What is a Deadlock in DBMS and what are the deadlock avoidance, detection, and prevention techniques?
AfterAcademy Tech
•
21 Mar 2020

Suppose you are travelling on a one-way road by car. Suddenly you see a car approaching from the opposite direction. Now, you wait for the person to take a back turn and provide the road to you. But, the person in front of you is waiting for you to give him space. This is a deadlock situation where you both are stuck and nobody is ready to take back turn. Such type of situation may occur in our computer system also. Such a situation is called a deadlock. In this blog, we will see in detail what is a deadlock and what are various deadlock handling techniques. So, let's get started.
NOTE: This is famous interview topic. So, understand it in the easiest way.
Deadlock
Deadlock is an unwanted condition where two or more processes waits indefinitely for the other process to free up their resources so that they can complete their work.
In Deadlock, one process is holding some resource and is wating for some other resource and at the same time, there is some other process that is holding that resource and is waiting for the resources held by the first process. So, both the processses are waiting for each other to release the resources and none of them are releasing the resources.
Example: Consider a situation where there are two processes P1 and P2 executing simultaneously. The process P1 is holding the resource R1 and needs R2 to complete its execution. The process P2 is holding the resource R2 and needs R1 to complete its execution. So, here one process is waiting for the other process to release its resource and hence both the process is unable to complete its execution and the system goes into a halt.
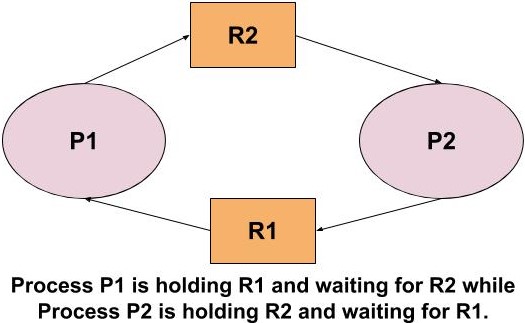
This is called the Deadlock situation. But there are some conditions that must be satisfied for Deadlock.
Necessary conditions for Deadlock
- Mutual Exclusion: This means that some of the resources involved cannot be used by more than one process at the same time. It means that if the resource(like a printer) is being used by any process and some other process comes then it has to wait for the resources to be released.
- No Preemption: If a process is holding a resource then its resources can not be forcibly taken from it.
- Hold & Wait: The process is holding some resources and is waiting for the other resources.
- Circular Wait: The process is waiting for the resource which is being held by the next process and this forms a chain of waiting. In the above example, Process P1 and Process P2 are forming a chain and waiting for the resource being held by each other.
If the above four conditions hold simultaneously then a Deadlock may occur.
Deadlock Handling Methods
- Deadlock Ignorance
- Deadlock Prevention
- Deadlock Avoidance
- Deadlock Detection
Deadlock Ignorance
This is the widely used technique to handle the deadlock. Whenever a deadlock situation occurs we simply ignore the deadlock. Why are we ignoring the deadlock? The deadlock occurs very rarely. So, why to write a full-fledged code to remove the deadlock. This will also affect the speed of the system. So, there is a kind of tradeoff. If we write the code for deadlock the system would be capable of handling the deadlock but the performance and speed of the system will degrade. But, the users are normally concerned with speed and they normally ignore the deadlock situation. Windows and Linux normally use the deadlock ignorance method. Whenever our system goes into a halt we simply restart the system and we are good to go.
Deadlock Prevention
There is a very famous proverb. “Prevention is better than cure”. So we try to prevent the deadlock from happening. As we know here are four necessary conditions for deadlock to occur. We will prevent any or all of the conditions from holding true.
- Removing Mutual Exclusion: The resources which we use should be sharable. Like CPU, it can be used by more than one process at a time. But, this not always the case. Some resources are non-sharable like printers. So, if the resources are non-sharable then this condition cannot be removed and hence the deadlock can't be prevented.
- Removing No Preemption: Here, we will forcibly preempt or stop a process and thus, the resources held by this process will be released. Now, these resources can be used by other process and deadlock can be removed. In the above example, we can stop the process P1 and thus, P1 will release the resource R1. Now, this R1 resource can be used by P2 to complete its execution and hence, the deadlock is removed.
- Removing Hold & Wait Condition: Before a process starts we will give all the resources required by it. Thus, a deadlock situation will never arise as it will never have to wait. Though this is practically impossible because we can't simply give all the resources to only one process.
- Removing Circular Wait: To avoid the circular wait, the resource may be numbered and each process can request the resource in increasing order of these numbers. This algorithm if implemented increases the complexity and leads to poor resource utilization.
Deadlock Avoidance
Most of the deadlock prevention algorithms have poor resource utilization or are practically impossible. So, we can try to avoid deadlocks by use of prior knowledge about the usage of the resources available, resources allocated, future resources requests, and future releases by the processes. Most deadlock avoidance algorithms need advance knowledge of the maximum number of resources of each type that it may need. The main challenge with this method is predicting the resources required before execution. Bankers Algorithms is a deadlock avoidance strategy.
Deadlock Detection
If deadlock prevention and avoidance are not done properly then the system may enter a deadlock state. So, we need to detect the deadlock and recover it.
Wait-for-graph is one of the methods of detecting deadlock. In this graph, the vertices represent processes and the directed edge form a process P1 to P2 indicates that P1 is waiting for a resource that is held by P2. The wait-for-graph below represents a deadlock situation in which the process P1 is waiting for the resource held by P2, P2 is waiting for the resource held by P3 and so on.
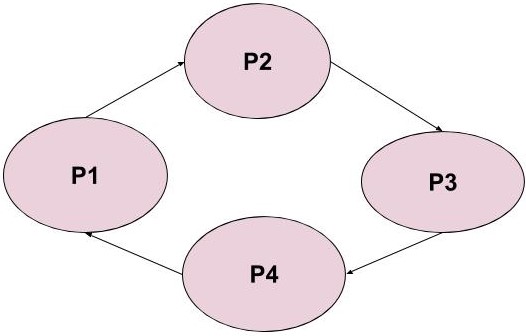
A cycle in wait-for-graph represents a deadlock if we have single instances of the resources. So, the system can maintain wait-for-graph and check for cycles to detect the deadlock. If there are multiple instances of a resource then a cycle may or may not represent a deadlock.
The deadlock once detected can be removed by the following ways:
- Terminating the process involved in the deadlock: This involves killing all the processes involved in the deadlock until the deadlock is removed.
- Resource Preemption: This involves taking back the resources from the processes allocating it to other processes so that deadlock is removed.
So, this was all about deadlock. Hope you learned something new today.
Do share this blog with your friends to spread the knowledge. Visit our YouTube channel for more content. You can read more blogs from here.
Keep Learning 🙂
Team AfterAcademy!
Written by AfterAcademy Tech
Share this article and spread the knowledge
Read Similar Articles
AfterAcademy Tech
What are Deadlock handling techniques in Operating System?
In this blog, we will learn four techniques of deadlock handling i.e. deadlock prevention, deadlock avoidance, deadlock detection and recovery, and deadlock ignorance. So, let's learn about these.

AfterAcademy Tech
What is a Phantom deadlock?
In this blog, we will learn about a specific deadlock, i.e., Phantom deadlock, and will also see some examples of its occurrence.

AfterAcademy Tech
What is Deadlock and what are its four necessary conditions?
In this blog, we will learn about the concept of deadlock in the Operating System and we will also see what are the four necessary conditions of deadlock. Let's learn.

AfterAcademy Tech
What is Cross-Join in DBMS?
In this blog, we will learn how to cross-join two tables in DBMS, and what are the benefits of doing it with example.
