What is Banker’s algorithm?
AfterAcademy Tech
•
02 Jun 2020

In the last blog, we have discussed four deadlock handling strategies i.e. deadlock prevention, deadlock avoidance, deadlock detection and recovery, and deadlock ignorance. In this blog, we will learn about one of the deadlock avoidance strategies i.e. banker’s algorithm. So, let's get started.
Banker’s Algorithm
Banker’s Algorithm is a deadlock avoidance algorithm. It is also used for deadlock detection. This algorithm tells that if any system can go into a deadlock or not by analyzing the currently allocated resources and the resources required by it in the future. There are various data structures which are used to implement this algorithm. So, let's learn about these first.
Data Structures used to implement Banker’s Algorithm
- Available: It is a 1-D array that tells the number of each resource type (instance of resource type) currently available. Example: Available[R1]= A, means that there are A instances of R1 resources are currently available.
- Max: It is a 2-D array that tells the maximum number of each resource type required by a process for successful execution. Example: Max[P1][R1] = A, specifies that the process P1 needs a maximum of A instances of resource R1 for complete execution.
- Allocation: It is a 2-D array that tells the number of types of each resource type that has been allocated to the process. Example: Allocation[P1][R1] = A, means that A instances of resource type R1 have been allocated to the process P1.
- Need: It is a 2-D array that tells the number of remaining instances of each resource type required for execution. Example: Need[P1][R1]= A tells that A instances of R1 resource type are required for the execution of process P1.
Need[i][j]= Max[i][j] - Allocation[i][j], where i corresponds any process P(i) and j corresponds to any resouce type R(j)
The Bankers Algorithm consists of the following two algorithms
- Request-Resource Algorithm
- Safety Algorithm
Resource- Request Algorithm
Whenever a process makes a request of the resources then this algorithm checks that if the resource can be allocated or not.
It includes three steps:
- The algorithm checks that if the request made is valid or not. A request is valid if the number of requested resources of each resource type is less than the Need(which was declared previously by the process). If it is a valid request then step 2 is executed else aborted.
- Here, the algorithm checks that if the number of requested instances of each resource is less than the available resources. If not then the process has to wait until sufficient resources are available else go to step 3.
- Now, the algorithm assumes that the resources have been allocated and modifies the data structure accordingly.
Available = Available - Request(i)
Allocation(i) = Allocation(i) + Request(i)
Need(i) = Need(i) - Request(i)
After the allocation of resources, the new state formed may or may not be a safe state. So, the safety algorithm is applied to check whether the resulting state is a safe state or not.
Safe state: A safe state is a state in which all the processes can be executed in some arbitrary order with the available resources such that no deadlock occurs.
- If it is a safe state, then the requested resources are allocated to the process in actual.
- If the resulting state is an unsafe state then it rollbacks to the previous state and the process is asked to wait longer.
Safety Algorithm
The safety algorithm is applied to check whether a state is in a safe state or not.
This algorithm involves the following four steps:
- Suppose currently all the processes are to be executed. Define two data structures as work and finish as vectors of length m(where m is the length of Available vector)and n(is the number of processes to be executed).
Work = Available
Finish[i] =false for i = 0, 1, … , n — 1.
2. This algorithm will look for a process that has Need value less than or equal to the Work. So, in this step, we will find an index i such that
Finish[i] ==false &&
Need[i]<= Work
If no such ‘i’ is present then go to step 4 else to step 3.
3. The process 'i' selected in the above step runs and finishes its execution. Also, the resources allocated to it gets free. The resources which get free are added to the Work and Finish(i) of the process is set as true. The following operations are performed:
Work = Work + Allocation
Finish[i] = true
After performing the 3rd step go to step 2.
4. If all the processes are executed in some sequence then it is said to be a safe state. Or, we can say that if
Finish[i]==true for all i,
then the system is said to be in a safe state.
Let's take an example to understand this more clearly.
Example
Suppose we have 3 processes(A, B, C) and 3 resource types(R1, R2, R3) each having 5 instances. Suppose at any time t if the snapshot of the system taken is as follows then find the system is in a safe state or not.
