What is Piggybacking?
AfterAcademy Tech
•
04 Feb 2020

Mostly the transmission of data is bidirectional i.e. full-duplex transmission. The data flows in both directions, so the control information i.e. acknowledgment, etc. also needs to be flowed in both the directions. This can be done by making two simplex connections. The first simplex connection for the sender has a separate channel, each for sending the data and receiving the acknowledgment. Similarly, for the receiver, it has a separate channel for sending the data and receiving the acknowledgment. But, due to this, the traffic would increase and half of the transmission would consist of acknowledgments. So, the bandwidth of the channel would be wasted. An improved solution to this problem is Piggybacking. So, let's get started and know more about it.
Piggybacking
Piggybacking is a method of attaching acknowledgment to the outgoing data packet. The concept of piggybacking is explained as follows:
Consider a two-way transmission between host A and host B. When host A sends a data frame to B, then B does not send the acknowledgment of the frame sent immediately. The acknowledgment is delayed until the next data frame of host B is available for transmission. The delayed acknowledgment is then attached to the outgoing data frame of B. This process of delaying acknowledgment so that it can be attached to the outgoing frame is called piggybacking.
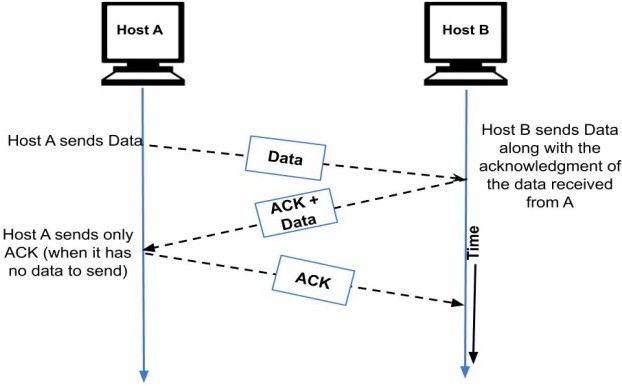
Now, as we are communicating between the host A and host B, three conditions can arise:
- When the host has both data and the acknowledgment to send, then it will attach the data along with the acknowledgment. In the above diagram, the host B will attach the data frame along with the acknowledgment of the last frame received from host A.
- When the host does not have any data to send then it will send only the acknowledgment. In the above diagram, when host A does not have any data frame to send. So, it will only send the acknowledgment of the last frame received.
- When the host has only data to send then it will send the data along with the acknowledgment of the last frame received. The duplicate acknowledgment will be discarded by the receiver and the data would be accepted.
Advantages of Piggybacking
- The available channel bandwidth is used efficiently.
Disadvantages of Piggybacking
- As there is delayed transmission of acknowledgment so if the acknowledgment is not received within the fixed time then the sender has to retransmit the data.
- There is additional complexity for implementing this method.
This is all about piggybacking. Hope you learned something new today.
Do share this blog with your friends to spread the knowledge. Visit our YouTube channel for more content. You can read more blogs from here.
Keep Learning 🙂
Team AfterAcademy!