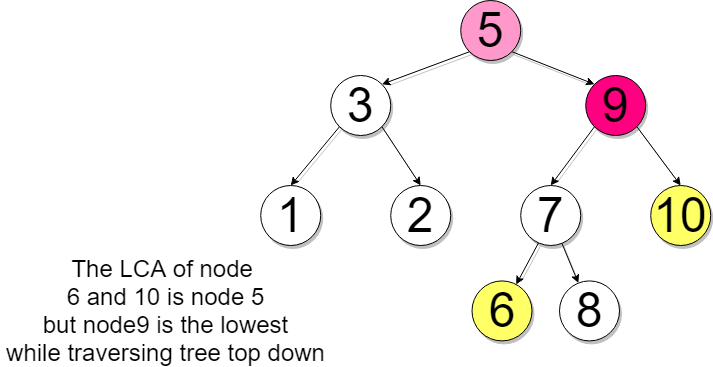
The node structure passed to your function will be
class TreeNode
{
int data
TreeNode left
TreeNode right
}
You may try solving the problem here
Solutions
We can solve this using the approaches as discussed while finding LCA in a binary tree. But, a binary search tree’s property could be utilized, to come up with a better algorithm with lesser complexity.
- Recursive Approach
- Iterative Approach
1. Recursive Approach
The lowest common ancestor for the two nodes node1 and node2 would be the last ancestor node common to both of them. Here last is defined in terms of the depth of the node.

If we boil down the above explanation then we could justify it in this form →
LCA is the last root satisfying min(node1, node2) <= root <= max(node1,node2) where node1 and node2 will be in the subtree of the root while traversing top to bottom in the tree.
Solution Steps
- Start traversing the tree from the root node.
- If both the nodes
node1andnode2are in the right subtree, then recursively move to the right subtree. - If both the nodes
node1andnode2are in the left subtree, then recursively move to the left subtree. - Otherwise, the current node is the lowest common ancestor.
Pseudo Code
TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode node1, TreeNode node2) {
if (node1.val > root.val and node2.val > root.val) {
// If both node1 and node2 are greater than parent
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, node1, node2)
}
else
if (node1.val < root.val and node2.val < root.val) {
// If both node1 and node2 are lesser than parent
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
} else {
// We have found the split point, i.e. the LCA node.
return root
}
}
Complexity Analysis
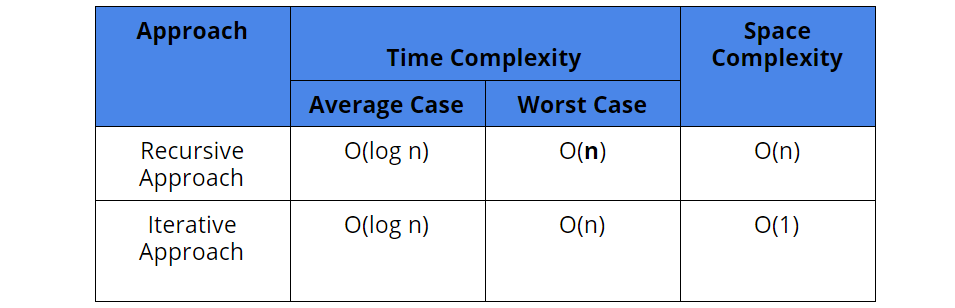
Time Complexity: O(log n) if the tree is balanced binary search tree otherwise, in the worst case, the complexity could be O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
Critical Ideas to Think
- Why did we reduce our search space to the left subtree if the value of root is greater than both the values of the nodes?
- How will the algorithm react if either of the nodes would not be present in the tree?
2. Iterative Approach
If we look closely the recursive solution and try to implement the same logic iteratively then you will find that we don’t need to backtrack to find the LCA node and just have to traverse down the tree and look for the split point of node1 and node2 which could be done without using any stack or queue.
Solution steps
- Start traversing the tree from the root node.
- If both the nodes
node1andnode2are in the right subtree, then iteratively move to the right subtree. - If both the nodes
node1andnode2are in the left subtree, then iteratively move to the left subtree. - Otherwise, the current node is the lowest common ancestor.
Pseudo Code
TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode node1, TreeNode node2) {
// Traverse the tree
while (root is not null) {
if (node1.val > root.val and node2.val > root.val) {
// If both node1 and node2 are greater than parent
root = root.right
}
else
if (node1.val < root.val and node2.val < root.val) {
// If both node1 and node2 are lesser than parent
root = root.left
}
else {
// We have found the split point, i.e. the LCA node.
return node
}
}
return null
}
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(log n) if the tree is balanced binary search tree otherwise, in the worst case, the complexity could be O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Critical Ideas to Think
- To traverse the tree iteratively, why didn’t we used any stack or queue?
- What if both the nodes i.e. node1 and node2 don’t exist in the tree?
- Will the above algorithm work if either of the nodes would itself be the LCA?
Comparison of Different Approaches
Suggested Problems to Solve
- LCA of any number of nodes in a binary tree
- Construct ancestor list from a given binary tree
- Longest common prefix using binary search
If you have any more approaches or you find an error/bug in the above solutions, please comment down below.
Happy Coding! Enjoy Algorithms!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, write a program to find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree. The question is asked previously in Amazon, Facebook, Adobe and requires an understanding of tree data structure.

AfterAcademy Tech
Binary Search Tree: Introduction, Operations and Applications
Binary Search Trees is one of the most important variation of binary tree and is extremely useful in practical applications. The blog discusses the operations and applications of this powerful data structure
AfterAcademy Tech
Recover Binary Search Tree-Interview Problem
Given a Binary Search Tree such that two of the nodes of this tree have been swapped by mistake. You need to write a program that will recover this BST while also maintaining its original structure

AfterAcademy Tech
Binary Search Tree vs Hash Table
In this blog, we will see the difference between a binary search tree and a hash table. We will see which data structure should be used when to solve our problems.