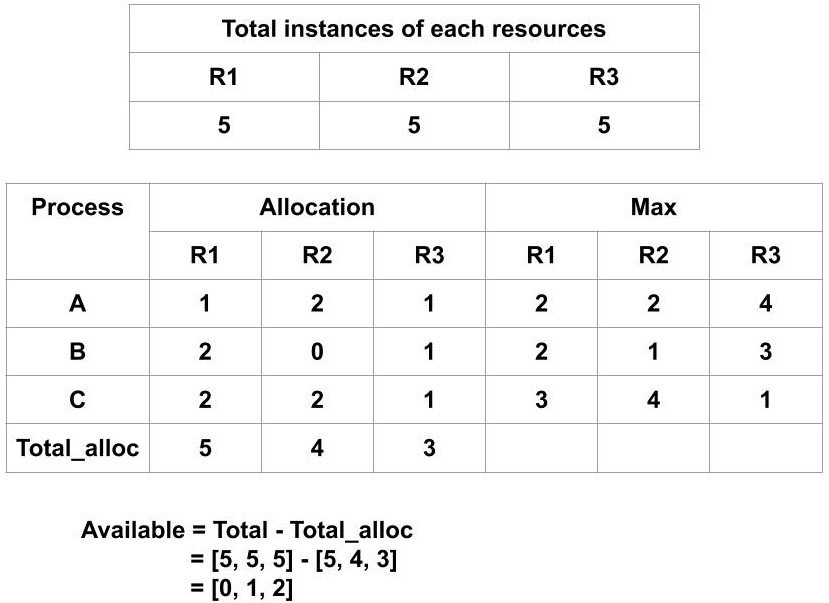
So, the total allocated resources(total_alloc)are [5, 4, 3]. Therefore, the Available(the resources that are currently available)resources are
Available = [0, 1, 2]
Now, we will make the Need Matrix for the system according to the given conditions. As we know, Need(i)=Max(i)-Allocation(i), so the resultant Need matrix will be as follows:
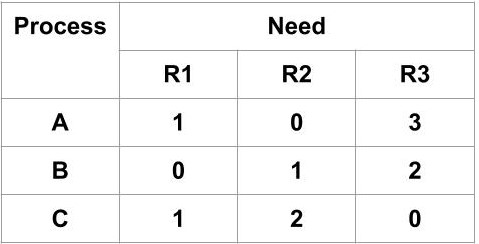
Now, we will apply the safety algorithm to check that if the given state is a safe state or not.
- Work=Available=[0, 1, 2]
- Also Finish[i]=false, for i=0,1,2, are set as false as none of these processes have been executed.
- Now, we check that Need[i]≤Work. By seeing the above Need matrix we can tell that only B[0, 1, 2] process can be executed. So, process B( i=1 )is allocated the resources and it completes its execution. After completing the execution, it frees up the resources.
- Again, Work=Work+Available i.e. Work=[0, 1, 2]+[2, 0,1]= [2, 1, 3] and Finish[1]= true.
- Now, as we have more instances of resources available we will check that if any other process resource needs can be satisfied. With the currently available resources[2, 1, 3], we can see that only process A[1, 2, 1] can be executed. So, process A( i=0 ) is allocated the resources and it completes its execution. After completing the execution, it frees up the resources.
- Again, Work=Work+Available i.e. Work=[2, 1, 3]+[1, 2, 1]= [3, 3, 4] and Finish[0]= true.
- Now, as we have more instances of resources available we will check that if the remaining last process resource requirement can be satisfied. With the currently available resources[3, 3, 4], we can see that process C[2, 2, 1] can be executed. So, process C( i=2 ) is allocated the resources and it completes its execution. After completing the execution, it frees up the resources.
- Fianlly, Work=Work+Available i.e. Work=[3, 3, 4]+[2, 2, 1]= [5, 5, 5] and Finish[2]= true.
- Finally, all the resources are free and there exists a safe sequence B, A, C in which all the processes can be executed. So. the system is in a safe state and deadlock will not occur.
This is how Banker's Algorithm is used to check if the system is in a safe state or not. Hope you learned something new today.
Do share this blog with your friends to spread the knowledge. Visit our YouTube channel for more content. You can read more blogs from here.
Keep Learning 🙂
Team AfterAcademy!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
Dijkstra’s Algorithm
In this blog, we will discuss Dijkstra's Algorithm. We will discuss what is the Dijkstra's Algorithm, how can we find the shortest path from source to other vertices using Dijkstra's Algorithm in Graph, Illustration using an example, its pseudo-code.
AfterAcademy Tech
Time and Space Complexity Analysis of Algorithm
In this blog, we will learn about the time and space complexity of an Algorithm. We will learn about worst case, average case, and best case of an algorithm. We will also see various asymptotic notations that are used to analyse an algorithm. So, let's learn the algorithm of an algorithm.
AfterAcademy Tech
What are Greedy Algorithms?
This blog deals with the introduction of greedy algorithms for beginners and enthusiasts.

AfterAcademy Tech
Comparison of Sorting Algorithms
In this blog, we will analyze and compare different sorting algorithms on the basis of different parameters like Time Complexity, Inplace/Outplace, Stability, etc.